
Blog dedicted to phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that are responsible for half of the photosynthesis that occurs on Earth. Oh, and they look like art... Follow to learn more about these amazing litter critters! Caution: Will share other ocean science posts!Run by an oceanographer and phytoplankton expert. Currently a postdoctoral researcher.Profile image: False Colored SEM image of Emiliania huxleyi, a coccolithophore, and the subject of my doctoral work. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/ Science Photo Library/ Getty ImagesHeader image: Satellite image of a phytoplankton bloom off the Alaskan Coast, in the Chukchi SeaCredit: NASA image by Norman Kuring/NASA's Ocean Color Web https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/92412/churning-in-the-chukchi-sea
158 posts
Latest Posts by simplyphytoplankton - Page 3


Migaloo is an albino humpback whale, usually sighted along the Australian coast, and occasionally in New Zealand waters. Migaloo was named by the Hervey Bay local aboriginal collective, and it means “white fella”. While several Humpback Whales have been spotted with almost 90% white pigment coverage, Migaloo is the only documented albino.
(source)
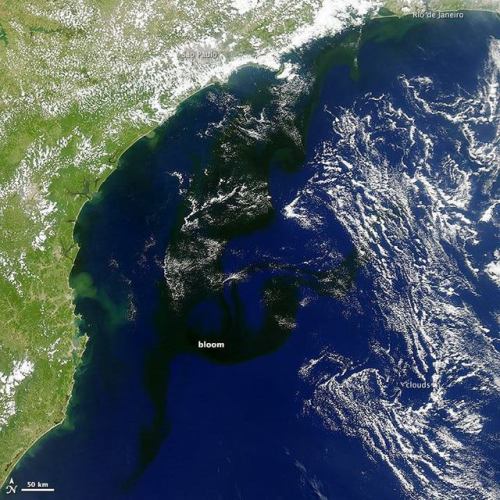

Covering the oceans in darkness….
Phytoplankton blooms produce some fascinating textures in Earth’s oceans, and consequently we’ve shared images of them taken from orbit many times (http://tinyurl.com/qhzwbr9, http://tinyurl.com/pwasxol). This bloom, however is a bit different from the others – in this photo from NASA’s Aqua satellite, it looks, well, black.
Keep reading

THE PARADOX OF THE PLANKTON EXPLAINED BY COMPUTER SIMULATION
The paradox of the plankton results from the clash between the observed diversity of plankton and the competitive exclusion principle, which states that, when two species compete for the same resource, ultimately only one will persist and the other will be driven to extinction. With phytoplankton this is different, despite the limited range of resources, as is light, nitrate, phosphate, silicic acid, iron, a large number of species coexist, all competing for the same sorts of resources.
Now, a new math model explains such biodiversity. To understand this paradox researchers created a conceptual model for a theoretical community. Where each member of that community consumes one type of resource, and consuming it causes the production of exactly two new resources. Also, any new member could only survive if there is an open niche, or if it was better to exploit a resource than a current member. But with this computer simulation, researchers discovered that its simple rules led to a virtual community that, like the bacterial or phytoplankton communities, this hypotethical community was diverse and stable, and in fact became increasingly stable to as organisms diversified.
Resource competition and metabolic commensalism -where one organism benefits from the other without affecting it- drive a healty and diverse ecosystem. Researchers demonstrate that even when supplied with just one resource, ecosystems can exhibit high diversity and increasing stability. Despite early stages where massive die-offs scenes occured, as time passed and community grew more stable, these became less common. Affortunately to phytoplancton species, two communities under ideal conditions can develop so differently from one another, without producing extintions.
Photo: Gordon T. Taylor.
Reference: Goyal and Maslov, 2018. Diversity, Stability, and Reproducibility in Stochastically Assembled Microbial Ecosystems, Physical Review Letters

What a Nut!— Invasive Species Week
This ctenophore (a stingless jellyfish-like animal) called a sea walnut is native to the east coast of North and South America. In 1982, it was discovered in the Black Sea, where it was transported by ballast water. It subsequently spread to the Caspian Sea. In both places, it multiplied and formed immense populations. The sea walnuts contributed to the collapse of local fisheries because they feed on zooplankton that the commercial fish also consume. Mnemiopsis leidy has also been discovered in the Mediterranean, Baltic, and North Seas.
Photo Credit: Marco Faasse, World Register of Marine Species
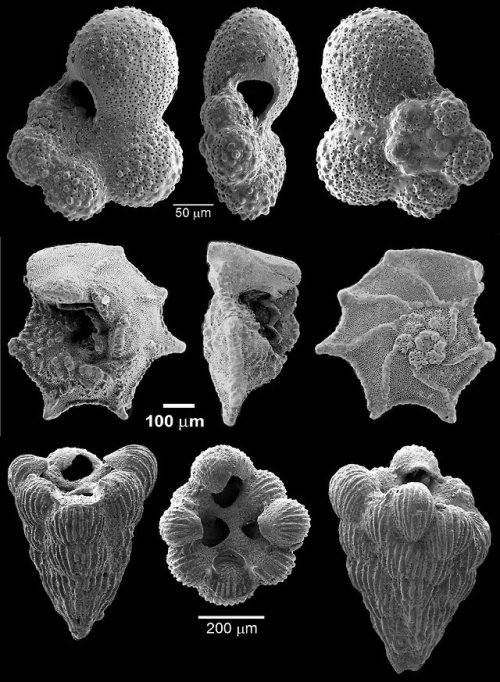

These microscopic beauties are foraminifera—single-celled organisms that live in the ocean. Since they make their shell using oxygen from the water, as ocean temperatures fluctuate through time and change the type of oxygen in the water the shells’ structure also changes. Paleontologists like the Smithsonian’s very own Brian Huber can use fossil foraminifera to track changes in Earth’s climate from over 540 million years ago.

The Great Escape!
One of the biggest threats to sea turtles, such as the loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) pictured here, is being accidentally caught and killed in fishing nets. Trapped in a net, the turtles are dragged through the water with no access to the surface to breathe, causing them to drown.
To address this problem, NOAA Fisheries worked with the shrimp trawling industry to install escape hatches into their nets called Turtle Excluder Devices, or TEDs. A crosshatch of bars in the middle of the net create a grid large enough for small shrimp to pass through, but not turtles and other large animals. When they hit the grid, they can then swim out through a hole in the net and escape.
Before TEDs were installed, an estimated 70 to 80 percent of turtle strandings on beaches were caused by shrimp nets. But since they were installed by U.S. shrimpers in the Gulf of Mexico in the late 1980s, strandings caused by shrimp nets are estimated to be down by at least 44 percent.
Photo: NOAA
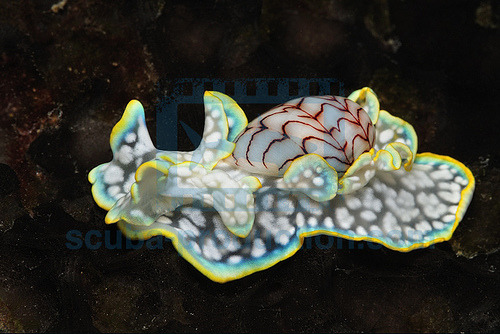
To post about the miniature melo (Micromelo undatus) may seem a bit odd, as it is not a nudibranch but a closely-related sea snail! Its thinly-calcified shell is easily seen covering half of its back and is patterned with dazzling brown-red lines, a stark contrast to the blue, white-spotted body below. It lives in many tropic waters, whether that be Japan or Florida, and reaches about 3cm in length. It eats polychaete worms, and uses their toxins as its own.

This impending issue has been known for some time. I believe it has a role in the resurgence of nationalism, immigration debates, and isolationism in certain countries - a bit of preemptive door slamming…
143 Million People May Soon Become Climate Migrants, World Bank Warns
Climate change will transform more than 143 million people into “climate migrants” escaping crop failure, water scarcity, and sea-level rise, a new World Bank report concludes.
Most of this population shift will take place in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Latin America—three “hot spots” that represent 55 percent of the developing world’s populations.
This worst-case scenario is part of a ground-breaking study focused on the impacts of slow-onset climate, as opposed to more visibly dramatic events such as extreme storms and flooding. The report, Groundswell—Preparing for Internal Climate Migration, also shifts the focus from cross-border migration, which has drawn global attention as refugees and migrants flee war, poverty and oppression, to in-country migration, which involves many more millions of people on the move in search of viable places to live. The 143 million represent 2.8 percent of the three regions’ population.




IMG_2667 by scott1e2310 on Flickr.






Underwater creatures: Photographer Marty Snyderman captures unique behaviors
Underwater photographer Marty Snyderman’s fascinating body of work brings to life some of the more unique behaviors of the animals of the deep. Snyderman has dedicated his professional life to documenting these creatures — including those that clean other fish, guard fertilized eggs in their mouths, and “fish” for their dinner using a natural worm or fishlike lure incorporating their own body as a fishing rod. In order to find such intriguing creatures, Snyderman, 67, said a lot of discussion must first take place between himself and fishermen, scientists, photographers or even local diving instructors. When photographing his subjects, he tries to stay within one or two feet of them whenever possible, something he admits can be tricky, given the sensitivity of the fish, whales, manta rays and other subjects. (Caters News)
Photography by Marty Snyderman
See more photos of underwater creatures and our other slideshows on Yahoo News.


(source)




Lakes and rivers of Antarctica


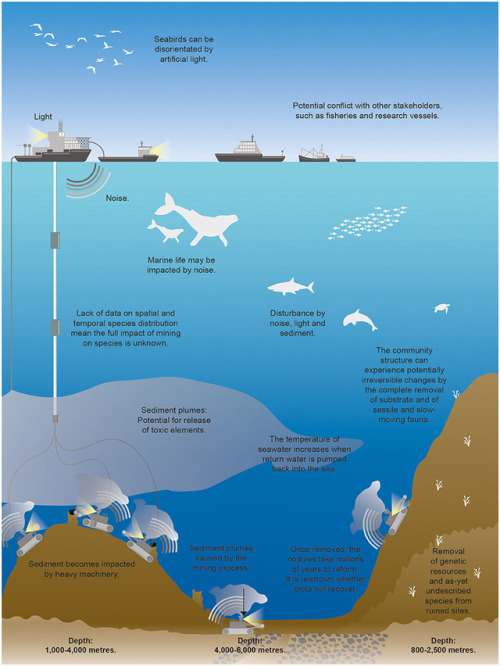
DEEP-SEA MINING COULD DESTROY MARINE ECOSYSTEMS
Despite deep-sea environments covers about half of the Earth’s surface and is home to a vast range of species, little is known about these environments, and mining could have long-lasting and unforeseen consequences, not just at mining sites but also across much larger areas.
According to a study published in scientific journal Frontiers in Marine Science, which is the first to give a global overview of all current plans to mine the seabed, in both national and international waters, and looks at the potential impacts including physical destruction of seabed habitats, creation of large underwater plumes of sediment and the effects of chemical, noise and light pollution arising from mining operations.
Rising demand for minerals and metals, including for use in the technology sector, has led to a resurgence of interest in exploration of mineral resources located on the seabed. Such resources, whether seafloor massive sulfides around hydrothermal vents, cobalt-rich crusts on the flanks of seamounts or fields of manganese nodules on the abyssal plains, cannot be considered in isolation of the distinctive, in some cases unique, assemblages of marine species associated with the same habitats and structures.
Some operations are already taking place, generally at relatively shallow depths near national coastlines. The first commercial enterprise, expected to target mineral-rich sulfides in deeper waters, at depths between 1,500 and 2,000 m on the continental shelf of Papua New Guinea, is scheduled to begin early in 2019.
Illustration: A schematic showing the potential impacts of deep-sea mining on marine ecosystems. Schematic not to scale.
Reference: Miller et al., 2018. An Overview of Seabed Mining Including the Current State of Development, Environmental Impacts, and Knowledge Gaps. Frontiers in Marine Science.
With Stephen Hawking’s passing, today is a sad day for science. But amongst all his praise and achievements in the fields of physics, for me personally his biggest achievement was making a grand, full life despite the terrible misfortune of being diagnosed with ALS. It would have been easy to become a recluse, embittered with the hand he’d been dealt, a brilliant misanthrope. But this was a man who maintained his sense of humor and refused to be mentally beaten. Three years ago, he told One Direction fans that the theory of alternate universes could provide a reality where Zayn Malik was still in the band. He conducted an interview with John Oliver where his factual, deadpan delivery was funnier than his interviewer, managing the cheekiest grins as he did so. And let us not forget that Stephen Hawking is the only person to have ever portrayed themselves in a Star Trek episode (Next Generation, “Descent, Part 1″), where he appeared alongside actors portraying Einstein and Sir Isaac Newton, whom he proceeded to defeat in poker.

Hawking’s observations on black hole radiation, string theory, alternate universes and artificial intelligence are things that will probably forever remain beyond most of us. But we could all learn a thing or two from his humanity.
Why Octopuses Could Never Disappoint
These cephalopods, who telegraph their moods by color changes and solve problems by using tools, have surprised me again and again.
And now it’s happened again. An octopus has astonished me.
This time, it’s a common octopus caught on camera in South African waters by a dive team for the documentary Blue Planet II, currently airing on BBC America in the United States.
The action is dramatic. A pyjama shark seizes the octopus. Just as the situation begins to look dire, the octopus stuffs the shark’s gills shut using its sinuous arms, making it impossible for the shark to breathe — until the shark releases it.
But without primary producers (phytoplankton) there would be no krill

They’re krilly small and unassuming, but krill form the backbone of many ocean ecosystems!
These tiny crustaceans consume phytoplankton, and in turn are food for whales, fish, and other marine animals. During their peak feeding times, blue whales can eat up to 8,000 pounds of krill each day!
(Photo: Maps For Good, taken in Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary)
Every once in a while, sanctuary researchers get a treat – like getting to see this tiny baby octopus! 🐙 .
Each summer, researchers conduct expeditions in our West Coast sanctuaries as part of the ACCESS conservation partnership. Researchers get to see creatures big and small when conducting surveys in places like Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary!

“I make sure that when I am boating that nothing goes into the water, I try to recycle everything I can, and I don’t eat seafood unless it is invasive lionfish. I also participate in as many coastal cleanups to help to remove all of the garbage along our shorelines and I try to encourage others to do the same. We have a long ways to go in ocean conservation, but national marine sanctuaries, along with national parks, monuments, and wildlife refuges, afford us the best opportunity to help leverage limited resources to address coastal and marine conservation."
– Mark Chiappone, research associate at Nova Southeastern University and assistant professor at Miami Dade College
What inspires you about the ocean?
(Photo: Scrawled filefish in Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Credit: Daryl Duda)

natgeo Photograph by @thomaspeschak This is a marine iguana, but I think they should be called ‘Ocean Godzilla’ instead. These are our planet’s only lizards that feed in the ocean and despite their fierce, dragon like appearance they are very sensitive to climate change. They rely exclusively on cold water seaweeds for nourishment which die off quickly as the water becomes too warm. For more “Ocean Godzilla” pics follow @thomaspeschak





First images of creatures from Antarctic depths revealed
Photos by Christian Åslund / Greenpeace
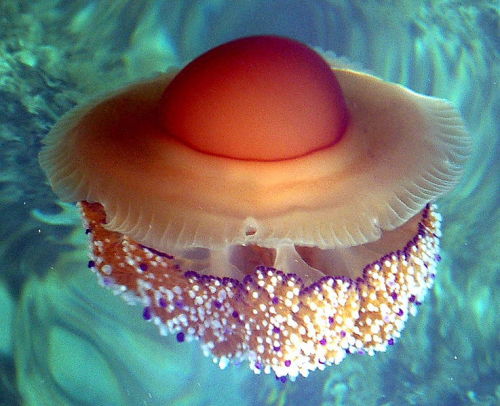







Fried Egg Jellyfish Are Kind of Adorable – & That’s No Yolk.
There are two species that hold the whimsical title of “Fried Egg Jellyfish”: Phacellophora camtschatica and Cotylorhiza tuberculata though the two are quite different from each other in all aspects beside appearance.
Phacellophora camtschatica is a huge jelly that prefers colder waters. It’s bell can reach up to 2 ft across and its dozens of tentacles reach over 20 ft long! If you don’t think this floating egg creature looks very menacing, you’d be right. It has a very weak sting and many small crustaceans take advantage of the jelly by riding on its bell (breakfast to go…?) while snatching up extra food.
Cotylorhiza tuberculata is a much smaller jellyfish that hangs out in warmer waters. It only reaches about 35 cm in diameter, so don’t go for this Fried Egg Jelly if you want a big breakfast. Unlike most jellyfish, C. tuberculata can swim on its own, without relying on the currents for movement. It’s sting (if you can even call it that) is so feeble that it has very little to no effect on humans at all. I mean, it does look like a breakfast food, after all… how powerful could it be?

Waves Crashing Sunset By Scraft | More

Höfn

Phot by Jero Prieto

