Your gateway to endless inspiration
Planets - Blog Posts
Solar System: 2016 Preview
What do we have planned for 2016? A return to the king of planets. A survey of mysterious Ceres. More postcards from Pluto. Anyone who follows solar system exploration in 2016 is in for quite a ride. Last year was one for the record books – and now here are 10 things to look forward to in the new year. See also: what we have planned agency wide for 2016.
Juno Arrives at Jupiter

July 4, 2016 is arrival day for the Juno mission, the first sent expressly to study the largest planet in the solar system since our Galileo mission in the 1990s. Humans have been studying Jupiter for hundreds of years, yet many basic questions about the gas world remain: How did it form? What is its internal structure? Exactly how does it generate its vast magnetic field? What can it tell us about the formation of other planets inside and outside our solar system? Beginning in July, we’ll be a little closer to the answers.
OSIRIS-REx Takes Flight

The OSIRIS-REx mission, short for Origins-Spectral Interpretation-Resource Identification-Security-Regolith Explorer, sets sail for an asteroid in September. The spacecraft will use a robotic arm to pluck samples from the asteroid Bennu to help better explain our solar system’s formation and even find clues to how life began.
Dawn Sees Ceres Up Close

After an odyssey of many years and millions of miles, in December the Dawn spacecraft entered its final, lowest mapping orbit around the dwarf planet Ceres. The intriguing world’s odd mountains, craters and salty deposits are ready for their close-ups. We can expect new images of the starkly beautiful surface for months.
Cassini Commences Its Grand Finale

In late 2016, the Cassini spacecraft will begin a daring set of orbits called the Grand Finale, which will be in some ways like a whole new mission. Beginning this year and extending into next, the spacecraft will repeatedly climb high above Saturn’s poles, flying just outside its narrow F ring 20 times. After a last targeted Titan flyby, the spacecraft will then dive between Saturn’s uppermost atmosphere and its innermost ring 22 times. As Cassini plunges past Saturn, the spacecraft will collect rich and valuable information far beyond the mission’s original plan.
New Horizons Sends More Postcards from Pluto

We have stared slack-jawed at the images and discoveries from last year’s Pluto flyby, but the fact is that most of the data that New Horizons collected remains on board the spacecraft. In 2016, we’ll see a steady release of new pictures — and very likely some expanded answers to longstanding questions.
Mars Missions March Forward

With five of our missions continuing their Martian quests, 2016 should be a good year for discoveries on the Red Planet.
Mars Odyssey
Mars Opportunity
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
Mars Curiosity
MAVEN
Mercury Transits the Sun

A transit is a very rare astronomical event in which a planet passes across the face of the sun. In May, Mercury will transit the sun, on of only thirteen Mercury transits each century on average.
LRO Keeps an Eagle Eye On the Moon

The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) will extend its run in 2016, scanning the moon’s surface with its sharp-eyed instruments, investigating everything from lava tube skylights to changes at the Apollo landing sites.
Spacecraft Fly Under Many Flags

Our partner agencies around the world will be flying several new or continuing planetary missions to destinations across the solar system:
Akatsuki at Venus
ExoMars
Mars Express
Mars Orbiter Mission
Rosetta at Comet 67/P
Technology Demonstration Missions Push the Envelope

We’re always looking for new frontiers on distant worlds, as well as the technology that will take us there. This year, several missions are planned to take new ideas for a spin in space:
Deep Space Atomic Clock
NODES
LDSD
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for January?

A meteor shower, a binocular comet and the winter circle of stars. Here are the details:
Quadrantid Meteor Shower

The Quadrantid meteor shower on Jan. 4 will either sizzle or fizzle for observers in the U.S. The shower may favor the U.S. or it could favor Europe depending on which prediction turns out to be correct. For viewing in the United States, observers should start at 3 a.m. EST. The peak should last about two hours with rates of 120 meteors per hour predicted in areas with a dark sky.
Comet Catalina

In the middle of the month, midnight to predawn will be primetime for viewing Comet Catalina. It should be visible with binoculars if you have a dark sky, but a telescope would be ideal. Between the 14th and 17th the comet will pass by two stunning galaxies: M51, the whirlpool galaxy and M101, a fainter spiral galaxy.
Constellation Orion

Winter is also the best time to view the constellation Orion in the southeastern sky. Even in the city, you’ll see that it’s stars have different colors. Not telescope needed, just look up a few hours after sunset! The colorful stars of Orion are part of the winter circle of stars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Well Do You Know Venus?
Similar in structure and size to Earth, Venus’ thick, toxic atmosphere traps heat in a runaway greenhouse effect. A permanent layer of clouds traps heat, creating surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead.

How did Venus get its name? It is named for the ancient Roman goddess of love and beauty. It is believed that Venus was named for the most beautiful of the ancient gods because it shone the brightest of the five planets known to ancient astronomers.

Here are a few fun facts that you might not know:
One day on Venus lasts as long as 243 Earth days (aka the time it takes for Venus to rotate or spin once)
Venus is a rocky planet, also known as a terrestrial planet
Venus’ thick and toxic atmosphere is made up mostly of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, with clouds of sulfuric acid droplets
Venus has no moons or rings
More than 40 spacecraft have explored the planet
No evidence of life has been found on Venus. The planet’s extreme high temperatures of almost 480 degrees Celsius (900 degrees Fahrenheit) makes it seem an unlikely place for life as we know it
Venus spins backwards when compared to the other planets. This means that the sun rises in the west and sets in the east
Night Light

Did you know that Venus is the brightest planet in Earth’s dark skies? Only the moon — which is not a planet — is brighter. Venus outshines the other planets because it is closer and its thick cloud cover is excellent at reflecting sunlight.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Well Do you Know Neptune?

Dark, cold and whipped by supersonic winds, Neptune is the last of the hydrogen and helium gas giants in our solar system. More than 30 times as far from the sun as Earth, the planet takes almost 165 Earth years to orbit our sun! In fact, in 2011, Neptune completed its first orbit since its discovery in 1846.

Here are a few things you might not know about the windiest planet:
If the sun were as tall as a typical front door, the Earth would be the size of a nickel and Neptune would be about as big as a baseball.
Neptune orbits our sun, a star. Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun at a distance of about 4.5 billion km (2.8 billion miles) or 30.07 AU.
One day on Neptune takes about 16 hours (the time it takes for Neptune to rotate or spin once)
Neptune makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Neptunian time) in about 165 Earth years (60,190 Earth days)
Neptune has six rings
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have visited Neptune
Neptune has 13 moons. They are named after various sea gods and nymphs in Greek mythology
Did you know that Neptune has storms?

Similar to Jupiter, Neptune has storms that create gigantic spots in its atmosphere…well, it did. When Voyager 2 flew past Neptune in 1989, it tracked and imaged the “Great Dark Spot” — a storm larger than the entire Earth! When the Hubble Space Telescope imaged Neptune the spot had disappeared, only to be replaced with two smaller storms, which in turn also disappeared.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Return to Venus

Japan's Akatsuki orbiter is making a second attempt to enter orbit around Venus today, Dec. 7. A malfunction in 2010 caused the spacecraft to miss its first orbit opportunity. The mission team came up with a plan to try again this week. In honor of Akatsuki, here are a few things you need to know about Venus, physics and other missions to explore our solar system's second planet:
1. Venus Climate Orbiter

The down-to-business names for Akatsuki - which means "Dawn" or "Daybreak" in Japanese - are Venus Climate Orbiter and Planet-C. Akatsuki is Japan's third deep space mission. At Venus, the orbiter will study Venusian meteorology. JAXA defines the mission's goals as:
Observing Venus as a whole to understand its perpetual cloud layer, deep atmosphere and surface
Close observations of cloud structures and convection
Searching for signs of lightning and air glow
2. Exploring Venus

Venus played a key role in early deep space exploration. Our Mariner 2 was the first successful interplanetary mission in 1962. And several Soviet spacecraft have made the tough descent and landing on Venus' hellish surface. HERE is a list of other missions to Venus.
3. All About Venus
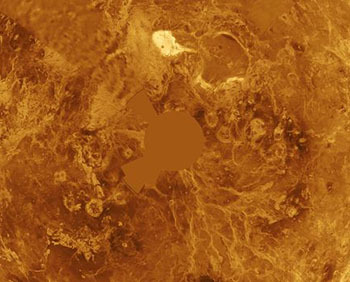
Similar in structure and size to Earth, Venus' thick, toxic atmosphere traps heat in a runaway greenhouse effect. A permanent layer of clouds traps heat, creating surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead. Glimpses below the clouds reveal volcanoes and deformed mountains. Venus spins slowly in the opposite direction of most planets.
4. Sizing Up the Solar System

Venus also played a key role in determining the distance between Earth and the sun - creating the Astronomical Unit, the basic measurement we use to define our place in the cosmos. Many 18th century explorers, including the legendary James Cook, undertook perilous journeys to define the astronomical unit by watching Venus cross the face of the sun.
5. It’s Just a Phase

Like the moon, Venus has phases. It can be full when Venus is on the far side of the sun, new when Venus is between the sun and Earth and a crescent at other points in between. Take a look at Galileo Galilei’s sketches of the phases of Venus HERE.
Follow Along:
As mentioned, Japan's Akatsuki orbiter is making a second attempt to enter orbit around Venus today, Dec. 7. Follow along HERE for updates on this attempt.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Well Do You Know Your Space Photos?
Can you guess the subject of each of these pictures? How many will you get right? Test your friends and family to see who knows their space photos the best.
1. Ice on Earth or a Picture of Mars?

2. Dry Land on Earth or a Close-Up of Jupiter?

3. Mercury or Our Moon?

4. Do You Think This is Mars or Our Home Planet?

5. Waves on Jupiter or Saturn?

6. Is this a picture of Mars or Earth?

7. Can You Tell Which is Europa and Which is the Bottom of a Frying Pan?

8. Close-Up of Our Moon or Dwarf Planet Ceres?

9. A Weird World or Our Own World?

10. The Red Planet or a Red Desert?

Answers
1. Mars. You might be surprised, but this image taken by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is of a light-toned deposit on the Martian surface. Some shapes in the terrain suggest erosion by a fluid moving north to south.
2. Earth. This image taken by our Earth Observing-1 satellite shows Lake Frome in central Australia. In this image, the salt lake appears bone-dry, filled with off-white sediment. This area of Australia receives 149 to 216 millimeters of rainfall a year on average, and the basins pass most of their time as saltpans.
3. Mercury. Our MESSENGER spacecraft captured this image of Mercury during a fly by in October 2008. It shows previously uncharted regions of the planet that have large craters with an internal smoothness similar to Earth’s own moon. It is thought that these craters were to have been flooded by lava flows that are old but not as old as the surrounding more highly cratered surface.
4. Earth. Surprisingly, this image take from the International Space Station shows the western half of the Arabian peninsula in Saudi Arabia. It not only contains large expanses of sand and gravel, but extensive lava fields known as haraat.
5. Saturn. Although this pattern of waves is similar to those seen on Jupiter, this is actually a picture of Saturn. The pattern of an iconic surfer’s wave, has been observed in many places all over the universe, including at the edges of Earth’s magnetic environment.
6. Mars. This image was taken by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and shows dunes of sand-sized materials that have been trapped on the floors of many Martian craters. The dunes are linear, thought to be due to shifting wind directions.
7. Left: Europa. Right: Frying Pan. Europa is one of Jupiter’s moons, and is about the same size as Earth’s moon.
8. Ceres. This image taken by our Dawn spacecraft shows an intriguing mountain on dwarf planet Ceres protruding from a relatively smooth area.
9. Earth. This image of the Bazman volcano is located in a remote region of souther Iran. While the volcano has the classic cone shape of a stratovolcano, it is also heavily dissected by channels that extend downwards from the summit.
10. Earth. This image of the Great Sandy Desert in northwest Australia shows a variety of dune forms across the region. The photo was taken by the Expedition 35 crew from the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com
NASA’s Fleet of Planet-hunters and World-explorers
Around every star there could be at least one planet, so we’re bound to find one that is rocky, like Earth, and possibly suitable for life. While we’re not quite to the point where we can zoom up and take clear snapshots of the thousands of distant worlds we’ve found outside our solar system, there are ways we can figure out what exoplanets light years away are made of, and if they have signs of basic building blocks for life. Here are a few current and upcoming missions helping us explore new worlds:
Kepler

Launched in 2009, the Kepler space telescope searched for planets by looking for telltale dips in a star’s brightness caused by crossing, or transiting, planets. It has confirmed more than 1,000 planets; of these, fewer than 20 are Earth-size (therefore possibly rocky) and in the habitable zone -- the area around a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of an orbiting planet. Astronomers using Kepler data found the first Earth-sized planet orbiting in the habitable zone of its star and one in the habitable zone of a sun-like star.
In May 2013, a second pointing wheel on the spacecraft broke, making it not stable enough to continue its original mission. But clever engineers and scientists got to work, and in May 2014, Kepler took on a new job as the K2 mission. K2 continues the search for other worlds but has introduced new opportunities to observe star clusters, young and old stars, active galaxies and supernovae.
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)

Revving up for launch around 2017-2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find new planets the same way Kepler does, but right in the stellar backyard of our solar system while covering 400 times the sky area. It plans to monitor 200,000 bright, nearby stars for planets, with a focus on finding Earth and Super-Earth-sized planets.
Once we’ve narrowed down the best targets for follow-up, astronomers can figure out what these planets are made of, and what’s in the atmosphere. One of the ways to look into the atmosphere is through spectroscopy.
As a planet passes between us and its star, a small amount of starlight is absorbed by the gas in the planet’s atmosphere. This leaves telltale chemical “fingerprints” in the star’s light that astronomers can use to discover the chemical composition of the atmosphere, such as methane, carbon dioxide, or water vapor.
James Webb Space Telescope

Launching in 2018, NASA’s most powerful telescope to date, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will not only be able to search for planets orbiting distant stars, its near-infrared multi-object spectrograph will split infrared light into its different colors- spectrum- providing scientists with information about an physical properties about an exoplanet’s atmosphere, including temperature, mass, and chemical composition.
Hubble Space Telescope

Hubble Space Telescope is better than ever after 25 years of science, and has found evidence for atmospheres bleeding off exoplanets very close to their stars, and even provided thermal maps of exoplanet atmospheres. Hubble holds the record for finding the farthest exoplanets discovered to date, located 26,000 light-years away in the hub of our Milky Way galaxy.
Chandra X-ray Observatory

Chandra X-ray Observatory can detect exoplanets passing in front of their parent stars. X-ray observations can also help give clues on an exoplanet’s atmosphere and magnetic fields. It has observed an exoplanet that made its star act much older than it actually is.
Spitzer Space Telescope

Spitzer Space Telescope has been unveiling hidden cosmic objects with its dust-piercing infrared vision for more than 12 years. It helped pioneer the study of atmospheres and weather on large, gaseous exoplanets. Spitzer can help narrow down the sizes of exoplanets, and recently confirmed the closest known rocky planet to Earth.
SOFIA

The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) is an airplane mounted with an infrared telescope that can fly above more than 99 percent of Earth's atmospheric water vapor. Unlike most space observatories, SOFIA can be routinely upgraded and repaired. It can look at planetary-forming systems and has recently observed its first exoplanet transit.
What’s Coming Next?
Analyzing the chemical makeup of Earth-sized, rocky planets with thin atmospheres is a big challenge, since smaller planets are incredibly faint compared to their stars. One solution is to block the light of the planets' glaring stars so that we can directly see the reflected light of the planets. Telescope instruments called coronagraphs use masks to block the starlight while letting the planet's light pass through. Another possible tool is a large, flower-shaped structure known as the starshade. This structure would fly in tandem with a space telescope to block the light of a star before it enters the telescope.
All images (except SOFIA) are artist illustrations.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
InSight Mission to Mars

Our InSight mission will place a fixed science outpost on Mars to study its deep interior. Findings and research from this project will address one of the most fundamental questions we have about planetary and solar system science – How in the world did these rocky planets form?
By investigating the interior structure and processes of Mars, the InSight mission will gain a better understanding of the evolutionary formation of planets, including Earth.
InSight will record Mars’ vital signs to learn more about the planet, including:

Seismic Activity:
A seismometer will be used to record the seismic activity on Mars. This will give us information on the crust, mantel and core; and the relationship between them.

Temperature:
A heat flow probe will be used to take Mars’ temperature and determine the change over the course of a full Martian year.

Reflexes:
By looking at how the rotation of Mars wobbles, we will better understand what the core size may be and its composition.

Launch for the InSight mission is scheduled for March 2016, and even though you can’t physically travel with the lander, you can send your name to the Red Planet onboard. Make sure to submit your name before Sept. 8!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for September?

Stargazing and looking up into the night sky is always a fun thing to do. This month, it will be especially exciting because there will be a total eclipse of a supermoon, plus the opportunity to see planets and the late-summer Milky Way!
What is a supermoon?

A supermoon is a new or full moon that occurs when it is at, or near its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit. There are usually 4 to 6 supermoons every year.
Observers can view the total eclipse on September 27, starting at 10:11 p.m. EDT until 11:23 p.m. This event will be visible in North and South America, as well as Europe and Africa. So make sure to mark your calendars!

This month, you will also be able to see the planets! Look for Mercury, Saturn, Pluto and Neptune in the evening sky. Uranus and Neptune at midnight, and Venus, Mars and Jupiter in the pre-dawn sky.

Finally, if you’re able to escape to a dark location, you might be able to see a great view of our Milky Way!
So, make sure to get outside this month and take a look at everything our night sky has to offer.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com