Your gateway to endless inspiration
Cygnus - Blog Posts

The trickster “Blinking Planetary”
Planetary nebula NGC 6826 is located about 4,200 light years from Earth in Cygnus. When observers look directly at it through a small telescope, they typically see only the nebula’s sparkling-white central star. However, by averting one’s gaze, glancing away from the central star, the nebula’s bulbous dust clouds come into view. This optical trickery earned this planetary nebula the name the "Blinking Planetary.”
Over the next several thousand years, the nebula will gradually disperse into space, and then the central star will slowly cool as it radiates its energy for billions of years as a white dwarf.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Far from Westeros, a Three-Eyed Raven Helps NASA Find Its Way
Perched on the outside of the International Space Station is Raven—a technology-filled module that helps NASA develop a relative navigation capability, which is essentially autopilot for spacecraft. Raven has been testing technologies to enable autonomous rendezvous in space, which means the ability to approach things in space without human involvement, even from the ground.

Developed by the Satellite Servicing Projects Division (SSPD), our three-eyed Raven has visible, infrared, and Lidar sensors and uses those “eyes” to image and track visiting spacecraft as they come and go from the space station. Although Raven is all-seeing, it only sees all in black and white. Color images do not offer an advantage in the case of Raven and Restore-L, which also utilize infrared and Lidar sensors.
The data from Raven’s sensors is sent to its processor, which autonomously sends commands that swivel Raven on its gimbal, or pointing system. When Raven turns using this system, it is able to track a vehicle. While these maneuvers take place, NASA operators evaluate the movements and make adjustments to perfect the relative navigation system technologies.

A few days ago, Raven completed its 21st observation of a spacecraft when it captured images of Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus vehicle delivering science investigations and supplies as part of its 11th commercial resupply services mission, including another SSPD payload called the Robotic External Leak Locator.

And just last month, Raven celebrated its two-year anniversary in space, marking the occasion with an observation of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon during the Demo-1 mission.

What is this—a spacecraft for ants??
While this shot of Dragon isn’t terribly impressive because of where the spacecraft docked on station, Raven has captured some truly great images when given the right viewing conditions.
From SpaceX Dragon resupply mission observations…

…to Cygnus supply vehicles.

Raven has observed six unique types of spacecraft.
It has also conducted a few observations not involving spacecraft, including the time it captured Hurricane Irma…

…or the time it captured station’s Dextre arm removing the Robotic Refueling Mission 3 payload, another mission developed by SSPD, from the Dragon spacecraft that delivered it to the orbiting laboratory.


Thus far, Raven has had a great, productive life aboard the station, but its work isn’t done yet! Whether it’s for Restore-L, which will robotically refuel a satellite, or getting humans to the Moon or Mars, the technologies Raven is demonstrating for a relative navigation system will support future NASA missions for decades to come.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
We Just Identified More Than 200 New (Potential) Planets
The Kepler space telescope is our first mission capable of identifying Earth-size planets around other stars. On Monday, June 19, 2017, scientists from many countries gathered at our Ames Research Center to talk about the latest results from the spacecraft, which include the identification of more than 200 potential new worlds! Here’s what you need to know:
We found 219 new planet candidates.

All of these worlds were found in a patch of sky near the Cygnus constellation in our Milky Way galaxy. Between 2009 and 2013, Kepler searched more than 200,000 stars in the region for orbiting planets. The 219 new planet candidates are part of the more than 4,000 planet candidates and 2,300 confirmed planets Kepler has identified to date.
Ten of these worlds are like our own.

Out of the 219 new planet candidates, 10 are possibly rocky, terrestrial worlds and orbit their star in the habitable zone – the range of distances from a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of a rocky planet.
Small planets come in two sizes.

Kepler has opened up our eyes to the existence of many small worlds. It turns out a lot of these planets are either approximately 1.5 times the size of Earth or just smaller than Neptune. The cool names given to planets of these sizes? Super Earths and mini-Neptunes.
Some of the new planets could be habitable.

Water is a key ingredient to life as we know it. Many of the new planet candidates are likely to have small rocky cores enveloped by a thick atmosphere of hydrogen and helium, and some are thought to be ocean worlds. That doesn’t necessarily mean the oceans of these planets are full of water, but we can dream, can’t we?
Other Earths are out there.

Kepler’s survey has made it possible for us to measure the number of Earth-size habitable zone planets in our galaxy. Determining how many planets like our own that exist is the big question we’ll explore next.
The hunt for new planets continues.

Kepler continues to search for planets in different regions of space. With the launch of our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in 2018, we’re going to search for planets nearest the sun and measure the composition of their atmospheres. In the mid-2020s, we have our sights on taking a picture of small planets like Earth with our Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST).
*All images of planets are artist illustrations.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V rocket carrying the Orbital ATK Cygnus module rolls to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 41 in this time-lapse video. The rollout is in preparation for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver supplies to the International Space Station.
Launch is currently scheduled for 11:11 a.m. EDT, watch live coverage: http://www.nasa.gov/live
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How will Cygnus Spacecraft Dock to Space Station?
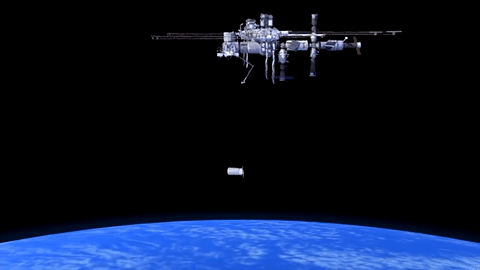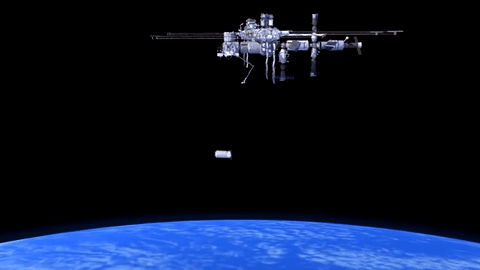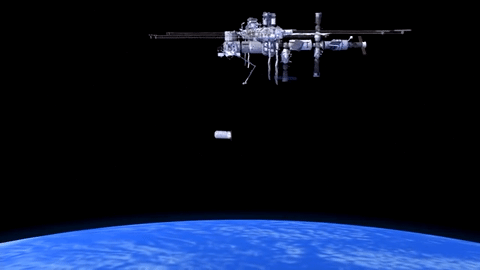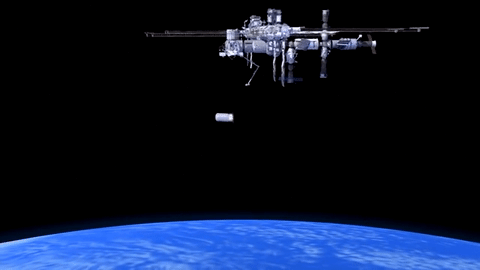
Orbital ATK’s Cygnus CRS-6 spacecraft launched to the International Space Station on March 22.
Cygnus will carry almost 7,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
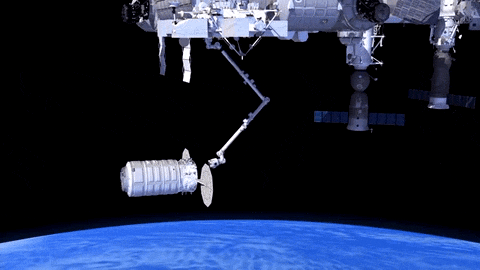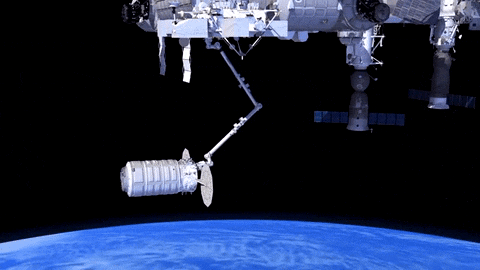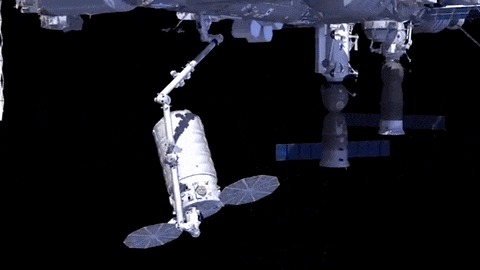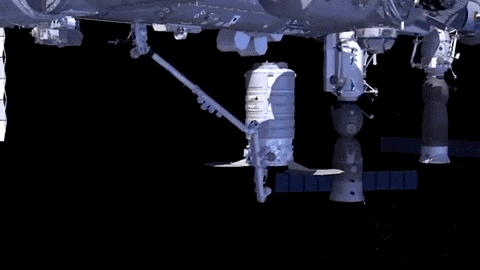
After launch in Florida, the spacecraft will arrive to the station on Saturday, March 26. Upon arrival, NASA astronaut and Expedition 46 Commander Tim Kopra will capture Cygnus at about 6:40 a.m. using the space station's Canadarm2 robotic arm to take hold of the spacecraft. Astronaut Tim Peake of ESA (European Space Agency) will support Kopra in a backup position.
Installation (when Cygnus is connected to space station) is expected to begin at 9:25 a.m. NASA TV coverage for installation resumes at 9:15 a.m.

After the Cygnus spacecraft is berthed (connected) to the space station, the contents will be emptied and brought inside for use. Any trash that is on the space station, can be put inside the empty Cygnus before it is undocked from station and sent to burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
Watch Capture
You can watch the capture of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft online. Stream live coverage starting at 5:30 a.m. EDT on Saturday, March 26. Capture is scheduled for 6:40 a.m.
Tune in again at 9:15 a.m. to watch #Cygnus installation to the station.
Watch online: nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Cygnus Cargo Craft: What’s Onboard?

New experiments are scheduled to arrive to the International Space Station with the launch of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo spacecraft on Tuesday. These science payloads will study fires, meteors, regolith, adhesion and 3-D printing in microgravity.
Take a look at the experiments:
Saffire-I

What is it? What happens when you set a fire in space? The Spacecraft Fire Experiment-I (Saffire-I) will find out!
How does it work? This experiment will intentionally light a large-scale fire inside an empty Cygnus resupply vehicle after it leaves the space station and before it re-enters Earth’s atmosphere.
Why is it important? The Saffire-I investigation provides a new way to study a realistic fire on an exploration vehicle, which has not been possible in the past because the risks for performing studies on manned spacecraft are too high. Instruments on the returning Cygnus will measure flame growth, oxygen use and more.
Meteor

What is it? A less heated investigation, Meteor Composition Determination (Meteor) will enable the first space-based observations of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere from space. Meteors are somewhat rare and are difficult to monitor from the ground because of Earth’s atmosphere.
How does it work? This investigation uses high-resolution video and image analysis of the atmosphere to acquire the physical and chemical properties of the meteoroid dust, such as size, density and chemical composition.
Why is it important? Studying the elemental composition of meteors adds to our understanding of how the planets developed, and continuous measurement of meteor interactions with Earth’s atmosphere could spot previously unforeseen meteors.
Strata-1

What is it? A more “grounded” investigation will study the properties and behavior of regolith, the impact-shatterd “soil” found on asteroids, comets, the moon and other airless worlds.
How does it work? The Strata-1 experimental facility exposes a series of regolith simulants, including pulverized meteorite material, glass beads, and regolith simulants composed of terrestrial materials and stored in multiple transparent tubes, to prolonged microgravity on the space station. Scientists will monitor changes in regolith layers and layering, size sorting and particle migration via video images and close examination after return of the samples to Earth.
Why is it important? The Strata-1 investigation could give us new answers about how regolith behaves and moves in microgravity, how easy or difficult it is to anchor a spacecraft in regolith, how it interacts with spacecraft and spacesuit materials and other important properties.
Gecko Gripper

What is it? From grounded to gripping, another investigation launching takes inspiration from small lizards. Geckos have specialized hairs on their feed called setae that let them stick to vertical surfaces without falling, and their stickiness doesn’t wear off after repeated use. The Gecko Gripper investigation tests a gecko-adhesive gripping device that can stick on command in the harsh environment of space.
How does it work? The gripping device is a material with synthetic hairs much like setae that are much thinner than a human hair. When a force is applied to make the tiny hairs bend, the positively charged part of a molecule within a slight electrical field attracts the negatively charged part of its neighbor resulting in “stickiness.” Once adhered, the gripper can bear loads up to 20 pounds. The gripper can remain in place indefinitely and can also be easily removed and reused.
Why is it important? Gecko Grippers have many applications on current and future space missions, including acting as mounting devices for payloads, instruction manuals and many other small items within the space station. In addition, this technology enables a new type of robotic inspection system that could prove vital for spacecraft safety and repair.
Additive Manufacturing Facility

What is it? From adhesion to additive, the new Additive Manufacturing Facility (AMF) will also launch on the flight. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is the process of building a part layer-by-layer, with an efficient use of the material.
How does it work? The AMF uses this technology to enable the production of components on the space station for both NASA and commercial objectives.
Why is it important? Parts, entire experiments and tools can be created on demand with this technology. The ability to manufacture on the orbiting laboratory enables on-demand repair and production capability, as well as essential research for manufacturing on long-term missions.
These sticky, stony and sizzling investigations are just a sampling of the wide range of science conducted on the orbiting laboratory that benefits future spaceflight and provides Earth-based benefits as well.
Watch the Launch!
You can watch the launch of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft online. Stream live coverage starting at 10 p.m. EDT on March 22. Launch is scheduled for 11:05 p.m., which is the start of a 30-minute launch window.
Watch online: nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Do Cargo Spacecraft Work?

Today is the day that our commercial partner, Orbital ATK, has set for the launch of its fourth contracted mission to the International Space Station. The Cygnus spacecraft will carry more than 7,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory.
How Does it Launch?

This mission is the first Cygnus mission to utilize NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and launch from the Cape Canaveral Air Force base in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The cargo will be launched inside the Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft using a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
But how does it get there? Is there someone on the ground controlling and directing it to the space station? Surprisingly, no. After launch, the Cygnus spacecraft is automated until it gets near the station. At that point, the robotic controllers use the CanadArm2 to reach out and grapple it (grab), and then berth (connect) it to the station.
What’s Inside?

In order to keep the thousands of pounds of supplies, science and hardware from moving during launch and in flight, the cargo is packed in bags and strapped to the walls.
The new experiments arriving to the space station will challenge and inspire future scientists and explorers. A few of the highlights are:
The Packed Bed Reactor Experiment (PBRE) - This experiment (image below) will study the behavior of gases and liquids when they flow simultaneously through a column filled with fixed porous media. The findings from this will be of interest in many chemical and biological processing systems as well as many geophysical applications.

BASS-M (Burning and Suppression of Solids – Milliken) - This experiment (image below) will evaluate flame retardant and/or resistant textiles as a mode of personal protection from fire-related hazards. Studying this in microgravity will aid in better designs for future textiles and benefit those who wear flame retardant and/or resistant protective apparel such as military personnel and civilian workers in the electrical and energy industries.

Space Automated Bioproduct Lab (SABL) - This equipment is a single locker-sized facility (image below) that will enable a wide variety of fundamental, applied and commercial life sciences research. It will also benefit K-16 education-based investigations aboard the space station. Research will be supported on microorganisms (bacteria, yeast, algae, fungi, viruses, etc.), animal cells and tissues and small plant and animal organisms.

Nodes Satellites – These satellites (image below) will be deployed from the space station to demonstrate new network capabilities critical to the operation of swarms of spacecraft. They will show the ability of multi-spacecraft swarms to receive and distribute ground commands, exchange information periodically and more.

Holiday Surprises - With the upcoming holidays the crew’s family has the opportunity to send Christmas gifts to their family members on the International Space Station.

What About After?
The spacecraft will spend more than a month attached to the space station before it’s detached for re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere in January 2016, disposing of about 3,000 pounds of trash. It will disintegrate while entering the atmosphere.

Want to Watch Launch?
Launch coverage begins at 4:30 p.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 3 on NASA Television. Cygnus is set to lift off on the Atlas V at 5:55 p.m., the beginning of a 30-minute launch window, from Space Launch Complex 41.
In addition to launch coverage, a post-launch briefing will be held approximately two hours after launch. All briefings will air live on NASA TV.
UPDATE: Due to poor weather conditions, today’s launch has been scrubbed and moved to tomorrow at 5:33 p.m. EST. The forecast for tomorrow calls for a 30% chance of acceptable conditions at launch time. Continuous countdown coverage will be available on NASA Television starting at 4:30 p.m.

UPDATE 2: The uncrewed Cygnus cargo ship launched at 4:44 p.m. EST on Sunday, Dec. 6 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to begin its three-day journey to the orbiting laboratory.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
An Exo-What...?

Simply put, an exoplanet is a planet that orbits another star. That said, just because a planet orbits a star (like Earth) does not mean that it is automatically stable for life. The planet must be within the habitable zone, which is the area around a star in which water has the potential to be liquid…aka not so close that all the water would evaporate, and not too far away where all the water would freeze.
Recently, with the help of our Kepler spacecraft, scientists have discovered the most Earth-like exoplanet ever, Kepler-452b. Pretty cool! This chart shows 12 other exoplanet discoveries that are less than twice the size of Earth, and live in the habitable zone of their host star. Kepler-452b is special because all previous findings have orbited stars that are smaller and cooler than Earth’s.

You may be thinking, “Okay, so what? There’s an Earth-like planet that spins around a similar sized sun.” Well, Kepler-452b orbits its sun at nearly the same distance from its star as Earth does from our sun, which means that conditions on the plant could be similar to those here on Earth!

We can already guess your next question…”When are we going to Kepler-452b?!” Well, this planet is located in the constellation Cygnus which is 1,400 light-years away, so not anytime soon. However, our Kepler spacecraft continues to search for Earth-like exoplanets and gather important scientific information about them.