Your gateway to endless inspiration
How Does It Work?? - Blog Posts
wtf is color theory????????
How Gravity Warps Light
Gravity is obviously pretty important. It holds your feet down to Earth so you don’t fly away into space, and (equally important) it keeps your ice cream from floating right out of your cone! We’ve learned a lot about gravity over the past few hundred years, but one of the strangest things we’ve discovered is that most of the gravity in the universe comes from an invisible source called “dark matter.” While our telescopes can’t directly see dark matter, they can help us figure out more about it thanks to a phenomenon called gravitational lensing.
The Gravity of the Situation
Anything that has mass is called matter, and all matter has gravity. Gravity pulls on everything that has mass and warps space-time, the underlying fabric of the universe. Things like llamas and doughnuts and even paper clips all warp space-time, but only a tiny bit since they aren’t very massive.

But huge clusters of galaxies are so massive that their gravity produces some pretty bizarre effects. Light always travels in a straight line, but sometimes its path is bent. When light passes close to a massive object, space-time is so warped that it curves the path the light must follow. Light that would normally be blocked by the galaxy cluster is bent around it, producing intensified — and sometimes multiple — images of the source. This process, called gravitational lensing, turns galaxy clusters into gigantic, intergalactic magnifying glasses that give us a glimpse of cosmic objects that would normally be too distant and faint for even our biggest telescopes to see.

Hubble “Sees” Dark Matter
Let’s recap — matter warps space-time. The more matter, the stronger the warp and the bigger its gravitational lensing effects. In fact, by studying “lensed” objects, we can map out the quantity and location of the unseen matter causing the distortion!
Thanks to gravitational lensing, scientists have measured the total mass of many galaxy clusters, which revealed that all the matter they can see isn’t enough to create the warping effects they observe. There’s more gravitational pull than there is visible stuff to do the pulling — a lot more! Scientists think dark matter accounts for this difference. It’s invisible to our eyes and telescopes, but it can’t hide its gravity!
The mismatch between what we see and what we know must be there may seem strange, but it’s not hard to imagine. You know that people can’t float in mid-air, so what if you saw a person appearing to do just that? You would know right away that there must be wires holding him up, even if you couldn’t see them.

Our Hubble Space Telescope observations are helping unravel the dark matter mystery. By studying gravitationally lensed galaxy clusters with Hubble, astronomers have figured out how much of the matter in the universe is “normal” and how much is “dark.” Even though normal matter makes up everything from pickles to planets, there’s about five times more dark matter in the universe than all the normal matter combined!
WFIRST Will Escalate the Search
One of our next major space telescopes, the Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST), will take these gravitational lensing observations to the next level. WFIRST will be sensitive enough to use weak gravitational lensing to see how clumps of dark matter warp the appearance of distant galaxies. By observing lensing effects on this small scale, scientists will be able to fill in more of the gaps in our understanding of dark matter.
WFIRST will observe a sky area 100 times larger than Hubble does, but with the same awesome image quality. WFIRST will collect so much data in its first year that it will allow scientists to conduct in-depth studies that would have taken hundreds of years with previous telescopes.

WFIRST’s weak gravitational lensing observations will allow us to peer even further back in time than Hubble is capable of seeing. Scientists believe that the universe’s underlying dark matter structure played a major role in the formation and evolution of galaxies by attracting normal matter. Seeing the universe in its early stages will help scientists unravel how it has evolved over time and possibly provide clues to how it may continue to evolve. We don’t know what the future will hold, but WFIRST will help us find out.

This science is pretty mind-bending, even for scientists. Learn more as our current and future telescopes plan to help unlock these mysteries of the universe...
Hubble: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html WFIRST: https://wfirst.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Do We Learn About a Planet’s Atmosphere?
The first confirmation of a planet orbiting a star outside our solar system happened in 1995. We now know that these worlds – also known as exoplanets – are abundant. So far, we’ve confirmed more than 4000. Even though these planets are far, far away, we can still study them using ground-based and space-based telescopes.
Our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope will study the atmospheres of the worlds in our solar system and those of exoplanets far beyond. Could any of these places support life? What Webb finds out about the chemical elements in these exoplanet atmospheres might help us learn the answer.
How do we know what’s in the atmosphere of an exoplanet?
Most known exoplanets have been discovered because they partially block the light of their suns. This celestial photo-bombing is called a transit.

During a transit, some of the star's light travels through the planet's atmosphere and gets absorbed.

The light that survives carries information about the planet across light-years of space, where it reaches our telescopes.
(However, the planet is VERY small relative to the star, and VERY far away, so it is still very difficult to detect, which is why we need a BIG telescope to be sure to capture this tiny bit of light.)
So how do we use a telescope to read light?

Stars emit light at many wavelengths. Like a prism making a rainbow, we can separate light into its separate wavelengths. This is called a spectrum. Learn more about how telescopes break down light here.

Visible light appears to our eyes as the colors of the rainbow, but beyond visible light there are many wavelengths we cannot see.
Now back to the transiting planet...
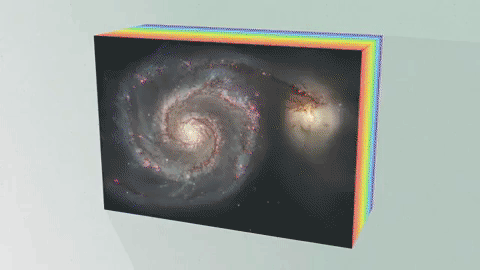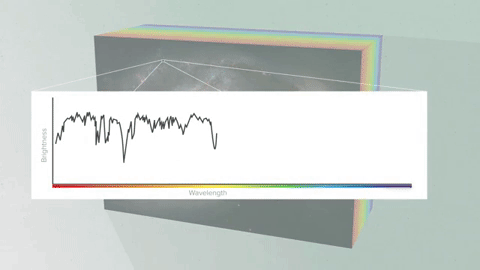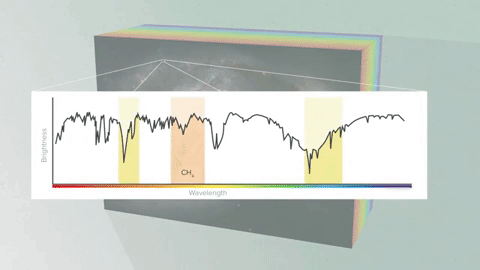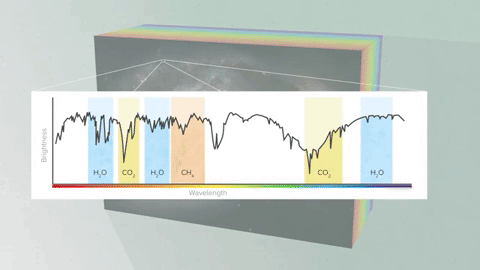
As light is traveling through the planet's atmosphere, some wavelengths get absorbed.

Which wavelengths get absorbed depends on which molecules are in the planet's atmosphere. For example, carbon monoxide molecules will capture different wavelengths than water vapor molecules.

So, when we look at that planet in front of the star, some of the wavelengths of the starlight will be missing, depending on which molecules are in the atmosphere of the planet.

Learning about the atmospheres of other worlds is how we identify those that could potentially support life...

...bringing us another step closer to answering one of humanity's oldest questions: Are we alone?

Watch the full video where this method of hunting for distant planets is explained:
To learn more about NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, visit the website, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Text and graphics credit Space Telescope Science Institute
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How Do Space Telescopes Break Down Light?
Space telescopes like Hubble and our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope use light not only to create images, but can also break light down into individual colors (or wavelengths). Studying light this way can give us a lot of detail about the object that emitted that light. For example, studying the components of the light from exoplanets can tell us about its atmosphere’s color, chemical makeup, and temperature. How does this work?
Remember the primary colors you learned about in elementary school?
Those colors are known as the pigment or subtractive colors. Every other color is some combination of the primary colors: red, yellow, and blue.

Light also has its own primary colors, and they work in a similar way. These colors are known as additive or light colors.

TVs make use of light’s colors to create the pictures we see. Each pixel of a TV screen contains some amount of red, green and blue light. The amount of each light determines the overall color of the pixel. So, each color on the TV comes from a combination of the primary colors of light: red, green and blue.

Space telescope images of celestial objects are also a combination of the colors of light.

Every pixel that is collected can be broken down into its base colors. To learn even more, astronomers break the red, green and blue light down into even smaller sections called wavelengths.
This breakdown is called a spectrum.
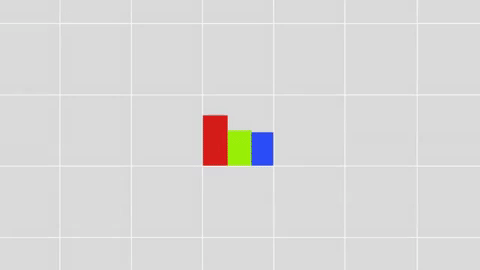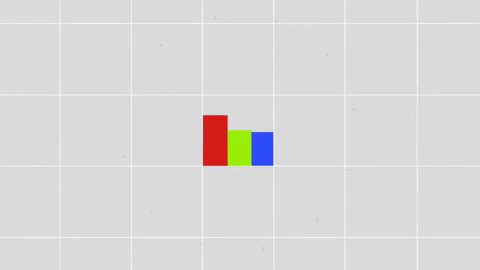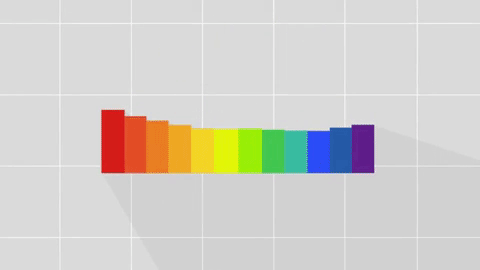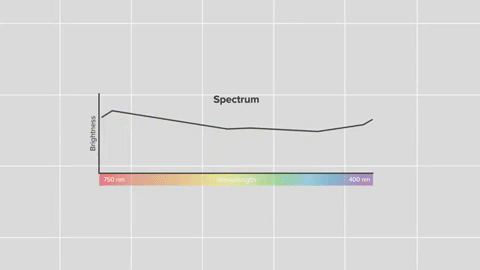
With the right technology, every pixel of light can also be measured as a spectrum.
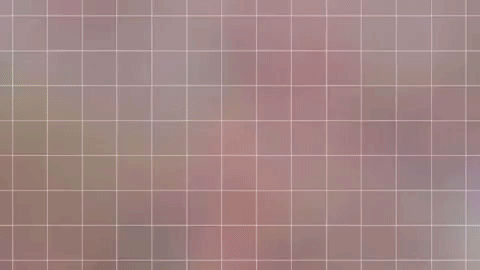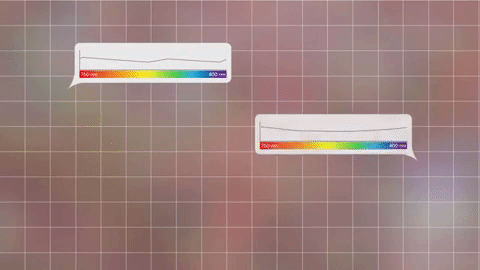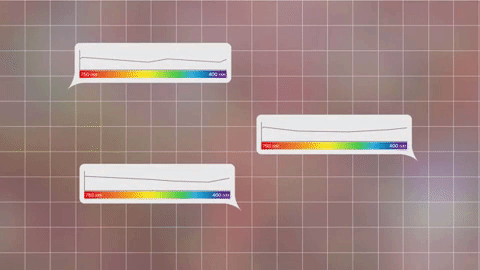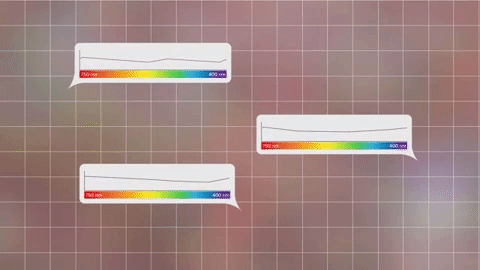
Images show us the big picture, while a spectrum reveals finer details. Astronomers use spectra to learn things like what molecules are in planet atmospheres and distant galaxies.
An Integral Field Unit, or IFU, is a special tool on the James Webb Space Telescope that captures images and spectra at the same time.
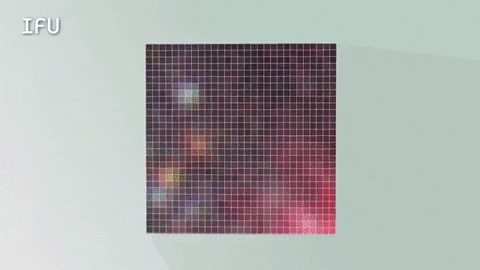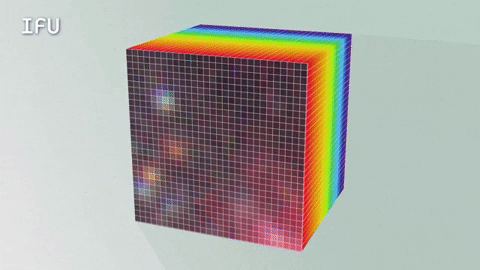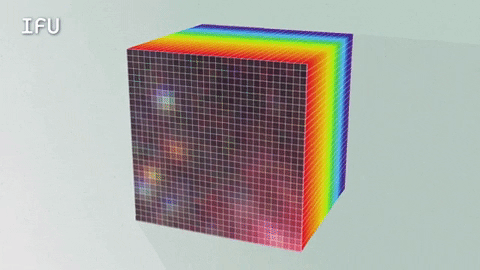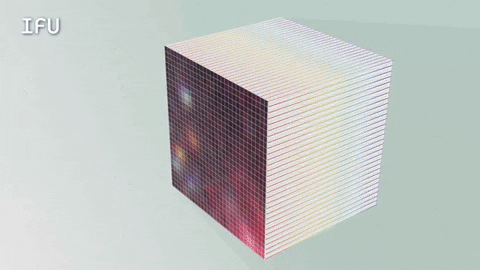
The IFU creates a unique spectrum for each pixel of the image the telescope is capturing, providing scientists with an enormous amount of valuable, detailed data. So, with an IFU we can get an image, many spectra and a better understanding of our universe.
Watch the full video where this method of learning about planetary atmospheres is explained:
The James Webb Space Telescope is our upcoming infrared space observatory, which will launch in 2021. It will spy the first galaxies that formed in the universe and shed light on how galaxies evolve, how stars and planetary systems are born and tell us about potentially habitable planets around other stars.
To learn more about NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, visit the website, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Text and graphics credit: Space Telescope Science Institute
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.