Your gateway to endless inspiration
Planets - Blog Posts
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Jupiter, we've got quite the photoshoot planned for you. Today, our Juno spacecraft is flying directly over the Great Red Spot, kicking off the first-ever close-up study of this iconic storm and passing by at an altitude of only 5,600 miles (9,000 kilometers). In honor of this historic event, below are 10 things to know about the planet's most famous feature.

1. A Storm That Puts Others to Shame
The Great Red Spot is a gigantic, high-pressure, ancient storm at Jupiter's southern hemisphere that's one of the longest lasting in the solar system. It's so large, about 1.3 Earths could fit inside of it. And you can bet you'll get swept away—the storm's tumultuous winds peak at about 400 mph.
2. How Old Is It?
The Great Red Spot has been swirling wildly over Jupiter's skies for the past 150 years—maybe even much longer. While people saw a big spot on Jupiter when they started stargazing through telescopes in the 1600s, it's still unclear whether they were looking at a different storm. Today, scientists know the Great Red Spot has been there for a while, but they still struggle to learn what causes its swirl of reddish hues.

3. Time for That Close-Up
Juno will fly over the Great Red Spot about 12 minutes after the spacecraft makes the closest approach to Jupiter of its current orbit at 6:55 p.m. on July 10, PDT (9:55 p.m. on July 10, EDT; 1:55 a.m. on July 11, Universal Time). Juno entered orbit around Jupiter on July 4, 2016.
4. Oh, So Mysterious
Understanding the Great Red Spot is not easy, and it's mostly Jupiter's fault. The planet a thousand times as big as Earth and consists mostly of gas. A liquid ocean of hydrogen surrounds its core, and the atmosphere consists mostly of hydrogen and helium. That translates into no solid ground (like we have on Earth) to weaken storms. Also, Jupiter's clouds make it hard to gather clear observations of its lower atmosphere.

This false-color image of Jupiter was taken on May 18, 2017, with a mid-infrared filter centered at a wavelength of 8.8 microns, at the Subaru Telescope in Hawaii, in collaboration with observations of Jupiter by NASA's Juno mission. Credit: NAOJ/NASA/JPL-Caltech
5. Help From Hawaii
To assist Juno's investigation of the giant planet's atmosphere, Earth-based telescopes lent their helpful eyes. On May 18, 2017, the Gemini North telescope and the Subaru Telescope—both located on Hawaii's Mauna Kea peak—simultaneously examined Jupiter in very high resolutions at different wavelengths. These latest observations helped provide information about the Great Red Spot's atmospheric dynamics at different depths and at other regions of Jupiter.
6. Curious Observations
Observations from Subaru showed the Great Red Spot "had a cold and cloudy interior increasing toward its center, with a periphery that was warmer and clearer," said Juno science team member Glenn Orton of our Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. "A region to its northwest was unusually turbulent and chaotic, with bands that were cold and cloudy, alternating with bands that were warm and clear."

This composite, false-color infrared image of Jupiter reveals haze particles over a range of altitudes, as seen in reflected sunlight. It was taken using the Gemini North telescope in Hawaii on May 18, 2017, in collaboration with observations of Jupiter by our Juno mission. Credits: Gemini Observatory/AURA/NSF/NASA/JPL-Caltech
7. Hot in Here
Scientists were stumped by a particular question: Why were the temperatures in Jupiter's upper atmosphere comparable to those found at Earth, even though Jupiter is more than five times the distance from the sun? If the sun isn't the heat source, then what is? Turns out, the storm in the Great Red Spot produces two kinds of turbulent energy waves that collide and heat the upper atmosphere. Gravity waves are much like how a guitar string moves when plucked, while acoustic waves are compressions of the air (sound waves). Heating in the upper atmosphere 500 miles (800 kilometers) above the Great Red Spot is thought to be caused by a combination of these two wave types "crashing," like ocean waves on a beach.

8. Color Theory
Scientists don't know exactly how the Great Red Spot's rich colors formed. Studies predict Jupiter's upper atmosphere has clouds consisting of ammonia, ammonium hydrosulfide, and water, but it's still unclear how or even whether these chemicals react. "We're talking about something that only makes up a really tiny portion of the atmosphere," said Amy Simon, an expert in planetary atmospheres at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "That's what makes it so hard to figure out exactly what makes the colors that we see." Over at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, researchers concluded that the ruddy color is likely a product of simple chemicals being broken apart by sunlight in the planet's upper atmosphere. "Our models suggest most of the Great Red Spot is actually pretty bland in color, beneath the upper cloud layer of reddish material," said Kevin Baines, a Cassini scientist at JPL.
9. Been There, Haven't Seen That
In January and February 1979, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft zoomed toward Jupiter, capturing images of the Great Red Spot during its approach. Still, we've never been as close as we're about to get during Juno's flyover on July 10.

10. Simply Beautiful
This image of a crescent Jupiter and the iconic Great Red Spot was created by a citizen scientist, Roman Tkachenko, using data from Juno's JunoCam instrument. JunoCam's raw images are available here for the public to peruse and enhance.Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
We've been up close and personal with Saturn for 13 years now, thanks to the Cassini mission.
From a tour of Saturn's many enthralling moons to an incredible view of Earth through its rings, the planet continues to captivate the imagination. This week, here are 10 things you need to know about our fascinating ringed neighbor.

1. Strange Sighting
When Galileo Galilei was observing Saturn in the 1600s, he noticed strange objects on each side of the planet. He drew in his notes a triple-bodied planet system with ears. These "ears" were later discovered to be the rings of Saturn.

2. Solar System Status
Saturn orbits our sun and is the sixth planet from the sun at an average distance of about 886 million miles or 9.5 AU.
3. Short Days
Time flies when you're on Saturn. One day on Saturn takes just 10.7 hours (the time it takes for Saturn to rotate or spin once). The planet makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Saturnian time) in 29 Earth years, or 10,756 Earth days. saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/news/2955/measuring-a-day

4. No Shoes Necessary
That's because you can't stand on Saturn—it's a gas-giant planet and doesn't have a solid surface. But you might want a jacket. The planet's temperatures can dip to -220 degrees F.
5. Few visitors
Only a handful of missions have made their way to Saturn: Pioneer 11, Voyager 1 and 2, and Cassini-Huygens, which is there now. Since 2004, Cassini has been exploring Saturn and its moons and rings—but will complete its journey on Sept. 15, 2017.

6. Saturn's Close-Up
This month is a great time to observe Saturn from Earth. Check out June's "What's Up?" video for a how-to guide.

7. Daring Dives
Saturn's spectacular ring system is made up of seven rings with several gaps and divisions between them. From now until September, the Cassini spacecraft is performing a set of daring dives every week between the planet and the rings. No other mission has ever explored this unique region before, and what we learn from these final orbits will help us understand of how giant planets—and planetary systems everywhere—form and evolve.

8. Many, Many Moons
Saturn has a total of 62 moons: 53 known moons, with an additional nine moons awaiting confirmation.

9. Curious Shapes
Saturn's moon Atlas looks like a flying saucer. See for yourself.

10. Would You Live on a Moon?
Saturn can't support life as we know it, but some of its moons have conditions that might support life. Ocean worlds could be the answer to life in space and two of Saturn's moons—Titan and Enceladus—are on that list.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Our Kepler Space Telescope team has identified 219 new planet candidates, 10 of which are near-Earth size and in the habitable zone of their respective stars. The habitable zone is the range of distance from a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of a rocky planet to possibly sustain life. This artist rendering is of one of the thousands of planets detected by Kepler beyond our solar system. These exoplanets, as they’re called, vary widely in size and orbital distances, showing us that most stars are home to at least one planet. Learn more.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What’s Up for March 2017?
What’s Up for March? The moon hides red star Aldebaran and crescents dazzle after dusk.

On March 4 the first quarter moon passes between Earth and the star Aldebaran, temporarily blocking our view of the star. This is called an occultation.

The occultation begins and concludes at different times, depending on where you are when you view it.

The event should be easy to see from most of the U.S., Mexico, most of Central America, the Western Caribbean and Bermuda.

Observers along a narrow path from Vancouver, British Columbia, to Hartford, Connecticut, will see the moon “graze” the star. The star will disappear and reappear repeatedly as hills and valleys on the moon alternately obscure and reveal it.

As seen from Earth, both Mercury and Venus have phases like our moon. That’s because they circle the sun inside Earth’s orbit.

Planets that orbit between Earth and the sun are known as inner or inferior planets.

Inferior planets can never be at “opposition,” which is when the planet and the sun are on opposite sides of Earth.

But inferior planets can be at “conjunction,” which is when a planet, the sun and Earth are all in a straight line.

Conjunction can happen once when the planet is on the opposite side of the sun from Earth and again when it’s on the same side of the sun as Earth.

When a planet is on the opposite side of the sun from Earth, we say it is at “superior conjunction.” As the planet moves out from behind the sun and gets closer to Earth, we see less and less of the lit side. We see phases, similar to our moon’s phases.

Mercury is at superior conjunction on March 6.

A few weeks later, the planet emerges from behind the sun and we can once again observe it. By the end of March we’ll see a last-quarter Mercury.

On April 20 Mercury reaches “inferior conjunction.”

Brilliant Venus is also racing toward its own inferior conjunction on March 25. Watch its crescent get thinner and thinner as the planet’s size appears larger and larger, because it is getting closer to Earth.

Finally, look for Jupiter to rise in the East. It will be visible all month long from late evening until dawn.

You can catch up on solar system missions and all of our missions at www.nasa.gov
Watch the full “What’s Up for March 2017″ video here:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Celestial Valentine’s Day Cards
Looking for a last minute Valentine’s Day card? Here are some out-of-this-world options for you:
From our solar system…





To distant galaxies…


And worlds far, far away…


Share your Valentine’s Day love with these celestial cards.
To find even more options, visit:
XO Travel Bureau: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/galleries/exoplanet-travel-bureau/ Mars Valentine’s: http://mars.nasa.gov/free-holiday-ecard/love-valentine/ Space Place Valentine’s: http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/valentines/en/ OSIRIS-REx Valentine’s: http://www.asteroidmission.org/galleries/#collectables
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
13 Reasons to Have an Out of This World Friday (the 13th)
1. Know that not all of humanity is bound to the ground

Since 2000, the International Space Station has been continuously occupied by humans. There, crew members live and work while conducting important research that benefits life on Earth and will even help us eventually travel to deep space destinations, like Mars.
2. Smart people are up all night working in control rooms all over NASA to ensure that data keeps flowing from our satellites and spacecraft

Our satellites and spacecraft help scientists study Earth and space. Missions looking toward Earth provide information about clouds, oceans, land and ice. They also measure gases in the atmosphere, such as ozone and carbon dioxide, and the amount of energy that Earth absorbs and emits. And satellites monitor wildfires, volcanoes and their smoke.

Satellites and spacecraft that face toward space have a variety of jobs. Some watch for dangerous rays coming from the sun. Others explore asteroids and comets, the history of stars, and the origin of planets. Some fly near or orbit other planets. These spacecraft may look for evidence of water on Mars or capture close-up pictures of Saturn’s rings.
3. The spacecraft, rockets and systems developed to send astronauts to low-Earth orbit as part of our Commercial Crew Program is also helping us get to Mars
Changes to the human body during long-duration spaceflight are significant challenges to solve ahead of a mission to Mars and back. The space station allows us to perform long duration missions without leaving Earth’s orbit.

Although they are orbiting Earth, space station astronauts spend months at a time in near-zero gravity, which allows scientists to study several physiological changes and test potential solutions. The more time they spend in space, the more helpful the station crew members can be to those on Earth assembling the plans to go to Mars.
4. Two new science missions will travel where no spacecraft has gone before…a Jupiter Trojan asteroid and a giant metal asteroid!

We’ve selected two missions that have the potential to open new windows on one of the earliest eras in the history of our solar system – a time less than 10 million years after the birth of our sun!

The first mission, Lucy, will visit six of Jupiter’s mysterious Trojan asteroids. The Trojans are thought to be relics of a much earlier era in the history of the solar system, and may have formed far beyond Jupiter’s current orbit.

The second mission, Psyche, will study a unique metal asteroid that’s never been visited before. This giant metal asteroid, known as 16 Psyche, is about three times farther away from the sun than is the Earth. Scientists wonder whether Psyche could be an exposed core of an early planet that could have been as large as Mars, but which lost its rocky outer layers due to a number of violent collisions billions of years ago.
5. Even astronauts eat their VEGGIES’s
NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough collected the third and final harvest of the latest round of the Veggie investigation, testing the capability to grow fresh vegetables on the International Space Station.

Understanding how plants respond to microgravity is an important step for future long-duration space missions, which will require crew members to grow their own food. Crew members have previously grown lettuce and flowers in the Veggie facility. This new series of the study expands on previous validation tests.
6. When you feel far away from home, you can think of the New Horizons spacecraft as it heads toward the Kuiper Belt, and the twin Voyager spacecraft are beyond the influence of our sun…billions of miles away

Our New Horizons spacecraft completed its Pluto flyby in July 2015 and has continued on its way toward the Kuiper Belt. The spacecraft continues to send back important data as it travels toward deeper space at more than 32,000 miles per hour, and is nearly 3.2 billion miles from Earth.

In addition to New Horizons, our twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-37-year journey since their 1977 launches, they are each much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between the stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago.
7. Earth has a magnetic field that largely protects it from the solar wind stripping away out atmosphere…unlike Mars

Findings from our MAVEN mission have identified the process that appears to have played a key role in the transition of the Martian climate from an early, warm and wet environment to the cold, arid planet Mars is today. MAVEN data have enabled researchers to determine the rate at which the Martian atmosphere currently is losing gas to space via stripping by the solar wind. Luckily, Earth has a magnetic field that largely protects it from this process.
8. There are humans brave enough to not only travel in space, but venture outside the space station to perform important repairs and updates during spacewalks

Spacewalks are important events where crew members repair, maintain and upgrade parts of the International Space Station. These activities can also be referred to as EVAs – Extravehicular Activities. Not only do spacewalks require an enormous amount of work to prepare for, but they are physically demanding on the astronauts. They are working in the vacuum of space in only their spacewalking suit.

When on a spacewalk, astronauts use safety tethers to stay close to their spacecraft. One end of the tether is hooked to the spacewalker, while the other end is connected to the vehicle. Spacewalks typically last around 6.5 hours, but can be extended to 7 or 8 hours, if necessary.
9. We’re working to create new aircraft that will dramatically reduce fuel use, emissions and noise…meaning we could change the way you fly!

The nation’s airlines could realize more than $250 billion dollars in savings in the near future thanks to green-related technologies that we are developing and refining. These new technologies could cut airline fuel use in half, pollution by 75% and noise to nearly one-eighth of today’s levels!
10. You can see a global image of your home planet…EVERY DAY

Once a day, we will post at least a dozen new color images of Earth acquired from 12 to 36 hours earlier. These images are taken by our EPIC camera from one million miles away on the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR). Take a look HERE.
11. Employees of NASA have always been a mission driven bunch, who try to find answers that were previously unknown
The film “Hidden Figures,” focuses on the stories of Katherine Johnson, Mary Jackson and Dorothy Vaughan, African-American women who were essential to the success of early spaceflight.
Today, we embrace their legacy and strive to include everyone who wants to participate in our ongoing exploration. In the 1960’s, we were on an ambitious journey to the moon, and the human computers portrayed in Hidden Figures helped get us there. Today, we are on an even more ambitious journey to Mars. We are building a vibrant, innovative workforce that reflects a vast diversity of discipline and thought, embracing and nurturing all the talent we have available, regardless of gender, race or other protected status. Take a look at our Modern Figures HERE.
12. A lot of NASA-developed tech has been transferred for use to the public
Our Technology Transfer Program highlights technologies that were originally designed for our mission needs, but have since been introduced to the public market. HERE are a few spinoff technologies that you might not know about.
13. If all else fails, here’s an image of what we (Earth) and the moon look like from Mars

From the most powerful telescope orbiting Mars comes a new view of Earth and its moon, showing continent-size detail on the planet and the relative size of the moon. The image combines two separate exposures taken on Nov. 20 by our High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
In the image, the reddish feature near the middle of the face of Earth is Australia.
What’s Up for December 2016?
What’s Up for December? Mars and Neptune above the crescent moon and a New Year’s Eve comet!

2016 ends with fireworks as three planets line up as if ejected from a Roman candle. Mercury, Venus and Mars are visible above the sunset horizon all month long.

As Venus climbs higher in the sky, it looks brighter and larger than it appeared last month.

On New Year’s Eve, Mars and Neptune appear very close to each other. Through telescopes, rusty red Mars and blue-green Neptune‘s colors contrast beautifully.

There are two meteor showers this month – the Geminds and the Ursids. The best time to see the reliable Geminids will be next year, when the full moon won’t be so bright and interfering. This year, however, we may luck out and see some of the brighter meteors on the evening of the 13th and the morning of the 14th.

The best time to view the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, or the little Dipper, will be from midnight on the 21st until about 1 a.m. on the 22nd, before the moon rises. They may be active on the 23rd and 24th, too.

We haven’t had a good easy-to-see comet in quite a while, but beginning in December and through most of 2017 we will have several binocular and telescopic comets to view.

The first we’ll be able to see is Comet 45P/Honda-Mrkos-Pajdušáková, which will appear low on the western horizon on December 15th. On that date, the comet will pass the pretty globular cluster M75.

By the 21st, it will appear edge-on, sporting a bluish-green head and a thin, sharp view of the fan-shaped tail.

On New Years Eve, the comet and the crescent moon will rendezvous to say farewell to 2016. A “periodic” comet is a previously-identified comet that’s on a return visit. Periodic comet 45P returns to the inner solar system every 5.25 years, and that’s the one that will help us ring in the new year.

Watch the full What’s Up for December video:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Questions for Our New Head of Science
Guess what?! We have a new lead for our science missions, and we’re excited to introduce him to you. Recently, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden has named Thomas Zurbuchen as the new head of our organization for science missions. Let’s get to know him...
Zurbuchen was most recently a professor of space science and aerospace engineering at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. He was also the university’s founding director of the Center for Entrepreneurship in the College of Engineering.

Zurbuchen’s experience includes research in solar and heliospheric physics, experimental space research, space systems and innovation and entrepreneurship.
We asked him a few questions to see what he has in store for science at NASA…let’s take a look:
1. What is your vision for science at NASA?
Right now, I am focusing on my team and I am learning how I can help them achieve the goals we have; to design and build the missions we are currently working on. Once the presidential transition is complete, we will engage in strategic activity with that team. It has been my experience that the best ideas always come from great and diverse teams working together. I intend to do that here as well.
2. What solar system destination are you most eager for NASA to explore?
Tough question to answer. Basically, I want to go where there are answers to the most important questions. One question on my mind is the origin of extraterrestrial life. Some parts of the answer to this question can be answered at Mars, some at Europa or other moons in the outer solar system like Enceladus. Other parts of the answer is around other stars, where we have found thousands of planets…some of which are amazingly similar to Earth!

3. With raw images posted to several websites from our missions, what’s one thing you hope members of the public can help NASA do with that powerful data?
I hope that people all over the world play with the data and find new ways to explore. It’s almost like hanging out in the most amazing libraries talking about nature. Many of the books in this library have never been opened and curious minds can find true treasures in there. I know that there are over a billion data-products NASA is making available about the Earth – it’s a treasure chest!
4. In your opinion, what big science breakthrough from the past informs missions of today?
In science, everything we do builds on successes and also failures of the past. Sometimes we forget our failures or near-failures, which tend to teach us a lot about what to do and what not to do. One of my favorite stories is about the Explorer 1 mission: first they observed almost nothing, until they realized that there was so much radiation that the detectors were chocking. The Van Allen Probes is a mission that are conducting the best exploration today of these radiation belts, discovered by Explorer 1. Our exploration history is full of stories like that.

5. Behind every pretty space image is a team of scientists who analyze all the data to make the discovery happen. What do you wish the public knew about the people and work that goes into each of those pretty pictures?
I wish people knew that every picture they see, every data-set they use, is a product of a team. One of the most exhilarating facts of working in space is to be able to work in teams composed of some of the nicest and most interesting people I have ever met. There are some super-famous people I run with every time we are in the same town, others who like to play music and listen to it, and some who have been in space or climbed mountains.
6. If you were a member of the public, what mission events in the next year would you be most excited about?
The public’s lives will be directly affected by our missions in our Earth Science portfolio. Some of them are done together with NOAA, our sister agency responsible for forecasts. For example, GOES will feature a lightning detector that will enable better predictions of storms. We are also launching CYGNSS in December. This NASA mission, composed of 8 spacecraft will provide unique and high-resolution data designed to provide a deeper understanding and better prediction for hurricanes globally.

7. NASA science rewrites textbooks all the time. What do you hope the kids of tomorrow will know as facts that are merely hypothesis today?
I hope they will know about life elsewhere. They will learn how life evolves, and where there is life today.
8. NASA has explored planets within our solar system. With the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope in 2020, what do you hope we learn about distant worlds?
James Webb is going to allow us to go back in time and look at the first stars and first galaxies. This is something we have never seen – we can only guess what will happen. James Webb is going to allow us to look at many, many more planets around other stars and will allow us to start doing the kind of research that links to the question about how habitable life is there.

9. What sort of elements make for an exciting new science discovery? What do you hope is the next big discovery?
Almost always, an exciting discovery is a surprise. Sometimes, discoveries happen because we are looking for something totally different. The biggest discoveries are the ones that change everything we thought before. All of a sudden, nature wags the finger at us and says “you are wrong!” That is how you know you are up to something new.
I hope the next big discovery tells us about the origin of the 95% of the universe we don’t know enough about. We call these 95% “Dark Energy” and “Dark Matter”, but – to be honest – we really don’t know. So, we are today living in a time where we know with 100% certainty that we don’t know what makes up 95% of our universe.
10. In your opinion, why should people care about the science at NASA?
They should care because we improve and protect lives on Earth. They should also care because we make the world we live in bigger. This is because we find things out we never knew, which creates new opportunities for humankind. Some of these opportunities are near-term – they are patents, innovations, companies or great educations. But, some of them are long-term – they change how we think about life itself.
Stay updated on science at NASA and Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen by following him on Twitter: @Dr_ThomasZ
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 “Out of This World" Facts About the James Webb Space Telescope
Wouldn’t it be neat to see a period of the universe’s history that we’ve never seen before? That’s exactly what the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will be able to do…plus more!

Specifically, Webb will see the first objects that formed as the universe cooled down after the Big Bang. We don’t know exactly when the universe made the first stars and galaxies – or how for that matter. That is what we are building Webb to help answer.
Here are 10 awesome facts about this next generation space telescope:
1. The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s largest and next premier space observatory. It will extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space telescope and observe the birthplaces of stars, galaxies, planets and life over billions of years.

2. It is named after James Webb, NASA’s second administrator and champion of our science.

3. At 3 stories high and the size of a tennis court, it will be 100 times more powerful than Hubble!

4. It is so big that it has to fold origami-style to fit in the rocket, which is only 5.4 meters wide...And then it will unfurl, segment by segment, once in space.

5. The telescope will observe infrared light with unprecedented sensitivity. It will see the first galaxies born after the Big Bang over 13.5 billion years ago.

6. Webb's infrared cameras are so sensitive they must be shielded from light from the sun, Earth, and moon. The 5-layer sunshield is like having sunblock of SPF 1 million.

7. Webb will orbit the sun 1 million miles from Earth, where the telescope will operate at temperatures below -390 F (-235 C).

8. Webb’s mirrors are coated with a super thin layer of gold only about 1000 atoms thick to optimize their reflectivity in the infrared.

9. Webb will launch from French Guiana in 2018. It is launched near the equator because the faster spin of Earth there gives the rocket an extra push.

10. Webb is an international mission, with contributions from the European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency. Once operational, scientists from all over the world will be able to use Webb to explore our solar system, planets outside our solar system, stars and galaxies.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
House of Horrors: Exoplanet Edition
Astronomers may be closer than ever to discovering a planet that’s habitable like our own, but along the way they’ve discovered some very scary exoplanets – places where conditions are far too harsh for life as we know it to exist.
Okay, but what IS an exoplanet???

We’ve rounded up some of the most frightening, deadly exoplanets, places that make even the scariest haunted house on Earth pale in comparison. Check them out...
Radiation Bath, Anyone?
The exoplanets PSR B1257+12 B, C & D were among the first discovered, and also happened to be three of the weirdest! The entire system is a graveyard, remnants of what used to be a normal, functional solar system before the star blew apart in a giant explosion known as a supernova.

The massive shockwave from the supernova stripped away any atmosphere or living creatures that might have once lived on these planets, leaving behind ghostly, rocky shells, dead planets orbiting the corpse of an extinct star.
Except that the system isn’t completely dead…the remaining core from the old star has become a zombie star called a pulsar. Literally spinning in its grave, it makes a full rotation every 6.22 milliseconds and emits an intense beam of radiation that can be detected from Earth. The star’s unfortunate planets are thus bathed in deadly radiation on a regular basis, making sure that this system remains a cosmic no-man’s land.
A Mighty Wind
The sound of howling wind is a must for any Earth-based haunted house, but weather conditions on HD 189733 b make it a very dangerous place to go trick-or-treating.
At first glance, this exoplanet looks like the typical “hot Jupiter” — a huge gas planet perched dangerously to a burning-hot star, with daytime temperatures around a balmy 1,770 degrees Fahrenheit. This exoplanet is also “tidally locked” in its orbit, which means that the same side of the planet always faces its star.

But when scientists measured the planet’s nighttime temperature, they were shocked to find that it was only 500 degrees cooler. How does the back side of the planet stay so warm?
The answer is wind! Insanely fast, dangerous wind that whisks heat from day-side to night-side at a speed of 4,500 mph, nearly six times the speed of sound! In fact, astronomers estimate that wind speeds might top out at 5,400 mph, conditions that make hurricanes on Earth look like a breezy day at the beach.
Newborn Exoplanet Around Scorching Star
This exoplanet, named K2-33b, is the youngest fully formed exoplanet ever detected. This planet is a bit larger than Neptune and whips tightly around its star every five days. Since this planet sits nearly 10 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our sun, it’s HOT!

No matter how cute you think infants are, this is one baby you’d want to stay away from.
Boil, Boil, Toil and Trouble
The planet HD 209458 b (aka. Osiris - the god of death) has a few things in common with Earth: water vapor, methane and carbon dioxide in its atmosphere, key ingredients for life on our planet. Don’t be fooled, though, because this planet is a rolling cauldron of almost unimaginable heat.

Even the hottest summer days on Earth don’t get as dangerous as the conditions here. A planet that orbits so close to its host star that its atmosphere is literally boiling off, ripped away from the planet as it whips around on its breakneck 3.5-day orbit.
All Alone and Very, Very Cold
While most of the exoplanets found so far are hellishly hot, OGLE-2005-BLG-390L b has the distinction of being extremely cold.
The planet takes about 10 Earth years to orbit its tiny dwarf star, and it’s a chilly trip; the average temperature on this exoplanet is 50 Kelvin, or minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit! A good costume for trick-or-treating on this frigid planet would be a toasty self-heating spacesuit, an oxygen supply, ice skates and plenty of hot cocoa.

Of course, don’t expect to find many houses with candy here, because despite the fact that it’s just a few times bigger than Earth, this exoplanet is an uninhabitable ice ball stuck in a perpetual winter freeze.
A Scorched World
Kepler-10b is a scorched world, orbiting at a distance that’s more than 20 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our own sun. The daytime temperatures are expected to be more than 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit, hotter than lava flows here on Earth.

Intense radiation from the star has kept the planet from holding onto an atmosphere, but flecks of silicates and iron that have boiled off a molten surface are swept away by the stellar radiation.
Learn more about worlds beyond our solar system at: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
A Space Odyssey: 21 Years of Searching for Another Earth
There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. We must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world. – Epicurus, c. 300 B.C.

Are we alone? Are there other planets like ours? Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
These are questions mankind has been asking for years—since the time of Greek philosophers. But for years, those answers have been elusive, if not impossible to find.
The month of October marks the 21st anniversary of the discovery of the first planet orbiting another sun-like star (aka. an exoplanet), 51 Pegasi b or “Dimidium.” Its existence proved that there were other planets in the galaxy outside our solar system.*

Even more exciting is the fact that astronomers are in hot pursuit of the first discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet orbiting a star other than the sun. The discovery of the so-called "blue dot" could redefine our understanding of the universe and our place in it, especially if astronomers can also find signs that life exists on that planet's surface.
Astronomy is entering a fascinating era where we're beginning to answer tantalizing questions that people have pondered for thousands of years.

Are we alone?
In 1584, when the Catholic monk Giordano Bruno asserted that there were "countless suns and countless earths all rotating around their suns," he was accused of heresy.

But even in Bruno's time, the idea of a plurality of worlds wasn't entirely new. As far back as ancient Greece, humankind has speculated that other solar systems might exist and that some would harbor other forms of life.
Still, centuries passed without convincing proof of planets around even the nearest stars.

Are there other planets like ours?
The first discovery of a planet orbiting a star similar to the sun came in 1995. The Swiss team of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of Geneva announced that they had found a rapidly orbiting gas world located blisteringly close to the star 51 Pegasi.

This announcement marked the beginning of a flood of discoveries. Exotic discoveries transformed science fiction into science fact:
a pink planet
worlds with two or even three suns
a gas giant as light as Styrofoam
a world in the shape of an egg
a lava planet

But what about another Earth?
Our first exoplanet mission**, Kepler, launched in 2009 and revolutionized how astronomers understand the universe and our place in it. Kepler was built to answer the question—how many habitable planets exist in our galaxy?

And it delivered: Thousands of planet discoveries poured in, providing statistical proof that one in five sun-like stars (yellow, main-sequence G type) harbor Earth-sized planets orbiting in their habitable zones– where it’s possible liquid water could exist on their surface.

Now, our other missions like the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes point at promising planetary systems (TRAPPIST-1) to figure out whether they are suitable for life as we know it.

Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
Now that exoplanet-hunting is a mainstream part of astronomy, the race is on to build instruments that can find more and more planets, especially worlds that could be like our own.

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), set for launch in 2017-2018, will look for super-Earth and Earth-sized planets around stars much closer to home. TESS will find new planets the same way Kepler does—via the transit method—but will cover 400 times the sky area.

The James Webb Space Telescope, to launch in 2018, wil be our most powerful space telescope to date. Webb will use its spectrograph to look at exoplanet atmospheres, searching for signs of life.

We still don’t know where or which planets are in the habitable zones of the nearest stars to Earth. Searching out our nearest potentially habitable neighbors will be the next chapter in this unfolding story.

*The first true discovery of extrasolar planets was actually a triplet of dead worlds orbiting the remains of an exploded star, called a pulsar star. Two of three were found by Dr. Alexander Wolszczan in 1992– a full three years before Dimidium’s discovery. But because they are so strange, and can’t support life as we know it, most scientists would reserve the “first” designation for a planet orbiting a normal star.
** The French CoRoT mission, launched in 2006, was the first dedicated exoplanet space mission. It has contributed dozens of confirmed exoplanets to the ranks and boasts a roster of some of the most well-studied planets outside our solar system.
To stay up-to-date on our latest exoplanet discoveries, visit: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Top 10 Star Trek Planets Chosen by Our Scientists
What would happen if the crew of the Starship Enterprise handed over the controls to our scientists and engineers? It turns out many are avid Star Trek fans with lengthy itineraries in mind.
1. Vulcan

What is perhaps the most famous Star Trek planet was placed by creator Gene Roddenberry in a real star system: 40 Eridani. This trinary system of three dwarf stars, about 16 light-years from Earth, could play host to exoplanets; none have been detected there so far. The most massive is 40 Eridani A, chosen as Vulcan’s sun.
2. Andoria

An icy “M-class” (Star Trek's term for “Earth-like”) moon of a much larger planet—a gas giant—that is home to soft-spoken humanoids with blue skin, white hair and stylish antennae. In our solar system, gas giants play host to icy moons, such as Jupiter’s Europa or Saturn’s Enceladus, that possess subsurface oceans locked inside shells of ice. Our missions are searching for lifeforms that might exist in these cold, dark habitats.
3. Risa

Another Trek M-class planet known for its engineered tropical climate and its welcoming humanoid population. The planet is said to orbit a binary, or double, star system—in Star Trek fan lore, Epsilon Ceti, a real star system some 79 light-years from Earth. The first discovery of a planet around a binary was Kepler-16b, which is cold, gaseous and Saturn-sized.
4. “Shore Leave” planet, Omicron Delta region

This is another amusement park of a planet, where outlandish characters are manufactured in underground factories straight from the crew members’ imaginations. In real life, astronauts aboard the International Space Station print out plastic tools and containers with their own 3-D printer.
5. Nibiru

“Star Trek: Into Darkness” finds Captain Kirk and Dr. McCoy fleeing from chalk-skinned aliens through a red jungle. Red or even black vegetation could exist on real planets that orbit cooler, redder stars, an adaptation meant to gather as much light for photosynthesis as possible. An example may be Kepler-186f, a planet only 10 percent larger than Earth in diameter. At high noon, the surface of this planet would look something like dusk on Earth.
6. Wolf 359

A star best known in the Star Trek universe as the site of a fierce battle in which a multitude of “Star Trek: Next Generation” ships are defeated by the Borg. But Wolf 359 is a real star, one of the closest to Earth at a distance of 7.8 light-years. Wolf 359 is also a likely observational target for the Kepler space telescope in the upcoming Campaign 14 of its “K2” mission.
7. Eminiar VII/Vendikar

These two planets are neighbors, sharing a star system. So, of course, they’ve been at war for centuries. While we have no signs of interplanetary war, multiple rocky worlds have been discovered orbiting single stars. A cool dwarf star called TRAPPIST-1 is orbited by three Earth-size planets; two have a chance of being the right temperature for liquid water, with possible Earth-like atmospheres.
8. Remus

The planets Romulus and Remus are home to the Romulan Empire (ancient Rome, anyone?), although Remus seemed to have gotten the raw end of the deal. Remus is tidally locked, one face always turned to its star. Tidally locked worlds might well be a real thing, with many possible candidates discovered with our Kepler space telescope. The habitable portion of the surface of such planets might be confined to a band between the day and night sides called the “terminator zone”—a.k.a. the twilight zone.
9. Janus VI

A rocky world lacking an atmosphere, perhaps similar to Mars. While humans must maintain an artificial underground environment to survive, the innards of the planet are a comfortable home to an alien species known as the “Horta.” Their rock-like biochemistry is based on silicon, rather than carbon, inspiring us to imagine the many forms life might take in the universe.
10. Earth

In the Star Trek universe, Earth is home to Starfleet Headquarters; the real Earth is, at least so far, the only life-bearing world we know. No true Earth analogs have been discovered among the real exoplanets detected so far. But a new generation of space telescopes, designed to capture direct images of exoplanets in Earth’s size range, might one day reveal an alternative “pale blue dot.”
Learn more about exoplanets at: exoplanets.nasa.gov
Link to full article: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/news/1378/top-10-star-trek-destinations-chosen-by-nasa-scientists/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things you should know this week:
1. Closeup of a King

For the first time since it entered orbit around Jupiter in July, our Juno spacecraft has flown close to the king of planets—this time with its eyes wide open. During the long, initial orbit, Juno mission managers spent time checking out the spacecraft "from stem to stern," but the science instruments were turned off as a precaution. During this latest pass, Juno's camera and other instruments were collecting data the whole time. Initial reports show that all went well, and the team has released a new close-up view that Juno captured of Jupiter's north polar region. We can expect to see more close-up pictures of Jupiter and other data this week.
+Check in with Juno
2. Getting Ready to Rocket

Our OSIRIS-REx mission leaves Earth next week, the first leg of a journey that will take it out to an asteroid called Bennu. The mission will map the asteroid, study its properties in detail, then collect a physical sample to send back home to Earth. The ambitious endeavor is slated to start off on Sept. 8.
+See what it takes to prep for a deep space launch
3. New Moon Rising

The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has already mapped the entire surface of Earth's moon in brilliant detail, but the mission isn't over yet. Lunar explorers still have questions, and LRO is poised to help answer them.
+See what’s next for the mission
4. A Mock-Eclipse Now

We don't have to wait until next year to see the moon cross in front of the sun. From its vantage point in deep space, our Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) sometimes sees just that. Such an event is expected on Sept. 1.
+See the latest sun pictures from SDO
5. Jupiter’s Cousins

Our galaxy is home to a bewildering variety of Jupiter-like worlds: hot ones, cold ones, giant versions of our own giant, pint-sized pretenders only half as big around. Astronomers say that in our galaxy alone, a billion or more such Jupiter-like worlds could be orbiting stars other than our sun. And we can use them to gain a better understanding of our solar system and our galactic environment, including the prospects for finding life.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Juno Spacecraft: What Do We Hope to Learn?

The Juno spacecraft has been traveling toward its destination since its launch in 2011, and is set to insert Jupiter’s orbit on July 4. Jupiter is by far the largest planet in the solar system. Humans have been studying it for hundreds of years, yet still many basic questions about the gas world remain.

The primary goal of the Juno spacecraft is to reveal the story of the formation and evolution of the planet Jupiter. Understanding the origin and evolution of Jupiter can provide the knowledge needed to help us understand the origin of our solar system and planetary systems around other stars.

Have We Visited Jupiter Before? Yes! In 1995, our Galileo mission (artist illustration above) made the voyage to Jupiter. One of its jobs was to drop a probe into Jupiter’s atmosphere. The data showed us that the composition was different than scientists thought, indicating that our theories of planetary formation were wrong.
What’s Different About This Visit? The Juno spacecraft will, for the first time, see below Jupiter’s dense clover of clouds. [Bonus Fact: This is why the mission was named after the Roman goddess, who was Jupiter’s wife, and who could also see through the clouds.]

Unlocking Jupiter’s Secrets
Specifically, Juno will…
Determine how much water is in Jupiter’s atmosphere, which helps determine which planet formation theory is correct (or if new theories are needed)
Look deep into Jupiter’s atmosphere to measure composition, temperature, cloud motions and other properties
Map Jupiter’s magnetic and gravity fields, revealing the planet’s deep structure
Explore and study Jupiter’s magnetosphere near the planet’s poles, especially the auroras – Jupiter’s northern and southern lights – providing new insights about how the planet’s enormous
Juno will let us take a giant step forward in our understanding of how giant planets form and the role these titans played in putting together the rest of the solar system.
For updates on the Juno mission, follow the spacecraft on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Tumblr.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What is it Like to Visit Jupiter?
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. For some perspective, if it were hollow, more than 1,300 Earths could fit inside of it! The giant planet contains two-thirds of all the planetary mass in the solar system and holds more than dozens of moons in its gravitational grip. But what about a visit to this giant planet?

Let’s be honest…Jupiter is not a nice place to visit. It’s a giant ball of gas and there’s nowhere to land. Any spacecraft – or person – passing through the colorful clouds gets crushed and melted. On Jupiter, the pressure is so strong it squishes gas into liquid. Its atmosphere can crush a metal spaceship like a paper cup.

Jupiter’s stripes and swirls are cold, windy clouds of ammonia and water. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a giant storm BIGGER THAN EARTH! This storm has lasted hundreds of years.

Since Jupiter’s atmosphere is made up of mostly hydrogen and helium, it’s poisonous. There’s also dangerous radiation, more than 1,000 times the lethal level for a human.
Scientists think that Jupiter’s core may be a thick, super hot soup…up to 50,000 degrees! Woah!
The Moons

Did you know that Jupiter has its own “mini solar system” of 50 moons? Scientists are most interested in the Galilean satellites – which are the four largest moons discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610.
Today, Galileo would be astounded to know some of the facts about these moons. The moon Io has active volcanos. Ganymede has its own magnetic field while Europa has a frozen crust with liquid-water underneath making it a tempting place to explore for future missions.

When Juno arrives to Jupiter on July 4, it will bring with it a slew of instruments such as infrared imager/spectrometer and vector magnetometer among the half a dozen other scientific tools in its payload.
Juno will avoid Jupiter's highest radiation regions by approaching over the north, dropping to an altitude below the planet's radiation belts – which are analogous to Earth’s Van Allen belts, but far more deadly – and then exiting over the south. To protect sensitive spacecraft electronics, Juno will carry the first radiation shielded electronics vault, a critical feature for enabling sustained exploration in such a heavy radiation environment.
Follow our Juno mission on the web, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Tumblr.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. The View from the Far Shore

The rugged shores of Pluto’s highlands come into sharp view in a newly released image from our New Horizons spacecraft. This latest view zooms in on the southeastern portion of Pluto’s great ice plains, where they border dark highlands formerly named Krun Macula.
2. Dawn’s Latest Light

Our Dawn mission has now completed more than 1,000 orbital revolutions since entering into Ceres’ gravitational grip in March 2015. The probe is healthy and performing its ambitious assignments impeccably. See what it has revealed lately HERE.
3. Counting Down

Our OSIRIS-REx mission to the asteroid Bennu is now entering the final preparations for its planned launch in September. In a new interview, the mission’s principal investigator reports on the final pre-flight tests happening at our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
4. Deep Dive

Three successful engine maneuvers to bring the lowest part of the spacecraft’s orbit down to just 74 miles (119 km) above the surface of Mars, the MAVEN mission’s fifth deep dip campaign has begun. MAVEN is studying the planet’s atmosphere up close.
5. Storm Season

Meanwhile, other robotic Mars orbiters have revealed that a pattern of three large regional dust storms occurs with similar timing most Martian years. The seasonal pattern was detected from dust storms’ effects on atmospheric temperatures, which spacecraft have been monitoring since 1997.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. Juno Eyes on Jupiter

After a journey of more than five years, the Juno spacecraft is ready for its detailed look at Jupiter—arrival date: July 4. Using Eyes on the Solar System and data from the Juno flight team, you can take a virtual ride onboard the spacecraft in the "Eyes on Juno" simulation.
2. Taking a Spacecraft for a Spin

Preparations for the launch of the OSIRIS-REx asteroid mission are spinning up, literally. Here, the spacecraft can be seen rotating on a spin table during a weight and center of gravity verification test at our Kennedy Space Center. Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 8. This spacecraft will travel to a near-Earth asteroid called Bennu and bring a small sample back to Earth for study.
3. Long-Range (Or at Least Long-Distance) Weather Report
Our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter acquires a global view of the red planet and its weather every day. Last week, dust storms continued along the south polar ice cap edge. Northern portions of Sirenum, Solis, and Noachis also experienced some local dust-lifting activity. A large dust storm propagated eastward over the plains of Arcadia at the beginning of the week, but subsided just a few days later over Acidalia.
4. Hello from the Dark Side

The New Horizons spacecraft took this stunning image of Pluto only a few minutes after closest approach in July 2015, with the sun on the other side of Pluto. Sunlight filters through Pluto's complex atmospheric haze layers. Looking back at Pluto with images like this gives New Horizons scientists information about Pluto's hazes and surface properties that they can't get from images taken on approach.
5. A Titanic Encounter

On June 7, our Cassini orbiter will fly very close by Saturn's giant, haze-shrouded moon Titan. Among the targets of its observations will be the edge of the vortex that swirls in Titan's thick atmosphere near its south pole.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for June 2016?

What's Up for June? Saturn at its best! Plus, good views of Mars, Jupiter and Jupiter's moons continue from dusk to dawn.

You don't have to stay up late to see Jupiter, Mars and Saturn this month, because they're all visible soon after sunset. Jupiter is the brightest of the three, visible in the western sky all evening.

The four Galilean moons are easily visible in binoculars or telescopes. If you think you're seeing 5 moons on June 10th, you're not. One of them is a distant star in the constellation Leo.

For telescope viewers, the time near Mars' closest approach to Earth, May 30th this year, is the best time to try to see the two moons of Mars: Phobos and Deimos. It takes patience, very steady skies and good charts! Mars is still large and bright in early June, but it fades as speedy Earth, in its shorter orbit around the sun, passes it.

Saturn has been close to Mars recently. This month Saturn reaches opposition, when Saturn, Earth and the sun are in a straight line with Earth in the middle, providing the best and closest views of the ringed beauty and several of its moons. You'll be able to make out cloud bands on Saturn, in delicate shades of cream and butterscotch. They're fainter than the bands of Jupiter. Through a telescope you'll see Saturn's rings tilted about as wide as they get: 26 degrees.

You'll also have a ring-side view of the Cassini division, discovered by Giovanni Domenico Cassini, namesake of our Cassini spacecraft, orbiting Saturn since 2004 and continuing through September 2017. When you look at Saturn through a telescope, you can't help but see several of its 4 brightest moons, and maybe more. If you just see one, that's Titan, 50% larger than our own moon. A telescope can also reveal more moons, like Saturn's two-colored moon Iapetus. It takes 3 months to orbit Saturn, and it's fairly easy to see.

There's a bright comet visible this month, Comet PanSTARRS. It's best seen from the southern hemisphere, but it's also visible from the U.S. low in the morning sky. Comet PanSTARRS can be seen through a telescope near the beautiful Helix Nebula on June 4, but it is visible all month.

Watch the full June “What’s Up” video for more: https://youtu.be/M7RtIa9zBYA
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are a few things you should know this week:
1. Science at the Edge

As the New Horizons spacecraft speeds away at more than 31,000 miles per hour (14 km/s) it continues to explore the Kuiper Belt, the region of icy bodies beyond Neptune. New Horizons has now twice observed 1994 JR1, a 90-mile-wide object orbiting more than 3 billion miles from the sun.
2. A Spaceship, Refined

This artist’s rendering shows our Europa mission spacecraft, which is being developed for a launch sometime in the 2020s. The mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to explore the giant planet’s moon Europa. This updated concept image shows tow large solar arrays extending from the sides of the spacecraft, to which the mission’s ice-penetrating radar antennas are attached. A saucer-shaped high-gain antenna is also side mounted with a magnetometer boom placed next to it. Find out more about the spacecraft HERE.
3. Sojourn at Saturn

The Cassini spacecraft is hard at work this week, orbiting Saturn to study the planet and its rings. The recent pictures are spectacular, take a look at them HERE.
4. Talking Juno

Our Juno mission arrives at Jupiter on July 4, and that presents a unique opportunity for educators, science communicators and anyone interested in space exploration. We are providing a growing set of Juno-related information resources. Take a look at them HERE.
5. Now THAT’S a Long Distance Call

How do explorers on Earth talk to astronauts and robotic spacecraft flung across the far reaches of space? They use the remarkable technology deployed by our Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) Program Office. This month, SCaN is celebrating its 10th anniversary of managing the ultimate network. Find out how it works HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Earth By The Numbers
Ahhh, Earth. Our home planet and oasis in space. You’re probably very familiar with this world, but here are a few things you may not know about our “Pale Blue Dot” of a planet.
From the vantage point of space, we are able to observe our planet globally using sensitive instruments to understand the delicate balance among its oceans, air, land and life. Satellite observations help study and predict weather, drought, pollution, climate change and many other phenomena that affect the environment, economy and society.
1. Known to Harbor Life

Of the nine planets, countless asteroids and meteors in our solar system, Earth is the only one known to harbor life. It has a thin layer of atmosphere that separates us from the coldness of space.
2. All By Its Lonesome

Unlike some other planets in the system that have three or more rings, the Earth has zero, but we do have one lonely moon that orbits us.
3. Moving At The Speed Of Life

Earth is the third planet from the sun and is located about 93,000,000 miles away from it. At this distance, the Earth moves at 66,000 miles per hour through space to complete its 365 day rotation.
4. You Can Breathe Easy

Earth’s atmosphere is 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and about 1% other ingredients. Most other planets in our solar system have an atmosphere, but Earth’s is the only one that’s breathable.
5. For Real?

Did you grow up thinking that each calendar year was 365 days long? It’s actually 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 56 seconds...in other words, it’s 365.2564 days long. This is why an extra day is add during a leap year: to help offset this time difference.
6. Far Out

We measure the distance of planets in our solar system in a measurement known as an Astronomical Unit, or AU. This measurement is based on the distance of the Earth from the sun. Earth is one AU from the sun, while Mars is 1.52 AU and Jupiter is 5.2 AU.
7. Taking Selfies...Before It Was Cool

The first ever photo of Earth was captured on October 24, 1946 when a V-2 test rocket was launched into space from New Mexico.
8. Slumped Over Already

The Earth doesn’t sit upright like you would think. It’s actually sitting on its side a bit, or rotational axis as it’s called, the Earth sits at a 23.45 degree rotational axis spin.
9. How Original...

How did it get the name Earth? The name “Earth” is at least 1,000 years old. All the planets in our system are named after Greek and Roman gods and goddesses, except for Earth. The name itself is of English and German origin and simply means “ground”.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Largest Collection of Planets EVER Discovered!
Guess what!? Our Kepler mission has verified 1,284 new planets, which is the single largest finding of planets to date. This gives us hope that somewhere out there, around a star much like ours, we can possibly one day discover another Earth-like planet.

But what exactly does that mean? These planets were previously seen by our spacecraft, but have now been verified. Kepler’s candidates require verification to determine if they are actual planets, and not another object, such as a small star, mimicking a planet. This announcement more than doubles the number of verified planets from Kepler.

Since the discovery of the first planets outside our solar system more than two decades ago, researchers have resorted to a laborious, one-by-one process of verifying suspected planets. These follow-up observations are often time and resource intensive. This latest announcement, however, is based on a statistical analysis method that can be applied to many planet candidates simultaneously.
They employed a technique to assign each Kepler candidate a planet-hood probability percentage – the first such automated computation on this scale, as previous statistical techniques focused only on sub-groups within the greater list of planet candidates identified by Kepler.
What that means in English: Planet candidates can be thought of like bread crumbs. If you drop a few large crumbs on the floor, you can pick them up one by one. But, if you spill a whole bag of tiny crumbs, you're going to need a broom. This statistical analysis is our broom.

The Basics: Our Kepler space telescope measures the brightness of stars. The data will look like an EKG showing the heart beat. Whenever a planet passes in front of its parent star a viewed from the spacecraft, a tiny pulse or beat is produced. From the repeated beats, we can detect and verify the existence of Earth-size planets and learn about their orbits and sizes. This planet-hunting technique is also known as the Transit Method.

The number of planets by size for all known exoplanets, planets that orbit a sun-like star, can be seen in the above graph. The blue bars represent all previously verified exoplanets by size, while the orange bars represent Kepler’s 1,284 newly validated planets announced on May 10.

While our original Kepler mission has concluded, we have more than 4 years of science collected that produced a remarkable data set that will be used by scientists for decades. The spacecraft itself has been re-purposed for a new mission, called K2 -- an extended version of the original Kepler mission to new parts of the sky and new fields of study.

The above visual shows all the missions we’re currently using, and plan to use, in order to continue searching for signs of life beyond Earth.
Following Kepler, we will be launching future missions to continue planet-hunting , such as the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), and the James Webb Space Telescope. We hope to continue searching for other worlds out there and maybe even signs of life-as-we-know-it beyond Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
In addition to the Mercury transit of the sun today, there are a few other things you should know about our solar system this week:
1. Mars, Ready for its Close-Up

Mars will soon be closer to Earth than it has been for 11 years, presenting a great opportunity for backyard sky watchers.
2. Fire and Ice
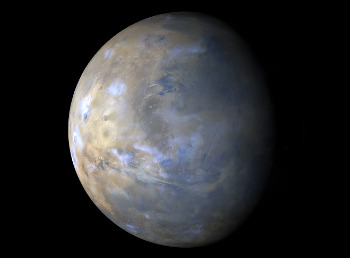
Our spacecraft have an even closer view of Mars, and that fact regularly leads to some intriguing discoveries. The latest: volcanoes may have erupted beneath an ice sheet there billions of years ago. The above image is a mineral map of part of the Martian surface.
3. Icy Hydra

Meanwhile, our New Horizons spacecraft has sent home the first compositional data about Pluto's four small moons. The new data show the surface of Hydra is dominated by nearly pristine water ice--confirming hints that scientists picked up in images showing Hydra's highly reflective surface.
4. Ceres, Ever Sharper

The mission director for our Dawn mission writes, "Ceres, which only last year was hardly more than a fuzzy blob against the stars, is now a richly detailed world, and our portrait grows more elaborate every day."
5. Join us at Jupiter

Our Juno mission arrives at the giant planet on Jul. 4. Meanwhile, all amateur astronomers are invited to take part in a worldwide effort to identify potential observations for the spacecraft to make once it's in orbit. Find out how to join HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Well Do You Know Mercury?
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system and is only slightly larger than Earth’s moon. To give you some perspective, if the sun were as tall as a typical front door, Earth would be the size of a nickel and Mercury would be about as big as a green pea.

Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. Daytime temperatures can reach 430 degrees Celsius (800 degrees Fahrenheit) and drop to –180 degrees Celsius (-290 degrees Fahrenheit) at night.
Here are a few fun facts about Mercury:
Mercury takes only 88 Earth days to orbit the sun
If we could stand on Mercury’s surface when it is at its closest point to the sun, the sun would appear more than three times larger than it does here on Earth
Mercury is home to one of the largest impact basins in the solar system: the Caloris Basin. The diameter of this impact basin is the length of 16,404 football fields (minus the end zones) placed end to end!
Mercury is one of only two planets in our solar system that do not have moons (Venus is the other one)
Mercury completes three rotations for every two orbits around the sun. That means that if you wanted to stay up from sunrise to sunrise on Mercury, you’d be up for 176 Earth days…you’d need a LOT of coffee!

Two missions have visited Mercury:
Mariner 10 was the first mission to Mercury, and 30 years later, our MESSENGER mission was the second to visit the planet. Mariner 10 was also the first spacecraft to reach one planet by using the gravity of another planet (in this case, Venus) to alter its speed and trajectory.

MESSENGER was the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury, The spacecraft had its own shades to protect it from the light of the sun. This is important since sunlight on Mercury can be as much as 11 times brighter than it is here on Earth. The spacecraft was originally planned to orbit Mercury for one year, but exceeded expectations and worked for over four years capturing extensive data. On April 30, 2015, the spacecraft succumbed to the pull of solar gravity and impacted Mercury’s surface.
Water Ice?
The MESSENGER spacecraft observed compelling support for the long-held hypothesis that Mercury harbors abundant water ice and other frozen volatile materials in its permanently shadowed polar craters.

This radar image of Mercury’s north polar region. The areas shown in red were captured by MESSENGER, compared to the yellow deposits imaged by Earth-based radar. These areas are believed to consist of water ice.
Mercury Transit of the Sun
For more than seven hours on Monday, May 9, Mercury will be visible as a tiny black dot crossing the face of the sun. This rare event – which happens only slightly more than once a decade – is called a transit.

Where: Skywatchers in Western Europe, South America and eastern North America will be able to see the entirety of the transit. The entire 7.5-hour path across the sun will be visible across the Eastern U.S. – with magnification and proper solar filters – while those in the West can observe the transit in progress at sunrise.

Watch: We will stream a live program on NASA TV and the agency’s Facebook page from 10:30 to 11:30 a.m. – an informal roundtable during which experts representing planetary, heliophysics and astrophysics will discuss the science behind the Mercury transit. Viewers can ask questions via Facebook and Twitter using #AskNASA. Unlike the 2012 Venus transit of the sun, Mercury is too small to be visible without magnification from a telescope or high-powered binoculars. Both must have safe solar filters made of specially-coated glass or Mylar; you can never look directly at the sun.
To learn more about our solar system and the planets, visit: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Worlds That Will Make You Believe Star Wars is Real
The fantastical planets in Star Wars preceded our discovery of real planets outside our solar system…but fiction isn’t too far from the facts. When we send our spacecraft into the solar system and point our telescopes beyond, we often see things that seem taken right out of the Star Wars universe.
Is there a more perfect time than May the 4th to compare real worlds to the ones depicted in Star Wars?
Probably not...so here are a few:
Mimas

Saturn’s moon, Mimas, has become known as the "Death Star" moon because of how its 80-mile wide Herschel crater creates a resemblance to the Imperial battle station, especially when seen in this view from our Cassini spacecraft.
Kepler-452b

The most recently revealed exoplanet dubbed as Earth’s bigger, older cousin, Kepler-452b, might make a good stand-in for Coruscant — the high tech world seen in several Star Wars films whose surface is encased in a single, globe-spanning city. Kepler-452b belongs to a star system 1.5 billion years older than Earth’s! That would give any technologically adept species more than a billion-year jump ahead of us.
CoRoT-7b

At 3,600 degrees Fahrenheit, CoRoT-7B is a HOT planet. Discovered in 2010 with France’s CoRoT satellite, it’s some 480 light-years away, and has a diameter 70% larger than Earth’s, with nearly five times the mass. Possibly the boiled-down remnant of a Saturn-sized planet, its orbit is so tight that its star looms much larger in its sky than our sun appears to us, keeping its sun-facing surface molten! This scorching planet orbiting close to its star could be a good analog for planet Mustafar from Star Wars.
Kepler-16b

Luke Skywalker’s home planet, Tatooine, is said to possess a harsh, desert environment, swept by sandstorms as it roasts under the glare of twin suns. Real exoplanets in the thrall of two or more suns are even harsher! Kepler-16b was the Kepler telescope’s first discovery of a planet in a “circumbinary” orbit (a.k.a, circling both stars, as opposed to just one, in a double star system). This planet, however, is likely cold, about the size of Saturn, and gaseous, though partly composed of rock.
OGLE-2005-BLG-390

Fictional Hoth is a frozen tundra that briefly serves as a base for the hidden Rebel Alliance. It’s also the nickname of real exoplanet OGLE-2005-BLG-390, a cold super-Earth whose surface temperature clocks in at minus 364 degrees Fahrenheit.
Kepler-22b

Kepler-22b, analog to the Star Wars planet Kamino…which was the birthplace of the army of clone soldiers, is a super-Earth that could be covered in a super ocean. The jury is still out on Kepler-22b’s true nature; at 2.4 times Earth’s radius, it might even be gaseous. But if the ocean world idea turns out to be right, we can envision a physically plausible Kamino-like planet.
Gas Giants

Gas giants of all stripes populate the real exoplanet universe; in Star Wars, a gas giant called Bespin is home to a “Cloud City” actively involved in atmospheric mining. Mining the atmospheres of giant gas planets is a staple of science fiction. We too have examined the question, and found that gases such as helium-3 and hydrogen could theoretically be extracted from the atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune.
Exomoons

Endor, the forested realm of the Ewoks, orbits a gas giant. Exomoon detection is still in its infancy for scientists on Earth. However, a possible exomoon (a moon circling a distant planet) was observed in 2014 via microlensing. It will remain unconfirmed, however, since each microlensing event can be seen only once.
May the 4th be with you!
Discover more about exoplanets here: https://exoplanets.jpl.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The Special Ingredients…of Earth!

With its blue skies, puffy white clouds, warm beaches and abundant life, planet Earth is a pretty special place. A quick survey of the solar system reveals nothing else like it. But how special is Earth, really?

One way to find out is to look for other worlds like ours elsewhere in the galaxy. Astronomers using our Kepler Space Telescope and other observatories have been doing just that!

In recent years they’ve been finding other planets increasingly similar to Earth, but still none that appear as hospitable as our home world. For those researchers, the search goes on.

Another group of researchers have taken on an entirely different approach. Instead of looking for Earth-like planets, they’ve been looking for Earth-like ingredients. Consider the following:

Our planet is rich in elements such as carbon, oxygen, iron, magnesium, silicon and sulfur…the stuff of rocks, air, oceans and life. Are these elements widespread elsewhere in the universe?

To find out, a team of astronomers led by the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), with our participation, used Suzaku. This Japanese X-ray satellite was used to survey a cluster of galaxies located in the direction of the constellation Virgo.

The Virgo cluster is a massive swarm of more than 2,000 galaxies, many similar in appearance to our own Milky Way, located about 54 million light years away. The space between the member galaxies is filled with a diffuse gas, so hot that it glows in X-rays. Instruments onboard Suzaku were able to look at that gas and determine which elements it’s made of.

Reporting their findings in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, they reported findings of iron, magnesium, silicon and sulfur throughout the Virgo galaxy cluster. The elemental ratios are constant throughout the entire volume of the cluster, and roughly consistent with the composition of the sun and most of the stars in our own galaxy.

When the Universe was born in the Big Bang 13.8 billon years ago, elements heavier than carbon were rare. These elements are present today, mainly because of supernova explosions.

Massive stars cook elements such as, carbon, oxygen, iron, magnesium, silicon and sulfur in their hot cores and then spew them far and wide when the stars explode.

According to the observations of Suzaku, the ingredients for making sun-like stars and Earth-like planets have been scattered far and wide by these explosions. Indeed, they appear to be widespread in the cosmos. The elements so important to life on Earth are available on average and in similar relative proportions throughout the bulk of the universe. In other words, the chemical requirements for life are common.

Earth is still special, but according to Suzaku, there might be other special places too. Suzaku recently completed its highly successful mission.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 5 Things to Know This Week
From Mars to the asteroid belt to Saturn, our hardworking space robots are exploring the solar system. These mechanical emissaries orbit distant worlds or rove across alien landscapes, going places that are too remote or too dangerous for people (for now).
We often show off the pictures that these spacecraft send home, but this week we’re turning that around: here are some of the best pictures of the space robots, taken by other robots (or themselves), in deep space.
1. So Selfless with the Selfies

The Mars Curiosity rover makes breathtaking panoramas of the Martian landscape — and looks good doing it. This mission is famous for the remarkable self portraits of its robotic geologist in action. See more Martian selfies HERE. You can also try this draggable 360 panorama HERE. Find out how the rover team makes these images HERE.
2. Two Spaceships Passing in the Moonlight

In a feat of timing on Jan. 14, 2014, our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter caught a snapshot of LADEE, another robotic spacecraft that was orbiting the moon at the time. LADEE zoomed past at a distance of only about five miles below.
3. Bon Voyage, Galileo

The history-making Galileo mission to Jupiter set sail from the cargo bay of another spacecraft, Space Shuttle Atlantis, on Oct. 18, 1989. Get ready for Juno, which is the next spacecraft to arrive at Jupiter in July.
4. Cometary Close-Up

Using a camera on the Philae lander, the Rosetta spacecraft snapped an extraordinary self portrait at comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko from a distance of about 10 miles. The image captures the side of Rosetta and one of its 14-meter-long solar wings, with the comet in the background. Learn more about Rosetta HERE.
5. Man and Machine

This snapshot captures a remarkable moment in the history of exploration: the one and only time a human met up in space with a robotic forerunner on location. The Surveyor 3 lander helped pave the way for the astronaut footsteps that came a few years later. See the story of Apollo 12 and this unique encounter HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are 5 things you should know this week:
1. From Pluto, with Love

Last Valentine’s Day, no one had even seen Pluto’s most famous feature, the heart-shaped Sputnik Planum. These days, the New Horizons spacecraft is sending more and more pictures back to Earth from its Pluto flyby last July. We received new ones almost on a weekly basis. For the latest love from the outer solar system, go HERE.
2. Saturn’s Rings: More (and Less) than Meets the Eye

The Cassini spacecraft is executing a series of maneuvers to raise its orbit above the plane of Saturn’s famous rings. This will offer some breathtaking views that you won’t want to miss. Meanwhile, Cassini scientists are learning surprising things, such as the fact that the most opaque sections of the rings are not necessarily the thickest.
3. Stay on Target

The Juno spacecraft recently completed a course correction maneuver to fine-tune its approach to Jupiter. After years of flight and millions of miles crossed, arrival time is now set to the minute: July 4th at 11:18 p.m. EST. See why we’re going to jupiter HERE.
4. The Many Lives of “Planet X”

The announcement of a potential new planet beyond Neptune creates an opportunity to look back at the ongoing search for new worlds in the unmapped reaches of our own solar system. Review what we’ve found so far, and what else might be out there HERE.
5. Answering the Call of Europa

There are a few places more intriguing that Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, home to an underground ocean with all the ingredients necessary for potential life. We’re undertaking a new mission to investigate, and the project’s top manager and scientist will be giving a live lecture to detail their plans. Join Barry Goldstein and Bob Pappalardo on Feb. 11 at 10 p.m. EST for a live lecture series on Ustream.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
We live during one of the great eras of exploration. At this very moment, there are dozens of spacecraft surveying the solar system, from Mars, to Saturn, to Pluto and beyond. What’s more, you can ride along with these expeditions — all you need is an internet connection to see the latest discoveries from deep space. Here are a few essential resources for the armchair astronaut:
1. It’s Like Facebook, but for Planets

Or is it more of a Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Solar System? Whatever you want to call it, our Planets page offers quick rundowns, as well as in-depth guides, for all the major bodies in the solar system. Explore from the sun all they way out to the Oort Cloud.
2. Robots to the Rescue

Saturn looks spectacular through a telescope, but there’s only so much you can learn about it from the ground. Going there in person is tough, too. While we are now preparing to send astronauts beyond Earth orbit, a human mission to Saturn won’t be possible in the near future. That’s where the space robots come in. For example, the Cassini spacecraft studies Saturn and its moons up close, sometimes even doing things like flying right through the geyser plumes of the ice moon Enceladus. See all the solar system missions, past and present, where they went and what they’ve seen HERE.
3. Keep Your Eyes on This One

If you still haven’t tried Eyes on the Solar System, you’re missing out. This online simulation lets you tour the planets and track the past, current and future positions of spacecraft — right in your web browser, all in 3D. Eyes on the Solar System uses real NASA data to help you take a virtual flight across both space and time.
4. Images in the Raw

You don’t have to wait for a news release to see pictures from planetary missions. Some missions allow you to see raw, unprocessed images sent straight from the spacecraft. What these images lack in explanatory captions they make up for in freshness — sometimes you can see pictures from Mars or Saturn that are mere hours old. There’s something exhilarating about being among the first human beings ever to see an alien landscape. Peruse our new raw image pages HERE.
5. Bring It On Home

After you’ve toured the far reaches of the solar system, you can always come home again. When you have spent time studying the harsh conditions of our neighboring planets, the charms of a unique paradise come into sharp focus, the place we call Earth. Watch a real-time video feed from Earth orbit HERE. You can also see a daily global view of our planet from a million miles away HERE. Download THIS Earth Now mobile app to hold the planet in your hands.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for February 2016?
Five morning planets, Comet Catalina passes Polaris and icy Uranus and icy Vesta meet near Valentine’s Day.

February mornings (until Feb. 20) feature Mercury, Venus, Saturn, Mars and Jupiter. The last time this five-planet dawn lineup happened was in 2005. The planets are easy to distinguish when you use the moon as your guide. Details on viewing HERE.
If you miss all five planets this month, you’ll be able to see them again in August’s sunset sky.

Last month, Comet Catalina’s curved dust tail and straight ion tail were visible in binoculars and telescopes near two galaxies that are close to the handle of the Big Dipper. Early this month, the comet nears Polaris, the North Star. It should be visible all month long for northern hemisphere observers.

There will be more opportunities to photograph Comet Catalina paired with other objects this month. It passes the faint spiral galaxy IC 342 and a pretty planetary nebula named NGC 1501 between Feb. 10 – 29. For binocular viewers, the magnitude 6 comet pairs up with a pretty string of stars, known as Kemble’s Cascade, on Feb. 24.

Finally, through binoculars, you should be able to pick out Vesta and Uranus near one another this month. You can use the moon as a guide on Feb. 12, and the cornerstone and the corner stars of Pegasus all month long.

For more information about What’s Up in the February sky, watch our monthly video HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
7 Facts That Will Make You Feel Very Small

Earth, our home planet, is the fifth largest planet in our solar system and the only planet we know of where life exists. Even though Earth seems extremely large to us, it is actually a tiny spec in the vast expanse of the universe. Here are 7 space facts that will make you feel very small.

1. Our sun is one of at least 100 BILLION stars, just in the Milky Way. Scientists calculate that there are at least 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe, each one brimming with stars. There are more stars than grains of sand on all of Earth’s beaches combined.
In 1995, the first planet beyond our solar system was discovered. Now, thousands of planets orbiting sun-like stars have been discovered, also known as exoplanets.

2. The Milky Way is a huge city of stars, so big that even at the speed of light (which is fast!), it would take 100,000 years to travel across it.

3. Roughly 70% of the universe is made of dark energy. Dark matter makes up about 25%. The rest — everything on Earth, everything ever observed with all of our instruments, all normal matter adds up to less than 5% of the universe.

4. If the sun were as tall as a typical front door, Earth would be the size of a nickel.

5. The sun accounts for almost all of the mass in our solar system. Leaving .2% for all the planets and everything else.

6. Edwin Hubble discovered that the Universe is expanding and that at one point in time (14 billion years ago) the universe was all collected in just one point of space.

7. Four American spacecraft are headed out of our solar system to what scientists call interstellar space. Voyager 1 is the farthest out — more than 11 billion miles from our sun. It was the first manmade object to leave our solar system. Voyager 2, is speeding along at more than 39,000 mph, but will still take more than 296,000 years to pass Sirius, the brightest star in our night sky.
Feeling small yet? Here’s a tool that will show you just how tiny we are compared to everything else out there: http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/features/cosmic/earth.html
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com