My ambition is handicapped by laziness. -C. Bukowski Me gustan las personas desesperadas con mentes rotas y destinos rotos. Están llenos de sorpresas y explosiones. -C. Bukowski. I love cats. Born in the early 80's, raised in the 90's. I like Nature, Autumn, books, landscapes, cold days, cloudy Windy days, space, Science, Paleontology, Biology, Astronomy, History, Social Sciences, Drawing, spending the night watching at the stars, Rick & Morty. I'm a lazy ass.
222 posts
Latest Posts by monstrous-mind - Page 3
🍂🍁🎃🍁🍂🌄
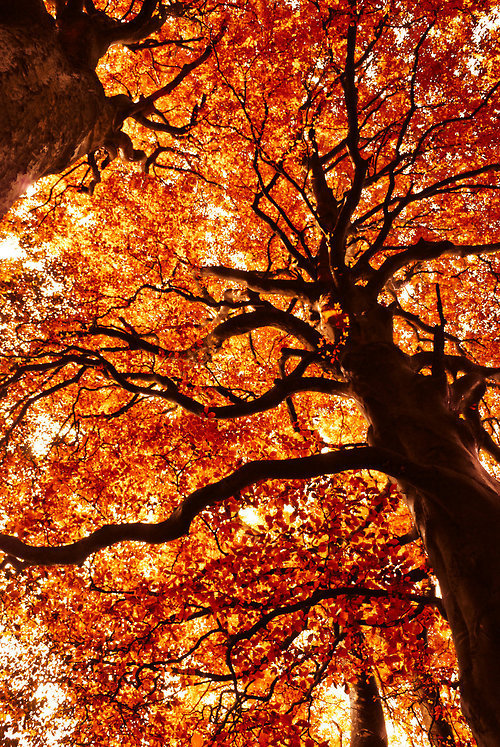










Autumn Colours
↳ Orange
🍃🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🐈🌄🎃💀




Roger Williams Park, Providence, RI. Photos by Frank C. Grace
🎃🍂🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🍂🎃🍃🐈🐾

🌄🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🐾🐈

🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🌬🍃🐈🌄

Hello September. May you the first of so many good things to come as the unofficial start to autumn 🍂
🍃🍂🍁🌄🐈

🍃🌄🍂🍁🐈

Huck
🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🍃🌬🌄🐈

Soon... Very soon 🌬🍃🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🐈

🐈🌃🌌

🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🍃🐈📚📖☕

🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁🍃🐈📚📖☕
source
🔭🌃🌌🐈🍂🍁

First Ever Image of a Multi-Planet System around a Sun-like Star Captured by ESO Telescope
The European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) has taken the first ever image of a young, Sun-like star accompanied by two giant exoplanets. Images of systems with multiple exoplanets are extremely rare, and — until now — astronomers had never directly observed more than one planet orbiting a star similar to the Sun. The observations can help astronomers understand how planets formed and evolved around our own Sun.
The two gas giants orbit their host star at distances of 160 and about 320 times the Earth-Sun distance. This places these planets much further away from their star than Jupiter or Saturn, also two gas giants, are from the Sun; they lie at only 5 and 10 times the Earth-Sun distance, respectively. The team also found the two exoplanets are much heavier than the ones in our Solar System, the inner planet having 14 times Jupiter’s mass and the outer one six times.
Source
🍃🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁

🐈🌌🚀



Alien Directed by Ridley Scott (1979)
🐈🔭🌃🌌
Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from inside it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of the region from which no escape is possible is called the event horizon. Although the event horizon has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, no locally detectable features appear to be observed. In many ways a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light.

The idea of a body so massive that even light could not escape was briefly proposed by astronomical pioneer and English clergyman John Michell in a letter published in November 1784. Michell’s simplistic calculations assumed that such a body might have the same density as the Sun, and concluded that such a body would form when a star’s diameter exceeds the Sun’s by a factor of 500, and the surface escape velocity exceeds the usual speed of light.

At the center of a black hole, as described by general relativity, lies a gravitational singularity, a region where the spacetime curvature becomes infinite. For a non-rotating black hole, this region takes the shape of a single point and for a rotating black hole, it is smeared out to form a ring singularity that lies in the plane of rotation. In both cases, the singular region has zero volume. It can also be shown that the singular region contains all the mass of the black hole solution. The singular region can thus be thought of as having infinite density.

How Do Black Holes Form?
Scientists think the smallest black holes formed when the universe began.
Stellar black holes are made when the center of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses. When this happens, it causes a supernova. A supernova is an exploding star that blasts part of the star into space.

Scientists think supermassive black holes were made at the same time as the galaxy they are in.
Supermassive black holes, which can have a mass equivalent to billions of suns, likely exist in the centers of most galaxies, including our own galaxy, the Milky Way. We don’t know exactly how supermassive black holes form, but it’s likely that they’re a byproduct of galaxy formation. Because of their location in the centers of galaxies, close to many tightly packed stars and gas clouds, supermassive black holes continue to grow on a steady diet of matter.

If Black Holes Are “Black,” How Do Scientists Know They Are There?
A black hole can not be seen because strong gravity pulls all of the light into the middle of the black hole. But scientists can see how the strong gravity affects the stars and gas around the black hole.
Scientists can study stars to find out if they are flying around, or orbiting, a black hole.

When a black hole and a star are close together, high-energy light is made. This kind of light can not be seen with human eyes. Scientists use satellites and telescopes in space to see the high-energy light.

On 11 February 2016, the LIGO collaboration announced the first observation of gravitational waves; because these waves were generated from a black hole merger it was the first ever direct detection of a binary black hole merger. On 15 June 2016, a second detection of a gravitational wave event from colliding black holes was announced.

Simulation of gravitational lensing by a black hole, which distorts the image of a galaxy in the background
Animated simulation of gravitational lensing caused by a black hole going past a background galaxy. A secondary image of the galaxy can be seen within the black hole Einstein ring on the opposite direction of that of the galaxy. The secondary image grows (remaining within the Einstein ring) as the primary image approaches the black hole. The surface brightness of the two images remains constant, but their angular size varies, hence producing an amplification of the galaxy luminosity as seen from a distant observer. The maximum amplification occurs when the background galaxy (or in the present case a bright part of it) is exactly behind the black hole.
Could a Black Hole Destroy Earth?
Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that.

Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now.
The sun will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole.
More posts about black holes
Source 1, 2 & 3
🎃🍂🍁🎃🍁🍂🎃🐈🐾

🔭🌃🌌🐈

Located over 50 million light years away, the large, distorted spiral NGC 1532 is seen locked in a gravitational struggle with dwarf galaxy NGC 1531 (right of center), a struggle the smaller galaxy will eventually lose.
Image Credit: Michel Meunier, Laurent Bernasconi, Janus Team
🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁









Halloween 🎃
🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁

Calling all active fall blogs in spring 2020!
Please reblog! My dash needs more autumn on it 🍂
🔭🌃🌌
Characteristics of the moons of Saturn
Saturn has 62 natural satellites. Here are some features of some of its moons, with mountains, valleys, and striking marks on their surfaces, often marked by asteroid bombardments causing small, huge craters.

Iapetus - Equatorial ridge
Iapetus’s equatorial ridge was discovered when the Cassini spacecraft imaged Iapetus on 31 December 2004. Peaks in the ridge rise more than 20 km above the surrounding plains, making them some of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. The ridge forms a complex system including isolated peaks, segments of more than 200 km and sections with three near parallel ridges.

Tethys - Odysseus crater
Odysseus is the largest crater on Saturn’s moon Tethys. It is 445 km across, more than 2/5 of the moon’s diameter, and is one of the largest craters in the Solar System.

Tethys - Ithaca Chasma
Ithaca Chasma is a valley (graben) on Saturn’s moon Tethys, named after the island of Ithaca, in Greece. It is up to 100 km wide, 3 to 5 km deep and 2,000 km long, running approximately three-quarters of the way around Tethys’ circumference, making it one of the longer valleys in the Solar System. Ithaca Chasma is approximately concentric with Odysseus crater.

Tethys - Red arcs
Unusual arc-shaped, reddish streaks cut across the surface of Saturn’s ice-rich moon Tethys in this enhanced-color mosaic. The red streaks are narrow, curved lines on the moon’s surface, only a few miles (or kilometers) wide but several hundred miles (or kilometers) long.

Rhea - Inktomi crater
Inktomi, also known as The Splat, is a prominent rayed impact crater 47.2 kilometres (29.3 mi) in diameter located in the southern hemisphere of Saturn’s moon Rhea.

Mimas - Herschel Crater
Herschel is a huge crater in the leading hemisphere of the Saturnian moon Mimas, on the equator at 100° longitude. It is so large that astronomers have expressed surprise that Mimas was not shattered by the impact that caused it. It measures 139 kilometres (86 miles) across, almost one third the diameter of Mimas. If there were a crater of an equivalent scale on Earth it would be over 4,000 km (2,500 mi) in diameter – wider than Canada – with walls over 200 km (120 mi) high.

Enceladus - Surface with fractures
Close up of one of the ‘tiger stripes” or fissures called Baghdad Sulcus. Both heat and occasional geysers issue from this formidable crack. Some of the material coating the landscape may be snow condensed from vapor. This closeup of the surface of Enceladus on November 21, 2009, viewed from approximately 1,260 miles (2,028 kilometers) away.

Dione - Contrasts
This image from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft shows a part of Dione’s surface that is covered by linear, curving features, called chasmata. One possibility is that this stress pattern may be related to Dione’s orbital evolution and the effect of tidal stresses over time. This view looks toward the trailing hemisphere of Dione.
Learn more: Iapetus, Tethys, Rhea, Mimas, Enceladus and Dione.
Images: NASA/JPL-Caltech





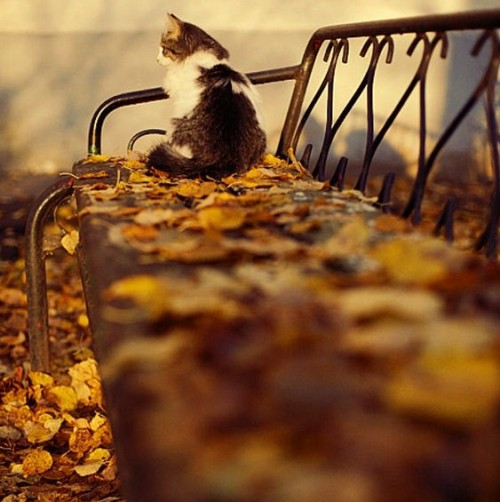
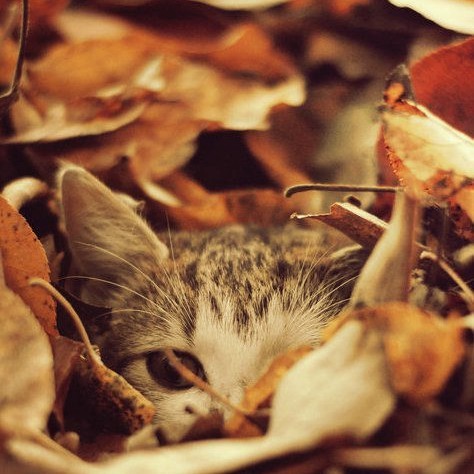
Autumn Kitty by Афиногенова Татьяна
🍂🍁🎃🐈🐾🎃🍁🍂






🛫🔭🌌
10 Amazing Space Discoveries by the World’s Largest Flying Observatory

On the night of May 26, 2010, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, the world’s largest flying observatory, first peered into the cosmos. Its mission: to study celestial objects and astronomical phenomena with infrared light. Many objects in space emit almost all their energy at infrared wavelengths. Often, they are invisible when observed in ordinary, visible light. Over the last decade, the aircraft’s 106-inch telescope has been used to study black holes, planets, galaxies, star-forming nebulas and more! The observations have led to major breakthroughs in astronomy, revolutionizing our understanding of the solar system and beyond. To celebrate its 10 years of exploration, here’s a look at the top 10 discoveries made by our telescope on a plane:
The Universe’s First Type of Molecule

Scientists believe that around 100,000 years after the big bang, helium and hydrogen combined to make a molecule called helium hydride. Its recent discovery confirms a key part of our basic understanding of the early universe.
A New View of the Milky Way

More than a pretty picture, this panorama of cosmic scale reveals details that can help explain how massive stars are born and what’s feeding our Milky Way galaxy’s supermassive black hole.
When Planets Collide

A double-star system that is more than 300 light-years away likely had an extreme collision between two of its rocky planets. A similar event in our own solar system may have formed our Moon.
How A Black Hole Feasts

Fear not, the dark, my friend. And let the feast begin! Magnetic fields in the Cygnus A galaxy are trapping material where it is close enough to be devoured by a hungry black hole.
Somewhere Like Home

The planetary system around Epsilon Eridani, a star located about 10 light-years away, has an architecture remarkably similar to our solar system. What’s more, its central star is a younger, fainter version of our Sun.
A Quiet Place

Black holes in many galaxies are actively consuming material, but our Milky Way galaxy’s central black hole is relatively quiet. Observations show magnetic fields may be directing material around, not into, the belly of the beast.
The Great Escape

Ever wonder how material leaves a galaxy? The wind flowing from the center of the Cigar Galaxy is so strong it’s pulling a magnetic field — and the mass of 50 to 60 million Suns — with it.
Exploding Star, New Worlds

What happens when a star goes boom? It turns out that supernova explosions can produce a substantial amount of material from which planets like Earth can form.
Stellar Sibling Rivalry

They say siblings need time and space to grow, but here’s one that really needs some room. A newborn star in the Orion Nebula is clearing a bubble of space around it, preventing any new luminous family members from forming nearby.
Clues to Life’s Building Blocks

Radiation from stars is making organic molecules in nebula NGC 7023, also known as the Iris Nebula, larger and more complex. The growth of these molecules is one of the steps that could lead to the emergence of life under the right circumstances.
SOFIA is a modified Boeing 747SP aircraft that allows astronomers to study the solar system and beyond in ways that are not possible with ground-based telescopes. Find out more about the mission at www.nasa.gov/SOFIA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
🔭🌃🌌🍂🍁🐈
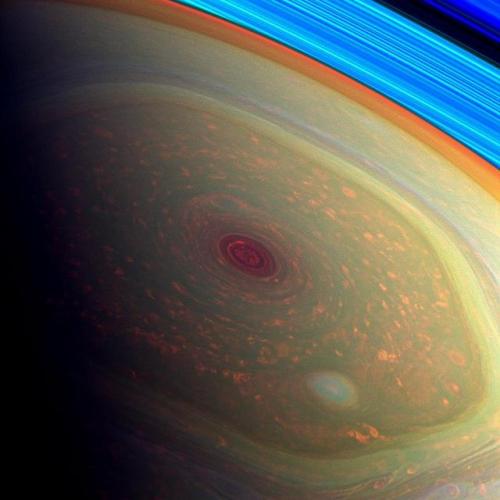
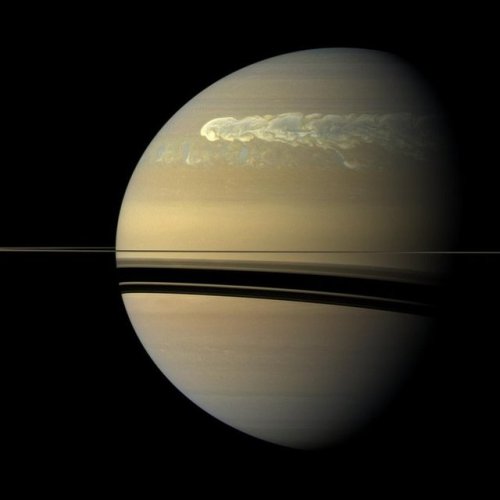








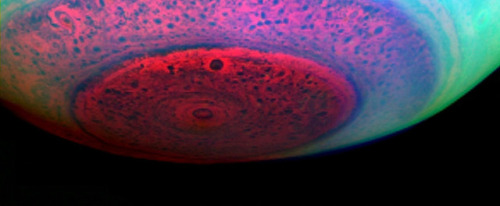
Saturn’s atmosphere exhibits a banded pattern similar to Jupiter’s, but Saturn’s bands are much fainter and are much wider near the equator. The nomenclature used to describe these bands is the same as on Jupiter. Saturn’s finer cloud patterns were not observed until the flybys of the Voyager spacecraft during the 1980s. Since then, Earth-based telescopy has improved to the point where regular observations can be made. The composition of the clouds varies with depth and increasing pressure.
The winds on Saturn are the second fastest among the Solar System’s planets, after Neptune’s. Voyager data indicate peak easterly winds of 500 m/s (1,800 km/h).
Thermography has shown that Saturn’s south pole has a warm polar vortex, the only known example of such a phenomenon in the Solar System. Whereas temperatures on Saturn are normally −185 °C, temperatures on the vortex often reach as high as −122 °C, suspected to be the warmest spot on Saturn.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute and Kevin M. Gill
🎃🍁🍂🐈🐾🍂🍁🎃

🍁🍂🎃🍂🍁

october by OneEyedJax on Flickr.





COSMOS: Possible Worlds 2020

🌄🍂🍁🎃🍁🍂
