Your gateway to endless inspiration
Progress Marches On - Blog Posts
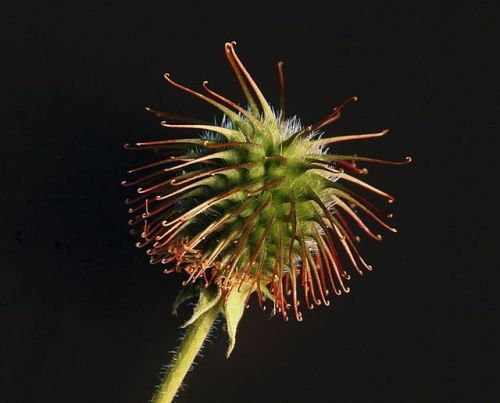

In 1941, Swiss engineer George de Mestral noticed after a hunting trip that burrs from burdock plants stuck to his pants and his dog’s fur.
He took the seed and looked at them through a microscope to find that this seed attaches to animal fur via the hooks on its surface to improve distribution.

Source: All of Nature on Blogspot
These hooks would latch onto anything loop-shaped, such as the fibers in his pants and his dog’s tangled fur. This inspired him to come up with the ‘Velcro’.
Velcro is a bio-mimicry of this burrs with small flexible hooks attached on its surface to attach to fluffy surfaces.


Although it goes by the name Velcro the generic name is a hook-and-loop fastener)

And depending on the load that needs to be held there are different types of hooks that are available:

The sound that the velcro makes when you rip it apart is oddly satisfying. It is made when the loops are ripped apart from the hooks.
It was always in my head that the hooks or the loops would break whenever you would rip it apart. But turns out, they are extremely flexible.

Source
For a long time I believed that this was the end of the story and that’s how far we had gone. But recently when I was trying to mount a board to the wall, I came across the 3M dual lock fasteners.
These use a mushroom shaped hook on both the sides to snap together in place.


Source
And evidently it turns out the mushroom fastener design were inspired from dragonflies who used it for stability during mating (check source video above for more).
This is great, but since this is made of plastic this surely would fail at higher temperatures. You need something robust to handle higher temperatures, and this is where the Metaklett comes into the picture:

A square metre of this fastener, called Metaklett (made of steel), is capable of supporting 35 tonnes at temperatures up to 800 ºC, (Video)
There is something exotic in the blend of nature and technology that is manifested in the Velcro, I just cannot put my hand on what it is.
Have a great day!
Injectable bandages

Above: Akhilesh K Gaharwar, Ph.D., of Texas A&M University, demonstrating injectability of nano engineered hydrogels, Credit: Gaharwar Lab, www.akgaharwar.com A gelling agent commonly used in making pastries just got a major promotion. It’s now a key ingredient for new “injectable bandages” that can simulate the structure of human tissue, stop bleeding and promote healing. Potential applications include helping troops wounded in the battlefield. This Texas A&M research is our featured podcast story - Sweet! http://bit.ly/2ILgNBY
Below: Schematic showing injectable bandage composed of 2D nanoparticles and common food additive - kappa carrageenan, Credit: Lokhande, et al.
Paper: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1742706118300564

Technology for the blind!
NSF-funded researchers at Texas A&M University have developed STAAR (Situated Touch Audio Annotator And Reader) e-reader that enables blind readers to read the same text sighted readers do. The system allows a user to scan the text with their fingers to hear the words. For more information: https://bit.ly/2Fm1HSU
Video credit: Texas A&M University
Two Steps Forward in the Search for Life on Mars
We haven’t found aliens but we are a little further along in our search for life on Mars thanks to two recent discoveries from our Curiosity Rover.

We detected organic molecules at the harsh surface of Mars! And what’s important about this is we now have a lot more certainty that there’s organic molecules preserved at the surface of Mars. We didn’t know that before.
One of the discoveries is we found organic molecules just beneath the surface of Mars in 3 billion-year-old sedimentary rocks.

Second, we’ve found seasonal variations in methane levels in the atmosphere over 3 Mars years (nearly 6 Earth years). These two discoveries increase the chances that the record of habitability and potential life has been preserved on the Red Planet despite extremely harsh conditions on the surface.

Both discoveries were made by our chem lab that rides aboard the Curiosity rover on Mars.

Here’s an image from when we installed the SAM lab on the rover. SAM stands for “Sample Analysis at Mars” and SAM did two things on Mars for this discovery.
One - it tested Martian rocks. After the arm selects a sample of pulverized rock, it heats up that sample and sends that gas into the chamber, where the electron stream breaks up the chemicals so they can be analyzed.
What SAM found are fragments of large organic molecules preserved in ancient rocks which we think come from the bottom of an ancient Martian lake. These organic molecules are made up of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. That’s a possible indicator of ancient life…although non-biological processes can make organic molecules, too.
The other action SAM did was ‘sniff’ the air.

When it did that, it detected methane in the air. And for the first time, we saw a repeatable pattern of methane in the Martian atmosphere. The methane peaked in the warm, summer months, and then dropped in the cooler, winter months.

On Earth, 90 percent of methane is produced by biology, so we have to consider the possibility that Martian methane could be produced by life under the surface. But it also could be produced by non-biological sources. Right now, we don’t know, so we need to keep studying the Mars!

One of our upcoming Martian missions is the InSight lander. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to give the Red Planet its first thorough checkup since it formed 4.5 billion years ago. It is the first outer space robotic explorer to study in-depth the “inner space” of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core.
Finding methane in the atmosphere and ancient carbon preserved on the surface gives scientists confidence that our Mars 2020 rover and ESA’s (European Space Agency’s) ExoMars rover will find even more organics, both on the surface and in the shallow subsurface.
Read the full release on today’s announcement HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.






1945-1952 - Space Station by Wernher von Braun - Von Braun was a leading aerospace engineer first in Germany until 1945, and after being captued by U.S. forces in the same year, he continued working for NASA in U.S. He made United States able to develop the Saturn/Apollo program, making humans landing on the moon. The pictures here by NASA show one of Wernher von Braun’s fantastic plans, designing a space station for humans. NASA said that “(Wernher von Braun is) without any doubt the greatest rocket scientist in history”. For further details on the space station, please study the following link, adding a lot of details to this concept: http://www.astronautix.com/craft/vonation.htm. The following quote is as well from that website: “In the first 1946 summary of his work during World War II, Wernher von Braun prophesied the construction of space stations in orbit. The design, a toroidal station spun to provide artificial gravity, would be made very familiar to the American public over the next six years. The design was elaborated at the First Symposium on Space Flight on 12 October 1951 at the Hayden Planetarium in New York City. The design was popularized in the series in Colliers magazine, illustrated with gorgeous Chesley Bonestell painting, in 1952. The 1946 version used 20 cylindrical sections, each about 3 m in diameter and 8 m long, to make up the toroid. The whole station was about 50 m in diameter and guy wires connecting and positioning the toroid to the 8 m-diameter central power module. This was equipped with a sun-following solar collector dish to heat fluid in a ball-shaped device. The heated fluid would run an electrical generator. Presumably visiting spacecraft would dock or transfer crew at the base of the power module.”
Help Explore Your Own Solar Neighborhood
We’re always making amazing discoveries about the farthest reaches of our universe, but there’s also plenty of unexplored territory much closer to home.

Our “Backyard Worlds: Planet 9” is a citizen science project that asks curious people like you — yes, you there! — to help us spot objects in the area around our own solar system like brown dwarfs. You could even help us figure out if our solar system hosts a mysterious Planet 9!

In 2009, we launched the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE). Infrared radiation is a form of light that humans can’t see, but WISE could. It scans the sky for infrared light, looking for galaxies, stars and asteroids. Later on, scientists started using it to search for near-Earth objects (NEOWISE) like comets and asteroids.

These searches have already turned up so much data that researchers have trouble hunting through all of it. They can’t do it on their own. That’s why we asked everyone to chip in. If you join Backyard Worlds: Planet 9, you’ll learn how to look at noisy images of space and spot previously unidentified objects.
You’ll figure out how to tell the difference between real objects, like planets and stars, and artifacts. Artifacts are blurry blobs of light that got scattered around in WISE’s instruments while it was looking at the sky. These “optical ghosts” sometimes look like real objects.

Why can’t we use computers to do this, you ask? Well, computers are good at lots of things, like crunching numbers. But when it comes to recognizing when something’s a ghostly artifact and when it’s a real object, humans beat software all the time. After some practice, you’ll be able to recognize which objects are real and which aren’t just by watching them move!

One of the things our citizen scientists look for are brown dwarfs, which are balls of gas too big to be planets and too small to be stars. These objects are some of our nearest neighbors, and scientists think there’s probably a bunch of them floating around nearby, we just haven’t been able to find all of them yet.
But since Backyard Worlds launched on February 15, 2016, our volunteers have spotted 432 candidate brown dwarfs. We’ve been able to follow up 20 of these with ground-based telescopes so far, and 17 have turned out to be real!

Image Credit: Ryan Trainor, Franklin and Marshall College
How do we know for sure that we’ve spotted actual, bona fide, authentic brown dwarfs? Well, like with any discovery in science, we followed up with more observation. Our team gets time on ground-based observatories like the InfraRed Telescope Facility in Hawaii, the Magellan Telescope in Chile (pictured above) and the Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico and takes a closer look at our candidates. And sure enough, our participants found 17 brown dwarfs!

But we’re not done! There’s still lots of data to go through. In particular, we want your help looking for a potential addition to our solar system’s census: Planet 9. Some scientists think it’s circling somewhere out there past Pluto. No one has seen anything yet, but it could be you! Or drop by and contribute to our other citizen science projects like Disk Detective.
Congratulations to the citizen scientists who spotted these 17 brown dwarfs: Dan Caselden, Rosa Castro, Guillaume Colin, Sam Deen, Bob Fletcher, Sam Goodman, Les Hamlet, Khasan Mokaev, Jörg Schümann and Tamara Stajic.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What we all need to understand about AI in a nutshell:
There’s an algorithm that can reliably predict, from aggregate facebook posts, the onset of a manic episode in a person suffering from bipolar disorder – more reliably even, than a trained psychotherapist, who only has access to the information a patient provides them in therapy sessions.
“Won’t technology like that help people with bipolar disorder?”
Theoretically, it could. But this algorithm wasn’t designed to help people with bipolar disorder.
This algorithm was designed to sell plane tickets to Las Vegas.
[source]
It absolutely does!!!!! There is so much we still don’t understand! So much to be discovered! So much unknown! So much unexplored territory!
it is absolutely my kind of thing. so much work, such intricate pieces! I would’ve loved to be on the team that put this together.



Creepy or adorable? Researchers at Harvard University have demonstrated the first autonomous, untethered, entirely soft robot: the octobot.
Instead of being controlled by electronics, the robot’s logic board is powered by chemical reactions and fluid passing along tiny channels. Scientist have struggled to create completely soft robots because rigid components like circuit boards, power sources and electronic controls are difficult to replace.
Learn more about the octobot and soft robotics here and see the full study published in Nature here.
Videos Credit: Harvard SEAS/Image Credit Lori Sanders

Scientists have figured out how to use nuclear waste as an energy source, converting radioactive gas into artificial diamonds that could be used as batteries.
These diamonds, which are able to generate their own electrical current, could potentially provide a power source for thousands of years, due to the longstanding half-life of the radioactive substances they’re made from.
“There are no moving parts involved, no emissions generated, and no maintenance required, just direct electricity generation,” says geochemist Tom Scott from the University of Bristol in the UK.
“By encapsulating radioactive material inside diamonds, we turn a long-term problem of nuclear waste into a nuclear-powered battery and a long-term supply of clean energy.”
Continue Reading.