103 posts
Latest Posts by redplanet44 - Page 3
Imagine the lightsabers from this
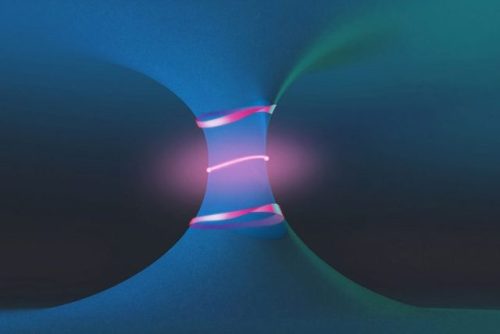
Scientists Observe New Exotic Phenomena in Photonic Crystals
Topological effects, such as those found in crystals whose surfaces conduct electricity while their bulk does not, have been an exciting topic of physics research in recent years and were the subject of the 2016 Nobel Prize in physics. Now, a team of researchers at MIT and elsewhere has found novel topological phenomena in a different class of systems — open systems, where energy or material can enter or be emitted, as opposed to closed systems with no such exchange with the outside.
This could open up some new realms of basic physics research, the team says, and might ultimately lead to new kinds of lasers and other technologies.
The results are being reported this week in the journal Science, in a paper by recent MIT graduate Hengyun “Harry” Zhou, MIT visiting scholar Chao Peng (a professor at Peking University), MIT graduate student Yoseob Yoon, recent MIT graduates Bo Zhen and Chia Wei Hsu, MIT Professor Marin Soljačić, the Francis Wright Davis Professor of Physics John Joannopoulos, the Haslam and Dewey Professor of Chemistry Keith Nelson, and the Lawrence C. and Sarah W. Biedenharn Career Development Assistant Professor Liang Fu.
Read more.
Hunt for Huntington!

Possible Biomarker for Huntington’s Identified
A new discovery of a potential biomarker for Huntington’s disease (HD) could mean a more effective way of evaluating the effectiveness of treatments for this neurological disease. The findings may provide insight into treatments that could postpone the death of neurons in people who carry the HD gene mutation, but who do not yet show symptoms of the disease.

Scientists make research ‘jelly’ grow more like biological tissues
Opens up new possibilities in tissue engineering and soft robotics
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) have found a way to direct the growth of hydrogel, a jelly-like substance, to mimic plant or animal tissue structure and shapes.
The team’s findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences today, suggest new applications in areas such as tissue engineering and soft robotics where hydrogel is commonly used. The team has also filed a patent at CMU and NTU.
In nature, plant or animal tissues are formed as new biomass is added to existing structures. Their shape is the result of different parts of those tissues growing at different rates.
Mimicking this behaviour of biological tissues in nature, the research team comprising CMU scientists Changjin Huang, David Quinn, K. Jimmy Hsia and NTU President-designate Prof Subra Suresh, showed that through manipulation of oxygen concentration, one can pattern and control the growth rate of hydrogels to create the desired complex 3D shapes.
Read more.
What doesn't tear you makes you doper


Substitutional defects ( 2 ) are point defects in which an impurity atom takes the place of a native atom within the crystal lattice. Semiconductors often intentionally add substitional defects through doping, such as adding boron or phosphorous to silicon to create an n- or p-type semiconductor, and certain alloys include extraneous elements to create substitional defects for solution hardening purposes.
Image source.
LISTEN UP YALL
scientists are saying we have about three years before all climate change effects are completely irreversible (meaning we are absolutely FUCKED). that’s just to avoid the worst of it (yes, all this shit with the fires and hurricanes is NOT the worst of it). so, i made a quick list of things people can do to start reducing their energy use and in turn, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and what not! -line/hang dry clothing - dryers use so much energy as it is and switching to the actually makes your clothing last so much longer! aka less energy spent on manufacturing and shipping clothing. -eat less meat - when i say this, it’s not specifically for the save the animals idea, but that is a huge bonus! factories that slaughter, process, and package meat use an insane amount of energy (another reason to switch to local as much as possible!!) -use less hot water - wash clothes in cold water, take shorter showers (or cold ones if you can handle that) -switch to reusable grocery bags -efficient light bulbs -carpool, walk, ride a bike, public transit -unplug electronics not in use - don’t leave things charging for too long. unplug your tv when it’s not being used. 40% of an item’s energy use is spent when it’s on standby!! -buy only what you need (look into minimalism guys, it’s real neat and saves money) -recycle -get a reusable water bottle instead of buying cases of plastic bottles - i bought one at walmart for 98 cents and i use it every single day. -plant your own garden or start a community garden! -composting -maintain air in car tires for better gas mileage -drive instead of taking airplanes -buy used items if they’re in good condition - why spend $20 on a shirt that you can find at goodwill for $1? same goes for books, CDs, and pretty much anything! save money AND cut down on energy use! -yall know that saying “reduce, reuse, recycle” -most importantly: TALK TO PEOPLE ABOUT THIS ISSUE - i mean your friends, your family, your local government, everyone!! these are all small things and it’s just a start but if we can get everyone in on habits like these, we could reduce the population’s carbon footprint by SO MUCH! we don’t wanna end up like that movie wall-e guys. this is serious!!





Rocket into sub-orbit on Blue Origin’s New Shepard! (December 15, 2017) It’s a pristine day in west Texas. The desert stretches far to the horizon out the capsule’s windows with the foothills of the Van Horn mountain range in the distance. The typical winter day is broken first by a deep rumble from below followed an instant later by clouds of smoke and a flash of flame. That’s the scene inside Blue Origin’s New Shepard crew capsule during launch as seen in new footage from this week’s test. Mannequin Skywalker - the company’s astronaut simulator - is seen rocketing to over 322,000 feet, or 61 miles, strapped in one of the cabin’s six seats.

Within seconds, the receding countryside below gives way to vast swaths of desert. The sky turns from thick and blue to pitch black in a matter of seconds as the vehicle races upwards. New Shepard would reach a maximum ascent velocity of Mach 2.94 during the flight. As the single BE-3 engine of the propulsion stage cuts out, the cabin becomes weightless as indicated by straps on the dummy’s chest. Hundreds of miles of the Earth below spread out in all directions from the cabin’s six panoramic windows. Measuring 2.4 by 3.6 feet, they’re the largest ever flown on a space vehicle. Weightless conditions and breathtaking views continue as the capsule begins its descent to Earth. It’s like the launch but in reverse; the black of space quickly fills with colour as the atmosphere is reentered. Because New Shepard is a suborbital vehicle and doesn’t boost the capsule fast enough to achieve significant atmospheric friction, there is no flaming meteor-in-the-sky or heat shield on the spacecraft. It simply falls through the sky, racing to meet the Earth below which it only just left. Back in the thicker atmosphere, three drogue parachutes help stabilize the cabin before the larger main canopies are unfurled. These help bring the capsule to a safe, soft landing at just one foot per second a few kilometers from the launch pad. According to Blue Origin’s founder and CEO, Jeff Bezos, the pinging heard inside the capsule in the video was due to one of the 12 experiments carried on board Mission 7. This was the first New Shepard flight granted a commercial launch license by the FAA, allowing them to carry commercial research payloads on the flight. Other flight milestones can also be discerned by the subtle audio and visual clues, such as MECO, stage separation, drogue cute deployment and mail parachute deployment. Read our full story on Mission 7 and the resumption of New Shepard testing by clicking here.
Check out the full video with audio by clicking here or below.
P/C: Blue Origin.

On November 9, 1967, the uncrewed Apollo 4 test flight made a great ellipse around Earth as a test of the translunar motors and of the high speed entry required of a crewed flight returning from the Moon. https://go.nasa.gov/2zybcxC

Journal reference: Cell Reports
Manual isolation of a single live mitochondria. The mitochondria can be seen under a microscope where a thin glass tube can be used to isolate the mitochondria from the dendrite region of the mouse neuron. Credit: Jacqueline Morris and Jaehee Lee, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania

Flame Nebula in Orion - For more images of the cosmos Click Here
Panorama of Jupiter

Jupiter seen by NASA’s Voyager spacecraft
Animation taken from video: Jeff Quitney
Biomimicry

Brittle starfish shows how to make tough ceramics
Nature inspires innovation. An international team lead by researchers at Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, together with ESRF -the European Synchrotron, Grenoble, France- scientists, have discovered how a brittle star can create material like tempered glass underwater. The findings are published in Science and may open new bio-inspired routes for toughening brittle ceramics in various applications that span from optical lenses to automotive turbochargers and even biomaterial implants.
A beautiful, brainless brittle star that lives in coral reefs has the clue to super tough glass. Hundreds of focal lenses are located on the arms of this creature, which is an echinoderm called Ophiocoma wendtii. These lenses, made of chalk, are powerful and accurate, and the deciphering of their crystalline and nanoscale structure has occupied Boaz Pokroy and his team, from the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, for the past three years. Thanks to research done on three ESRF beamlines, ID22, ID13 and ID16B, among other laboratories, they have figured out the unique protective mechanism of highly resistant lenses.
As an example, take tempered glass. It is produced by exerting compressive pressure on the glass which compresses it and leaves it more compact than in its natural state. Glass tempering is performed by rapidly heating and then rapidly cooling the material. In this process, the outside of the material cools more quickly than the inside and thereby compresses the inside. Ophiocoma wendtiilenses are created in the open sea, at room temperature, unlike tempered glass. “We have discovered a strategy for making brittle material much more durable under natural conditions. It is ‘crystal engineering’ and tempering without heating and quenching – a process that could be very useful in materials engineering,” explains Pokroy.
Read more.
So the other night during D&D, I had the sudden thoughts that:
1) Binary files are 1s and 0s
2) Knitting has knit stitches and purl stitches
You could represent binary data in knitting, as a pattern of knits and purls…
You can knit Doom.
However, after crunching some more numbers:
The compressed Doom installer binary is 2.93 MB. Assuming you are using sock weight yarn, with 7 stitches per inch, results in knitted doom being…
3322 square feet
Factoring it out…302 people, each knitting a relatively reasonable 11 square feet, could knit Doom.
Like the crazy eye of the universe

The Hydrogen Atom
PINning down future problems

Study finds hackers could use brainwaves to steal passwords
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham suggest that brainwave-sensing headsets, also known as EEG or electroencephalograph headsets, need better security after a study reveals hackers could guess a user’s passwords by monitoring their brainwaves.
EEG headsets are advertised as allowing users to use only their brains to control robotic toys and video games specifically developed to be played with an EEG headset. There are only a handful on the market, and they range in price from $150 to $800.
Nitesh Saxena, Ph.D., associate professor in the UAB College of Arts and Sciences Department of Computer and Information Sciences, and Ph.D. student Ajaya Neupane and former master’s student Md Lutfor Rahman, found that a person who paused a video game and logged into a bank account while wearing an EEG headset was at risk for having their passwords or other sensitive data stolen by a malicious software program.
“These emerging devices open immense opportunities for everyday users,” Saxena said. “However, they could also raise significant security and privacy threats as companies work to develop even more advanced brain-computer interface technology.”
Saxena and his team used one EEG headset currently available to consumers online and one clinical-grade headset used for scientific research to demonstrate how easily a malicious software program could passively eavesdrop on a user’s brainwaves. While typing, a user’s inputs correspond with their visual processing, as well as hand, eye and head muscle movements. All these movements are captured by EEG headsets. The team asked 12 people to type a series of randomly generated PINs and passwords into a text box as if they were logging into an online account while wearing an EEG headset, in order for the software to train itself on the user’s typing and the corresponding brainwave.
“In a real-world attack, a hacker could facilitate the training step required for the malicious program to be most accurate, by requesting that the user enter a predefined set of numbers in order to restart the game after pausing it to take a break, similar to the way CAPTCHA is used to verify users when logging onto websites,” Saxena said.
The team found that, after a user entered 200 characters, algorithms within the malicious software program could make educated guesses about new characters the user entered by monitoring the EEG data recorded. The algorithm was able to shorten the odds of a hacker’s guessing a four-digit numerical PIN from one in 10,000 to one in 20 and increased the chance of guessing a six-letter password from about 500,000 to roughly one in 500.
EEG has been used in the medical field for more than half a century as a noninvasive method for recording electrical activity in the brain. Electrodes are placed on the surface of the scalp to detect brain waves. An EEG machine then amplifies the signals and records them in a wave pattern on graph paper or a computer. EEG can be combined with a brain-computer interface to allow a person to control external devices. This technology was once highly expensive and used mostly for scientific research, like the production of neuroprosthetic applications to help disabled patients control prosthetic limbs by thinking about the movements. However, it is now being marketed to consumers in the form of a wireless headset and is becoming popular in the gaming and entertainment industries.
“Given the growing popularity of EEG headsets and the variety of ways in which they could be used, it is inevitable that they will become part of our daily lives, including while using other devices,” Saxena said. “It is important to analyze the potential security and privacy risks associated with this emerging technology to raise users’ awareness of the risks and develop viable solutions to malicious attacks.”
One potential solution proposed by Saxena and his team is the insertion of noise anytime a user types a password or PIN while wearing an EEG headset.
It`s gonna be Moon Soon season in India!! @neysastudies
The last time any country put boots or, rather, little metal feet, on the Moon was in 2013, when China landed its Yutu rover there. Before that, you’d have to look back to the 1970s to find anything built by Earthlings that camped out on the surface of the Moon.
But in 2018, India says it will be ready to join the ranks of the moon lander. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is getting ready to land its very first lunar rover by the end of March 2018, as part of its Chandrayaan-2 mission.
Continue Reading.
Well, money is usually made from paper.
If money did grow on trees, we’d probably be more concerned about protecting the environment.
Roommate -> roomsister

November 28 2017
Afternoon study session at my university’s library with my astronaut friend @redplanet44 ☆
Heavy metal is in our blood!
Anytime you don’t feel powerful, remember this:

Supergiant stars are beasts! Their life is a fight between gravity pushing in and heat pushing out. They fuse heavier and heavier elements in their core until they get to iron. They can’t fuse any more. Iron absorbs more energy than it returns, so gravity takes over. The star’s core collapses and the star dies in an explosive supernova that outshines its entire galaxy.

The heat of a supernova fuses new elements during the explosion, which are then spread out into space via the nebula remnant. Nebulae are the birthplaces of new stars and solar systems.

The iron in your blood came from one of the most powerful explosions in the universe.

You have something in your blood that can kill stars and build solar systems.
Disabled? Most abled person!











follow @the-future-now

Lego’s new “Women of NASA” set is now available, and the product has already risen to the top of Amazon’s list of best-selling toys.
The set of 231 plastic pieces costs about $25 and went on sale Wednesday morning. Its instant popularity is not surprising to those who have been following Lego’s laudable — and presumably profitable — trend of selling toys that are more inclusive of women.
“Women of NASA” features four mini figurines of pioneering women from the space agency: the astronauts Sally Ride and Mae Jemison, the astronomer Nancy Grace Roman, and the computer scientist Margaret Hamilton.
Continue Reading.
-My sun and stars!
-Moon of my life!
5 things that may surprise you about the Moon
…In honor of International Observe the Moon Night
October 28th is International Observe the Moon Night, a worldwide, public celebration of lunar science and exploration held annually since 2010 thanks to our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission team and partners. One day each year, everyone on Earth is invited to observe and learn about the Moon together, and to celebrate the cultural and personal connections we all have with our planet’s nearest neighbor.

Here are 5 things that might surprise you about the Moon.
1. There has been a spacecraft there for 100 lunar days

In October 2017, LRO celebrates one hundred days of collecting scientific data at the Moon. One hundred Moon days. From our perspective on Earth, one lunar day is one full phase cycle, or about 29.5 Earth days. That’s 100 opportunities to observe changes from night to day, photograph the surface at different Sun angles, measure rising and falling temperatures, study the way certain chemicals react to the daily light and temperature cycle, and increase our understanding of the Moon as a dynamic place.
2. You can still see the paths left by Apollo astronauts’ boot prints and rovers

Much of the lunar surface is covered in very fine dust. When Apollo astronauts landed on the Moon, the descent stage engine disturbed the dust and produced a distinct bright halo around the lunar module. As astronauts moved around, their tracks exposed the darker soil underneath, creating distinct trails that we know, thanks to LRO, are still visible today. The Moon has no atmosphere, so there is no wind to wipe away these tracks.
3. The Moon has tattoos!

Observations from LRO show mysterious patterns of light and dark that are unique to the Moon. These lunar swirls look painted on, like the Moon got ‘inked.’ Lunar swirls, like these imaged at Reiner Gamma by LRO, are found at more than 100 locations across the lunar surface. Lunar swirls can be tens of miles across and appear in groups or as isolated features.
Researchers think these patterns form in places where there’s still a remnant of the Moon’s magnetic field. There are still many competing theories about how swirls form, but the primary idea is that the local magnetic field deflects the energetic particles in the solar wind, so there’s not as much weathering of the surface. The magnetically shielded areas would then look brighter than everything around them.
4. There were once active volcanoes, that shaped what we see now

Early astronomers named the large dark spots that we see on the near side of the Moon “maria,” Latin for “seas,” because that’s what they thought they were. We now know that the dark spots are cooled lava, called basalt, formed from ancient volcanic eruptions. The Moon’s volcanoes are no longer active, but their past shapes the Moon that we see today. The Moon doesn’t have large volcanoes like ones in Hawaii, but it does have smaller cones and domes.
Other small features derived from volcanic activity include rivers of dried lava flows, like the ones visible in this image of Vallis Schroteri taken by LRO, and dark areas formed from eruptive volcanoes that spewed fire. For many years, scientists thought the Moon’s volcanic activity died out long ago, but there’s some evidence for relatively “young” volcanism, suggesting that the activity gradually slowed down instead of stopping abruptly.
5. Anyone, anywhere can participate in International Observe the Moon Night.

How to celebrate International Observe the Moon Night
Attend an event – See where events are happening near you by visiting http://observethemoonnight.org
Host an event – Call up your neighbors and friends and head outdoors – no special equipment is needed. Let us know how you celebrated by registering your event!
Don’t let cloudy weather get you down! Observe the Moon in a variety of ways from the comfort of indoors – View stunning lunar vistas through images and videos, or explore the Moon on your own with QuickMap or Moon Trek
Join the worldwide conversation with #ObserveTheMoon on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook
For regular Moon-related facts, updates and science, follow @NASAMoon on Twitter
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Eye o' Sofia
Chasing the Shadow of Neptune’s Moon Triton
Our Flying Observatory

Our flying observatory, called SOFIA, carries a 100-inch telescope inside a Boeing 747SP aircraft. Scientists onboard study the life cycle of stars, planets (including the atmosphere of Mars and Jupiter), nearby planetary systems, galaxies, black holes and complex molecules in space.
AND on Oct. 5, SOFIA is going on a special flight to chase the shadow of Neptune’s moon Triton as it crosses Earth’s surface!
In case you’re wondering, SOFIA stands for: Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy.
Triton

Triton is 1,680 miles (2,700 km) across, making it the largest of the 13 moons orbiting Neptune. Unlike most large moons in our solar system, Triton orbits in the opposite direction of Neptune, called a retrograde orbit. This backward orbit leads scientists to believe that Triton formed in an area past Neptune, called the Kuiper Belt, and was pulled into its orbit around Neptune by gravity.
The Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past Neptune and Triton in 1989 and found that Triton’s atmosphere is made up of mostly nitrogen…but it has not been studied in nearly 16 years!
Occultations are Eclipse-Like Events

An occultation occurs when an object, like a planet or a moon, passes in front of a star and completely blocks the light from that star. As the object blocks the star’s light, it casts a faint shadow on Earth’s surface.
But unlike an eclipse, these shadows are not usually visible to the naked eye because the star and object are much smaller and not nearly as bright as our sun. Telescopes with special instruments can actually see these shadows and study the star’s light as it passes near and around the object – if they can be in the right place on Earth to catch the shadow.
Chasing Shadows

Scientists have been making advanced observations of Triton and a background star. They’ve calculated exactly where Triton’s faint shadow will fall on Earth! Our SOFIA team has designed a flight path that will put SOFIA (the telescope and aircraft) exactly in the center of the shadow at the precise moment that Triton and the star will align.
This is no easy feat because the shadow is moving at more than 53,000 mph while SOFIA flies at Mach 0.85 (652 mph), so we only have about two minutes to catch the shadow!! But our SOFIA team has previously harnessed the aircraft’s mobility to study Pluto from inside the center of its occultation shadow, and is ready to do it again to study Triton!
What We Learn From Inside the Shadow

From inside the shadow, our team on SOFIA will study the star’s light as it passes around and through Triton’s atmosphere. This allows us to learn more about Triton’s atmosphere, including its temperature, pressure, density and composition!
Our team will use this information to examine if Triton’s atmosphere has changed since our Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past it in 1989. That’s a lot of information from a bit of light inside a shadow! Similar observations of Uranus in 1977, from our previous flying observatory, led to the discovery of rings around that planet!
International Ground-Based Support

Ground-based telescopes across the United States and Europe – from Scotland to the Canary Islands – will also be studying Triton’s occultation. Even though most of these telescopes will not be in the center of the shadow, the simultaneous observations, from different locations on Earth, will give us information about how Triton’s atmosphere varies across its latitudes.
This data from across the Earth and from onboard SOFIA will help researchers understand how Triton’s atmosphere is distorted at different locations by its high winds and its strong tides!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Two most important phenomens to live for: coffee and ISS in the space
Coffee in Space: Keeping Crew Members Grounded in Flight
Happy National Coffee Day, coffee lovers!
On Earth, a double shot mocha latte with soymilk, low-fat whip and a caramel drizzle is just about as complicated as a cup of coffee gets. Aboard the International Space Station, however, even just a simple cup of black coffee presents obstacles for crew members.

Understanding how fluids behave in microgravity is crucial to bringing the joys of the coffee bean to the orbiting laboratory. Astronaut Don Pettit crafted a DIY space cup using a folded piece of overhead transparency film. Surface tension keeps the scalding liquid inside the cup, and the shape wicks the liquid up the sides of the device into the drinker’s mouth.

The Capillary Beverage investigation explored the process of drinking from specially designed containers that use fluid dynamics to mimic the effect of gravity. While fun, this study could provide information useful to engineers who design fuel tanks for commercial satellites!

The capillary beverage cup allows astronauts to drink much like they would on Earth. Rather than drinking from a shiny bag and straw, the cup allows the crew member to enjoy the aroma of the beverage they’re consuming.

On Earth, liquid is held in the cup by gravity. In microgravity, surface tension keeps the liquid stable in the container.

The ISSpresso machine brought the comforts of freshly-brewed coffees and teas to the space station. European astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti enjoyed the first cup of espresso brewed using the ISSpresso machine during Expedition 43.


Now, during Expedition 53, European astronaut Paolo Nespoli enjoys the same comforts.

Astronaut Kjell Lindgren celebrated National Coffee Day during Expedition 45 by brewing the first cup of hand brewed coffee in space.

We have a latte going on over on our Snapchat account, so give us a follow to stay up to date! Also be sure to follow @ISS_Research on Twitter for your daily dose of space station science.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Hey ISS, I'm looking at you!
![How To Identify That Light In The Sky [750 × 702] Visit Http://spaceviewsandbeyond.blogspot.com/2017/09/how-to-identify-that-light-in-sky-750.html](https://64.media.tumblr.com/05baaab06b7833133047b40e82461e65/tumblr_owry6wNqxo1w094hwo1_500.jpg)
How to Identify that Light in the Sky [750 × 702] Visit http://spaceviewsandbeyond.blogspot.com/2017/09/how-to-identify-that-light-in-sky-750.html for more space pics
And also math is a common language for spanish and chinese people. The original esperanto :)

Cooking With Neil DeGrasse Tyson
Sound metal, don't you think?

Engineers 3-D print high-strength aluminum, solve ages-old welding problem using nanoparticles
HRL Laboratories has made a breakthrough in metallurgy with the announcement that researchers at the famous facility have developed a technique for successfully 3D printing high-strength aluminum alloys—including types Al7075 and Al6061—that opens the door to additive manufacturing of engineering-relevant alloys. These alloys are very desirable for aircraft and automobile parts and have been among thousands that were not amenable to additive manufacturing—3D printing—a difficulty that has been solved by the HRL researchers. An added benefit is that their method can be applied to additional alloy families such as high-strength steels and nickel-based superalloys difficult to process currently in additive manufacturing.
“We’re using a 70-year-old nucleation theory to solve a 100-year-old problem with a 21st century machine,” said Hunter Martin, who co-led the team with Brennan Yahata. Both are engineers in the HRL’s Sensors and Materials Laboratory and PhD students at University of California, Santa Barbara studying with Professor Tresa Pollock, a co-author on the study. Their paper 3D printing of high-strength aluminum alloys was published in the September 21, 2017 issue of Nature.
Additive manufacturing of metals typically begins with alloy powders that are applied in thin layers and heated with a laser or other direct heat source to melt and solidify the layers. Normally, if high-strength unweldable aluminum alloys such as Al7075 or AL6061 are used, the resulting parts suffer severe hot cracking—a condition that renders a metal part able to be pulled apart like a flaky biscuit.
Read more.
Should make a Webbinar about it
Webb 101: 10 Facts about the James Webb Space Telescope
Did you know…?

1. Our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope will act like a powerful time machine – because it will capture light that’s been traveling across space for as long as 13.5 billion years, when the first stars and galaxies were formed out of the darkness of the early universe.

2. Webb will be able to see infrared light. This is light that is just outside the visible spectrum, and just outside of what we can see with our human eyes.

3. Webb’s unprecedented sensitivity to infrared light will help astronomers to compare the faintest, earliest galaxies to today’s grand spirals and ellipticals, helping us to understand how galaxies assemble over billions of years.

Hubble’s infrared look at the Horsehead Nebula. Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage Team
4. Webb will be able to see right through and into massive clouds of dust that are opaque to visible-light observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope. Inside those clouds are where stars and planetary systems are born.

5. In addition to seeing things inside our own solar system, Webb will tell us more about the atmospheres of planets orbiting other stars, and perhaps even find the building blocks of life elsewhere in the universe.

Credit: Northrop Grumman
6. Webb will orbit the Sun a million miles away from Earth, at the place called the second Lagrange point. (L2 is four times further away than the moon!)

7. To preserve Webb’s heat sensitive vision, it has a ‘sunshield’ that’s the size of a tennis court; it gives the telescope the equivalent of SPF protection of 1 million! The sunshield also reduces the temperature between the hot and cold side of the spacecraft by almost 600 degrees Fahrenheit.

8. Webb’s 18-segment primary mirror is over 6 times bigger in area than Hubble’s and will be ~100x more powerful. (How big is it? 6.5 meters in diameter.)

9. Webb’s 18 primary mirror segments can each be individually adjusted to work as one massive mirror. They’re covered with a golf ball’s worth of gold, which optimizes them for reflecting infrared light (the coating is so thin that a human hair is 1,000 times thicker!).

10. Webb is so sensitive, it could detect the heat signature of a bumblebee at the distance of the moon, and can see details the size of a US penny at the distance of about 40 km.

BONUS! Over 1,200 scientists, engineers and technicians from 14 countries (and more than 27 U.S. states) have taken part in designing and building Webb. The entire project is a joint mission between NASA and the European and Canadian Space Agencies. The telescope part of the observatory was assembled in the world’s largest cleanroom at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland.
Webb is currently being tested at our Johnson Space Flight Center in Houston, TX.

Afterwards, the telescope will travel to Northrop Grumman to be mated with the spacecraft and undergo final testing. Once complete, Webb will be packed up and be transported via boat to its launch site in French Guiana, where a European Space Agency Ariane 5 rocket will take it into space.

Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
CRISP(ie)R news than anything!

A powerful technique for editing genomes is now more precise. By tweaking an enzyme, researchers have reduced the error rate for the technique, known as CRISPR–Cas9 — in some cases to undetectable levels, they report on 6 January in Nature1.
Researchers use CRISPR–Cas9 to make precise changes to genomes that remove or edit a faulty gene. It has worked on nearly every creature on which they have tested it, including human embryos.
The technique relies on an enzyme called Cas9, that uses a ‘guide RNA’ molecule to home in on its target DNA. Cas9 cuts the DNA at that site, and the cell’s natural DNA repair machinery then takes over to mend the cut — deleting a short fragment of DNA or stitching in a new sequence in the process.
But the technology is not infallible: sometimes the Cas9 enzyme creates unwanted mutations. As CRISPR inches out of the laboratory and towards the clinic — with debates raging overwhether it should be deployed in embryos — researchers have pushed to reduce the error rate.
The latest study moves the field closer to that goal, says lead author Keith Joung, a pathologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “This is a significant move forward,” he says. “We can very much reduce the probability of off-targets.”
Continue Reading.


