Your gateway to endless inspiration
Astronauts - Blog Posts
Welcome Home HERA Mission XVII!
With the Human Exploration Research Analog (HERA) habitat, we complete studies to prepare us for exploration to asteroids, Mars, and the Moon… here on Earth! The studies are called analogs, and they simulate space missions to study how different aspects of deep space affect humans. During a HERA mission, the crew (i.e., the research participants) live and work very much as astronauts do, with minimal contact with anyone other than Mission Control for 45 days.
The most recent study, Mission XVII, just “returned to Earth” on June 18. (i.e., the participants egressed, or exited the habitat at our Johnson Space Center in Houston after their 45-day study.) We talked with the crew, Ellie, Will, Chi, and Michael, about the experience. Here are some highlights!
Why did you decide to participate in HERA Mission XVII?

HERA Mission VXII participants (from left to right) Ellie, Will, Chi, and Michael.
“My master’s is in human factors,” said Chi, who studies the interaction between humans and other systems at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University. “I figured this would be a cool way to study the other side of the table and actually participate in an analog.” For Michael, who holds a PhD in aerospace engineering and researches immunology and radio biology, it was an opportunity to experience life as an astronaut doing science in space. “I’ve flown [experiments] on the space station and shuttle,” he said. “Now I wanted to see the other side.” For Will, a geosciences PhD, it provided an opportunity to contribute to space exploration and neuroscience, which he considers two of the biggest fields with the most potential in science. “Here, we have this project that is the perfect intersection of those two things,” he said. And Ellie, a pilot in the Air Force, learned about HERA while working on her master’s thesis on Earth and space analogs and how to improve them for deep-space studies. “A lot of my interests are similar to Chi’s,” she said. “Human factors and physiological aspects are things that I find very fascinating.”
NASA missions all have patches, and HERA Mission XVII is no different. Did you get to design your patch?

HERA Mission VXII patch, which reads “May the Force be with you” in Latin and features Star Wars iconography. It’s a reference to the mission’s start date, May 4th aka Star Wars Day!
“We did!” They said …with a little the help from Michael’s brother, who is a designer. He drew several different designs based on the crew’s ideas. They picked one and worked together on tweaks. “We knew we were going [inside the habitat] on May Fourth,” Michael said. “We knew it would be Star Wars Day. So we did a Star Wars theme.” The patch had to come together fairly quickly though, since a Star Wars Day “launch” wasn’t the initial plan. “We were supposed to start two weeks earlier,” Ellie said. “It just so happened the new start date was May the Fourth!” Along with the Star Wars imagery, the patch includes a hurricane symbol, to pay tribute to hurricane Harvey which caused a previous crew to end their mission early, and an image of the HERA habitat. Will joked that designing the patch was “our first team task.”
How much free time did you have and what did you do with it?

HERA Mission XVII crew looking down the ladders inside the habitat.
“It was a decent amount,” Michael said. “I could have used more on the harder days, but in a way it’s good we didn’t have more because it’s harder to stay awake when you have nothing to do.” (The mission included a sleep reduction study, which meant the crew only got five hours of sleep a night five days a week.) “With the time I did have, I read a lot,” he said. He also drew, kept a journal, and “wrote bad haikus.” Because of the sleep study, Ellie didn’t read as much. “For me, had I tried to read or sit and do anything not interactive, I would have fallen asleep,” she said.

The crew’s art gallery, where they hung drawing and haikus they wrote.
Journaling and drawing were popular ways to pass the time. “We developed a crew art gallery on one of the walls,” Will said. They also played board games—in particular a game where you score points by making words with lettered tiles on a 15×15 grid. (Yes that one!) “Playing [that game] with two scientists wasn’t always fun though,” Ellie joked, referencing some of the more obscure vocabulary words Will and Michael had at the ready. “I was like, ‘What does that word mean?’ ‘Well that word means lava flow,” she said laughing. (The rest of the crew assured us she fared just fine.)
Chi tried reading, but found it difficult due to the dimmed lights that were part of an onboard light study. She took on a side project instead: 1000 paper cranes. “There is a story in Japan—I’m half Japanese—that if you make a 1000 cranes, it’s supposed to grant you a wish,” she said. She gave hers to her grandmother.

The whole crew having dinner together on “Sophisticated Saturdays!” From left to right: Will, Ellie, Chi, and Michael. They’re wearing their Saturday best, which includes the usual research equipment.
On weekends, the crew got eight hours of sleep, which they celebrated with “Sophisticated Saturdays!” “Coming in, we all brought an outfit that was a little fancy,” Ellie said. (Like a tie, a vest, an athletic dress—that kind of thing.) “We would only put it on Saturday evenings, and we’d have dinner on the first level at the one and only table we could all sit at and face each other,” she said. “We would pretend it was a different fancy restaurant every week.”

The table set for a “civilized” Saturday dinner. Once the crew’s hydroponics grew, they were able to add some greenery to the table.
“It was a way to feel more civilized,” Will said, who then offered another great use of their free time: establishing good habits. “I would use the free time to journal, for example. I’d just keep it up every day. That and stretching. Hydrating. Flossing.”
Like real astronauts, you were in contact with Mission Control and further monitored by HERA personnel. Was it weird being on camera all the time?

HERA personnel and the monitors they use for a typical HERA mission.
“I was always aware of it,” Michael said, “but I don’t think it changed my behavior. It’s not like I forgot about it. It was always there. I just wasn’t willing to live paranoid for 45 days.” Ellie agreed. “It was always in the back of my mind,” she said, further adding that they wore microphones and various other sensors. “We were wired all the time,” she said.
After the study, the crew met up with the people facilitating the experiments, sometimes for the first time. “It was really fun to meet Mission Control afterwards,” Will said. “They had just been this voice coming from the little boxes. It was great getting to meet them and put faces to the voices,” he said. “Of course, they knew us well. Very well.”
For more information on HERA, visit our analogs homepage.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Exploring an Asteroid Without Leaving Earth
This 45 day mission – which began May 5, 2018 and ends today, June 18 – will help our researchers learn how isolation and close quarters affect individual and group behavior. This study at our Johnson Space Center prepares us for long duration space missions, like a trip to an asteroid or even to Mars.

The Human Research Exploration Analog (HERA) that the crew members will be living in is one compact, science-making house. But unlike in a normal house, these inhabitants won’t go outside for 45 days. Their communication with the rest of planet Earth will also be very limited, and they won’t have any access to internet. So no checking social media, kids!
The only people they will talk with regularly are mission control and each other.

The HERA XVII crew is made up of 2 men and 2 women, selected from the Johnson Space Center Test Subject Screening (TSS) pool. The crew member selection process is based on a number of criteria, including criteria similar to what is used for astronaut selection. The four would-be astronauts are:
William Daniels
Chiemi Heil
Eleanor Morgan
Michael Pecaut

What will they be doing?
The crew are going on a simulated journey to an asteroid, a 715-day journey that we compress into 45 days. They will fly their simulated exploration vehicle around the asteroid once they arrive, conducting several site surveys before 2 of the crew members will participate in a series of virtual reality spacewalks.

They will also be participating in a suite of research investigations and will also engage in a wide range of operational and science activities, such as growing and analyzing plants and brine shrimp, maintaining and “operating” an important life support system, exercising on a stationary bicycle or using free weights, and sharpening their skills with a robotic arm simulation.

During the whole mission, they will consume food produced by the Johnson Space Center Food Lab – the same food that the astronauts enjoy on the International Space Station – which means that it needs to be rehydrated or warmed in a warming oven.
This simulation means that even when communicating with mission control, there will be a delay on all communications ranging from 1 to 5 minutes each way.
A few other details:
The crew follows a timeline that is similar to one used for the space station crew.
They work 16 hours a day, Monday through Friday. This includes time for daily planning, conferences, meals and exercise.
Mission: May 5 - June 18, 2018

But beware! While we do all we can to avoid crises during missions, crews need to be able to respond in the event of an emergency. The HERA crew will conduct a couple of emergency scenario simulations, including one that will require them to respond to a decrease in cabin pressure, potentially finding and repairing a leak in their spacecraft.
Throughout the mission, researchers will gather information about living in confinement, teamwork, team cohesion, mood, performance and overall well-being. The crew members will be tracked by numerous devices that each capture different types of data.
Learn more about the HERA mission HERE.
Explore the HERA habitat via 360-degree videos HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

We asked real life astronauts YOUR questions! Was your submission sent to space?
Astronauts Drew Feustel & Ricky Arnold recently recorded answers to your questions in a Video Answer Time session. We collected your questions and sent them to space to be answered by the astronauts on Friday, May 18. We recorded their answers and will post them tomorrow, May 30, here on our Tumblr.
Was your question selected to be sent to the International Space Station? Check our Tumblr tomorrow, starting at noon EDT to find out!
About the astronauts:
Andrew J. Feustel was selected by NASA in 2000. He has been assigned to Expedition 55/56, which launched in March 2018. The Lake Orion, Michigan native has a Ph.D. in the Geological Sciences, specializing in Seismology, and is a veteran of two spaceflights. Follow Feustel on Twitter and Instagram.
Richard R. Arnold II was selected as an astronaut by NASA in May 2004. The Maryland native worked in the marine sciences and as a teacher in his home state, as well as in countries such as Morocco, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia. Follow Arnold on Twitter and Instagram.
Don’t forget check our Tumblr tomorrow at noon EDT to see if your question was answered by real-life astronauts in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Ever want to ask a real life astronaut a question? Here’s your chance!
Astronauts Drew Feustel & Ricky Arnold will be taking your questions in a Video Answer Time session. We’ll collect your questions and send them to space to be answered by the astronauts on Friday, May 18. We’ll record their answers and post them on Wednesday, May 23 here on NASA’s Tumblr. Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Andrew J. Feustel was selected by NASA in 2000. He has been assigned to Expedition 55/56, which launched in March 2018. The Lake Orion, Michigan native has a Ph.D. in the Geological Sciences, specializing in Seismology, and is a veteran of two spaceflights. Follow Feustel on Twitter and Instagram.
Richard R. Arnold II was selected as an astronaut by NASA in May 2004. The Maryland native worked in the marine sciences and as a teacher in his home state, as well as in countries such as Morocco, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia. Follow Arnold on Twitter and Instagram.
And don’t forget to submit your questions by 5 p.m. EDT on Tuesday, May 15 at http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Exploring an Asteroid Without Leaving Earth
This 45 day mission – which begins Feb. 1, 2018 – will help our researchers learn how isolation and close quarters affect individual and group behavior. This study at our Johnson Space Center prepares us for long duration space missions, like a trip to an asteroid or even to Mars.

The Human Research Exploration Analog (HERA) that the crew members will be living in is one compact, science-making house. But unlike in a normal house, these inhabitants won’t go outside for 45 days. Their communication with the rest of planet Earth will also be very limited, and they won’t have any access to internet. So no checking social media, kids!
The only people they will talk with regularly are mission control and each other.

The HERA XVI crew is made up of 2 men and 2 women, selected from the Johnson Space Center Test Subject Screening (TSS) pool. The crew member selection process is based on a number of criteria, including criteria similar to what is used for astronaut selection. The four would-be astronauts are:
Kent Kalogera
Jennifer Yen
Erin Hayward
Gregory Sachs
What will they be doing?
The crew are going on a simulated journey to an asteroid, a 715-day journey that we compress into 45 days. They will fly their simulated exploration vehicle around the asteroid once they arrive, conducting several site surveys before 2 of the crew members will participate in a series of virtual reality spacewalks.

They will also be participating in a suite of research investigations and will also engage in a wide range of operational and science activities, such as growing and analyzing plants and brine shrimp, maintaining and “operating” an important life support system, exercising on a stationary bicycle or using free weights, and sharpening their skills with a robotic arm simulation.

During the whole mission, they will consume food produced by the Johnson Space Center Food Lab – the same food that the astronauts enjoy on the International Space Station – which means that it needs to be rehydrated or warmed in a warming oven.
This simulation means that even when communicating with mission control, there will be a delay on all communications ranging from 1 to 5 minutes each way.
A few other details:
The crew follows a timeline that is similar to one used for the space station crew.
They work 16 hours a day, Monday through Friday. This includes time for daily planning, conferences, meals and exercise.
Mission: February 1, 2018 - March 19, 2018

But beware! While we do all we can to avoid crises during missions, crews need to be able to respond in the event of an emergency. The HERA crew will conduct a couple of emergency scenario simulations, including one that will require them to respond to a decrease in cabin pressure, potentially finding and repairing a leak in their spacecraft.
Throughout the mission, researchers will gather information about living in confinement, teamwork, team cohesion, mood, performance and overall well-being. The crew members will be tracked by numerous devices that each capture different types of data.
Learn more about the HERA mission HERE.
Explore the HERA habitat via 360-degree videos HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Human Expansion Across Solar System
On this day in 1972, two NASA astronauts landed on the Moon. Now, 45 years later, we have been instructed to return to the lunar surface.
Today at the White House, President Trump signed the Space Policy Directive 1, a change in national space policy that provides for a U.S.-led program with private sector partners for a human return to the Moon, followed by missions to Mars and beyond.

Among other dignitaries on hand for the signing, were NASA astronauts Sen. Harrison “Jack” Schmitt, Buzz Aldrin, Peggy Whitson and Christina Koch.
Schmitt landed on the moon 45 years to the minute that the policy directive was signed as part of our Apollo 17 mission, and is the most recent living person to have set foot on our lunar neighbor.

Above, at the signing ceremony instructing us to send humans back to the lunar surface, Schmitt shows First Daughter Ivanka Trump the Moon sample he collected in 1972.
The effort signed today will more effectively organize government, private industry and international efforts toward returning humans on the Moon, and will lay the foundation that will eventually enable human exploration of Mars.
To learn more, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/new-space-policy-directive-calls-for-human-expansion-across-solar-system
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What’s That in the Night Sky?
The night sky has really been showing off lately. During the past week, we’ve had the chance to see some amazing sights by simply just looking up!
On Wednesday, Dec. 29, we were greeted by a flyby of the International Space Station over much of the east coast.
When the space station flies overhead, it’s usually easy to spot because it’s the third brightest object in the night sky. You can even enter your location into THIS website and get a list of dates/times when it will be flying over you!
One of our NASA Headquarters Photographers ventured to the Washington National Cathedral to capture the pass in action.

Then, on Saturday, Dec. 2, just one day before the peak of this month’s supermoon, the space station was seen passing in front of the Moon.
Captured by another NASA HQ Photographer, this composite image shows the space station, with a crew of six onboard, as its silhouette transits the Moon at roughly five miles per second.

Here’s an animated version of the transit.

To top off all of this night sky greatness, are these beautiful images of the Dec. 3 supermoon. This marked the first of three consecutive supermoons taking the celestial stage. The two others will occur on Jan. 1 and Jan. 31, 2018.

A supermoon occurs when the moon’s orbit is closest to Earth at the same time that it is full.

Are you this pilot? An aircraft taking off from Ronald Reagan National Airport is seen passing in front of the Moon as it rose on Sunday.
Learn more about the upcoming supermoons:
To learn more about what you can expect to spot in the sky this month, visit: https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/news/2017/12/04/whats-up-december-2017
Discover when the International Space Station will be visible over your area by visiting: https://spotthestation.nasa.gov/
Learn more about our Moon at: https://moon.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Let’s Talk About Food...in Space!
It’s Thanksgiving time...which means you’re probably thinking about food...
Ever wonder what the astronauts living and working on the International Space Station eat during their time 250 miles above the Earth? There’s no microwave, but they get by using other methods.
Here are some fun facts about astronaut food…

Astronauts are assigned their own set of silverware to use during their mission (they can keep it afterward too). Without a dishwasher in orbit, they use special wipes to sterilize their set between uses, but it’s still better for everyone if they keep track of and use their own! So many sets of silverware were ordered during the space shuttle program that crews on the space station today still use silverware engraved with the word “shuttle” on them! So #retro.

You probably know that astronauts use tortillas instead of bread to avoid crumbs floating everywhere. Rodolfo Neri Vela, a payload specialist from Mexico, who flew on the space shuttle in 1985, introduced tortillas to the space food system. Back then, we would buy fresh tortillas the day before launch to send on the 8-10 day space shuttle missions.

We then learned how to reduce the water activity when formulating tortillas, which coupled with the reduction of oxygen during packaging would prevent the growth of mold and enable them to last for longer shuttle missions. Now, we get tortillas from the military. In August 2017, acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot ate a meal that included tortillas from 2015!

Our food menu is mostly all made from scratch so it can meet the requirements of the nutrition team and ensure astronauts eat enough fruits and vegetables. The space station is stocked with a standard menu that includes a mix of the more than 200 food and drink options available. This ensures lots of variety for the station crews but not too many of each individual item.

The food is packaged into bulk overwrap bags, referred to as BOBs, which are packed into cargo transfer bags for delivery to the space station. Each astronaut also gets to bring nine personalized BOBs for a mission, each containing up to 60 food and drink options so they can include more of their favorites – or choose to send a few specific items for everyone to share on a particular holiday like Thanksgiving. As a result, the crew members often share and swap their food to get more variety. Astronauts also can include any food available at the grocery store as long as it has an 18-month shelf life at room temperature and meets the microbiological requirements.

Fresh fruit and vegetables are a special treat for astronauts, so nearly every cargo resupply mission includes fresh fruit and veggies – and sometimes ice cream!

The Dragon spacecraft has freezers to bring science samples back to Earth. If there is space available on its way to orbit, the ground crew may fill the freezer with small cups of ice cream or ice cream bars.

Some food arrives freeze-dried, and the astronauts rehydrate it by inserting a specific amount of hot or ambient water from a special machine.
Other food comes ready to eat but needs to be reheated, which crew members do on a hot-plate like device. We recently also sent an oven style food warmer to station for the crew to use. And of course, some food like peanuts just get packaged for delivery and are ready to eat as soon as the package is opened!

Our nutritional biochemists have discovered that astronauts who eat more fish in space lost less bone, which is one of the essential problems for astronauts to overcome during extended stays in space. In the limited area aboard the space shuttle, not all crew members loved it when their coworkers ate the (aromatic) fish dishes, but now that the space station is about the size of a six-bedroom house, that’s not really a problem.

Astronauts on station have had the opportunity to grow (and eat!) a modest amount of fresh vegetables since the first lettuce harvest in August 2015, with new crops growing now and more coming soon. Crew members have been experimenting using the Veggie growth chamber, and soon plant research will also occur in the new Advanced Plant Habitat, which is nearly self-sufficient and able to control every aspect of the plant environment!
Growing food in space will be an important component of future deep space missions, and our nutritionists are working with these experiments to ensure they also are nutritious and safe for the crew to eat.
Thanksgiving in Space

The crew on the space station will enjoy Thanksgiving together. Here’s a look at their holiday menu:
Turkey
Mashed Potatoes
Cornbread Stuffing
Candied Yams
Cran-Apple Dessert
Learn more about growing food on the space station HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Resupply Mission Brings Mealworms and Mustard Seeds to Space Station
Orbital ATK will launch its Cygnus cargo spacecraft to the International Space Station on November 11, 2017 from Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. It will be packed with cargo and scientific experiments for the six humans currently living and working on the orbiting laboratory.

The cargo spacecraft is named the S.S. Gene Cernan after former NASA astronaut Eugene Cernan, who is the last man to have walked on the moon.

Here are some of the really neat science and research experiments that will be delivered to the station:
What’s Microgravity Got to do with Bacterial Antibiotics?
Antibiotic resistance could pose a danger to astronauts, especially since microgravity has been shown to weaken human immune response. E. coli AntiMicrobial Satellite (EcAMSat) will study microgravity’s effect on bacterial antibiotic resistance.

Results from this experiment could help us determine appropriate antibiotic dosages to protect astronaut health during long-duration human spaceflight and help us understand how antibiotic effectiveness may change as a function of stress on Earth.
Laser Beams…Not on Sharks…But on a CubeSat
Traditional laser communication systems use transmitters that are far too large for small spacecraft. The Optical Communication Sensor Demonstration (OCSD) tests the functionality of laser-based communications using CubeSats that provide a compact version of the technology.

Results from OCSD could lead to improved GPS and other satellite networks on Earth and a better understanding of laser communication between small satellites in low-Earth orbit.
This Hybrid Solar Antenna Could Make Space Communication Even Better
As space exploration increases, so will the need for improved power and communication technologies. The Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray Antenna (ISARA), a hybrid power and communication solar antenna that can send and receive messages, tests the use of this technology in CubeSat-based environmental monitoring.

ISARA may provide a solution for sending and receiving information to and from faraway destinations, both on Earth and in space.
More Plants in Space!
Ready for a mouthful…The Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Microgravity via Rhizobium-Legume Symbiosis…aka the Biological Nitrogen Fixation experiment, will examine how low-gravity conditions affect the nitrogen fixation process of the Microclover legume (a plant in the pea family). Nitrogen fixation is a process where nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia. This crucial element of any ecosystem is also a natural fertilizer that is necessary for most types of plant growth.

This experiment could tell us about the space viability of the legume’s ability to use and recycle nutrients and give researchers a better understanding of this plant’s potential uses on Earth.
What Happens When Mealworms Live in Space?
Mealworms are high in nutrients and one of the most popular sources of alternative protein in developing countries. The Effects of Microgravity on the Life Cycle of Tenebrio Molitor (Tenebrio Molitor) investigation studies how the microgravity environment affects the mealworm life cycle.

In addition to alternative protein research, this investigation will provide information about animal growth under unique conditions.
Mustard Seeds in Microgravity
The Life Cycle of Arabidopsis thaliana in Microgravity experiment studies the formation and functionality of the Arabidopsis thaliana, a mustard plant with a genome that is fully mapped, in microgravity conditions.

The results from this investigation could contribute to an understanding of plant and crop growth in space.
Follow @ISS_Research on Twitter for more information about the science happening on space station.
Watch the launch live HERE on Nov. 11, liftoff is scheduled for 7:37 a.m. EDT!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Astronaut Candidates Report for Duty
Fourteen new Astronaut Candidates have reported to our Johnson Space Center in Houston for duty on Monday, Aug. 21! Two astronauts from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), along with our 12 new astronaut candidates arrived for their first day of work. We selected these 12 individuals from a record number of more than 18,000 applicants.

This excited group of outstanding individuals will begin 2 years of training, along with 2 Canadian astronauts, in 5 key areas before being assigned to a mission.
What 5 areas? Let’s take a look...
1. Operate in T-38 Jets

Astronauts must be able to safely operate in the T-38 jets as either a pilot or back seater.
2. Operate + Maintain the International Space Station

Astronauts learn to operate and maintain the complex systems aboard the International Space Station. Did you know they recycle their water there? Today’s coffee is...well, tomorrow’s coffee too.
3. Learn How to Spacewalk

Or should we say waterwalk? Astronauts demonstrate the skills to complete complex spacewalk tasks in our Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory. This 6.2 million gallon pool contains a mockup of the space station and is a close simulation to microgravity.
4. Learn to Operate a Robot

Astronauts train in Canada for 2 weeks to learn how to capture visiting vehicles and more with the space station’s Canadarm 2 robotic arm.
5. Learn a Foreign Language

Astronauts must be fluent in both English and Russian, the two official languages on the International Space Station.
But before they begin all this training...they had to report for duty...

This group reported for Johnson Space Center on eclipse day and was sworn in as NASA’s Astronaut Candidate Class of 2017.

They even got to experience the partial solar eclipse together, what a great first day!

Follow their training journey online by following @NASA_Astronauts on Twitter.
Get to know them better and watch their individual interviews here: go.nasa.gov/NewAstronauts.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Expedition 52 Begins Aboard Space Station
When humans launch to the International Space Station, they are members of expeditions. An expedition is long duration stay on the space station. The first expedition started when the crew docked to the station on Nov. 2, 2000.
Expedition 52 began in June 2017 aboard the orbiting laboratory and will end in September 2017.

FUN FACT: Each Expedition begins with the undocking of the spacecraft carrying the departing crew from the previous Expedition. So Expedition 52 began with the undocking of the Soyuz MS-03 spacecraft that brought Expedition 51 crew members Oleg Novitskiy and Thomas Pesquet back to Earth, leaving NASA astronauts Peggy Whitson and Jack Fischer and Roscosmos cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin aboard the station to await the arrival of the rest of the Expedition 52 crew in July.

This expedition includes dozens of out of this world science investigations and a crew that takes #SquadGoals to a whole new level.

Take a look below to get to know the crew members and some of the science that will occur during the space station’s 52nd expedition.
Crew

Fyodor Yurchikhin (Roscosmos) – Commander
Born: Batumi, Adjar ASSR, Georgian SSR Interests: collecting stamps and space logos, sports, history of cosmonautics and reading Spaceflights: STS-112, Exps. 15, 24/25, 36/37, 51 Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2o9PO9F

Jack Fischer (NASA) – Flight Engineer
Born: Louisville, Colorado. Interests: spending time with my family, flying, camping, traveling and construction Spaceflights: Expedition 51 Twitter: @Astro2Fish Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2o9FY7o

Peggy Whitson (NASA) – Flight Engineer
Born: Mount Ayr, Iowa Interests: weightlifting, biking, basketball and water skiing Spaceflights: STS-111, STS – 113, Exps. 5, 16, 50, 51, 52 Twitter: @AstroPeggy Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2rpL58x

Randolph Bresnik (NASA) – Flight Engineer
Born: Fort Knox, Kentucky Interests: travel, music, photography, weight training, sports, scuba diving, motorcycling, and flying warbirds Spaceflights: STS-129 and STS-135 Twitter: @AstroKomrade Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2rq5Ssm

Sergey Ryazanskiy (Roscosmos) – Flight Engineer
Born: Moscow, Soviet Union Interests: Numismatics, playing the guitar, tourism, sport games Spaceflights: Exps. 37/38 Twitter: @Ryazanskiy_ISS Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2rpXfOK

Paolo Nespoli (ESA) – Flight Engineer
Born: Milan, Italy Interests: scuba diving, piloting aircraft, assembling computer hardware, electronic equipment and computer software Spaceflights: STS-120, Exps. 26/27 Bio: https://go.nasa.gov/2rq0tlk
What will the crew be doing during Expedition 52?

In addition to one tentatively planned spacewalk, crew members will conduct scientific investigations that will demonstrate more efficient solar arrays, study the physics of neutron stars, study a new drug to fight osteoporosis and study the adverse effects of prolonged exposure to microgravity on the heart.

Roll-Out Solar Array (ROSA)
Solar panels are an efficient way to generate power, but they can be delicate and large when used to power a spacecraft or satellites. They are often tightly stowed for launch and then must be unfolded when the spacecraft reaches orbit.

The Roll-Out Solar Array (ROSA), is a solar panel concept that is lighter and stores more compactly for launch than the rigid solar panels currently in use. ROSA has solar cells on a flexible blanket and a framework that rolls out like a tape measure.
Neutron Star Interior Composition Explored (NICER)
Neutron stars, the glowing cinders left behind when massive stars explode as supernovas, are the densest objects in the universe, and contain exotic states of matter that are impossible to replicate in any ground lab.

The Neutron Star Interior Composition Explored (NICER) payload, affixed to the exterior of the space station, studies the physics of these stars, providing new insight into their nature and behavior.
Systemic Therapy of NELL-1 for Osteoporosis (Rodent Research-5)
When people and animals spend extended periods of time in space, they experience bone density loss. The Systemic Therapy of NELL-1 for osteoporosis (Rodent Research-5) investigation tests a new drug that can both rebuild bone and block further bone loss, improving health for crew members.

Fruit Fly Lab-02
Exposure to reduced gravity environments can result in cardiovascular changes such as fluid shifts, changes in total blood volume, heartbeat and heart rhythm irregularities, and diminished aerobic capacity. The Fruit Fly Lab-02 study will use the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) to better understand the underlying mechanisms responsible for the adverse effects of prolonged exposure to microgravity on the heart.

Watch their progress HERE!
Expedition 52 Mission Patch
Our planet is shown surrounded by an imaginary constellation shaped like a house, depicting the theme of the patch: “The Earth is our home.” It is our precious cradle, to be preserved for all future generations. The house of stars just touches the Moon, acknowledging the first steps we have already taken there, while Mars is not far away, just beyond the International Space Station, symbolized by the Roman numeral “LII,” signifying the expedition number.

The planets Saturn and Jupiter, seen orbiting farther away, symbolize humanity’s exploration of deeper space, which will begin soon. A small Sputnik is seen circling the Earth on the same orbit with the space station, bridging the beginning of our cosmic quest till now: Expedition 52 will launch in 2017, sixty years after that first satellite. Two groups of crew names signify the pair of Soyuz vehicles that will launch the astronauts of Expedition 52 to the Station.
Click here for more details about the expedition and follow @ISS_Research on Twitter to stay up to date on the science happening aboard YOUR orbiting laboratory!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Meet America’s new astronauts! These 12 humans have been selected as part of our 2017 astronaut class and will report for duty at our Johnson Space Center in August.
Get to know each of them here: https://nasa.tumblr.com/post/161552645129/meet-americas-newastronauts
Meet America’s #NewAstronauts
We’re so excited to introduce America’s new astronauts! After evaluating a record number of applications, we’re proud to present our 2017 astronaut class!

These 12 new astronaut candidates were chosen from more than 18,300 people who submitted applications from December 2015 to February 2016. This was more than double the previous record of 8,000 set in 1978.

Meet them…
Kayla Barron

This Washington native graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy with a Bachelor’s degree in Systems Engineering. A Gates Cambridge Scholar, Barron earned a Master’s degree in Nuclear Engineering from the University of Cambridge.
She enjoys hiking, backpacking, running and reading.
Zena Cardman

Zena is a native of Virginia and completed a Bachelor of Science degree in Biology and Master of Science degree in Marine Sciences at The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Her research has focused on microorganisms in subsurface environments, ranging from caves to deep sea sediments.
In her free time, she enjoys canoeing, caving, raising backyard chickens and glider flying.
Raja Chari

Raja is an Iowa native and graduated from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1999 with Bachelor’s degrees in Astronautical Engineering and Engineering Science. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology and graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has accumulated more than 2,000 hours of flight time in the F-35, F-15, F-16 and F-18 including F-15E combat missions in Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Matthew Dominick

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from the University of San Diego and a Master of Science degree in Systems Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School. He graduated from U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has more than 1,600 hours of flight time in 28 aircraft, 400 carrier-arrested landigns and 61 combat missions.
Bob Hines

Bob is a Pennsylvania native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from Boston University. He is a graduate of the U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School, where he earned a Master’s degree in Flight Test Engineering. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Alabama.
During the last five years, he has served as a research pilot at NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
Warren Hoburg

Nicknamed “Woody”, this Pennsylvania native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and a Doctorate in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from the University of California, Berkley.
He is an avid rock climber, moutaineer and pilot.
Jonny Kim

This California native trained and operated as a Navy SEAL, completing more than 100 combat operations and earning a Silver Star and Bronze Star with Combat “V”. Afterward, he went on to complete a degree in Mathematics at the University of San Diego and a Doctorate of Medicine at Harvard Medical School.
His interests include spending time with his family, volunteering with non-profit vertern organizations, academic mentoring, working out and learning new skills.
Robb Kulin

Robb is an Alaska native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Denver, before going on to complete a Master’s degree in Materials Science and a Doctorate in Engineering at the University of California, San Diego.
He is a private pilot and also enjoys playing piano, photography, packrafting, running, cycling, backcountry skiing and SCUBA diving.
Jasmin Moghbeli

This New York native earned a Bachlor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering with Information Technology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, followed by a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School.
She is also a distinguished graduate of the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School and has accumulated mofre than 1,600 hours of flight time and 150 combat missions.
Loral O’Hara

This Texas native earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering at the University of Kansas and a Master of Science degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Purdue University.
In her free time, she enjoys working in the garage, traveling, surfing, diving, flying, sailing, skiing, hiking/orienteering, caving, reading and painting.
Frank Rubio

Frank is a Florida native and graduated from the U.S. Military Academy and earned a Doctorate of Medicine from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences.
He is a board certified family physician and flight surgeon. At the time of his selection, he was serving in the 10th Special Forces Group (Airborne).
Jessica Watkins

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Geological and Environmental Sciences at Stanford University, and a Doctorate in Geology from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
She enjoys soccer, rock climbing, skiing and creative writing.

After completing two years of training, the new astronaut candidates could be assigned to missions performing research on the International Space Station, launching from American soil on spacecraft built by commercial companies, and launching on deep space missions on our new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Questions About the 2017 Astronaut Class
We will select between eight and 14 new astronaut candidates from among a record-breaking applicant class of more than 18,300, almost three times the number of applications the agency received in 2012 for the recent astronaut class, and far surpassing the previous record of 8,000 in 1978.

The candidates will be announced at an event at our Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas at 2 p.m. EDT on June 7. You can find more information on how to watch the announcement HERE.
1. What are the qualifications for becoming an astronaut?

Applicants must meet the following minimum requirements before submitting an application.
Bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution in engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science or mathematics.
Degree must be followed by at least 3 years of related, progressively responsible, professional experience or at least 1,000 hours of pilot-in-command time in jet aircraft
Ability to pass the NASA Astronaut physical.
For more information, visit: https://astronauts.nasa.gov/content/faq.htm
2. What have selections looked like in the past?

There have been 22 classes of astronauts selected from the original “Mercury Seven” in 1959 to the most recent 2017 class. Other notable classes include:
The fourth class in 1965 known as “The Scientists: because academic experience was favored over pilot skills.
The eighth class in 1978 was a huge step forward for diversity, featuring the first female, African American and Asian American selections.
The 16th class in 1996 was the largest class yet with 44 members – 35 U.S. astronauts and 9 international astronauts. They were selected for the frequent Space Shuttle flights and the anticipated need for International Space Station crewmembers.
The 21st class in 2013 was the first class to have 50/50 gender split with 4 female members and 4 male members.
3. What vehicles will they fly in?

They could be assigned on any of four different spacecraft: the International Space Station, our Orion spacecraft for deep space exploration or one of two American-made commercial crew spacecraft currently in development – Boeing’s CST-199 Starliner or the SpaceX Crew Dragon.
4. Where will they go?

These astronauts will be part of expanded crews aboard the space station that will significantly increase the crew time available to conduct the important research and technology demonstrations that are advancing our knowledge for missions farther into space than humans have gone before, while also returning benefits to Earth. They will also be candidates for missions beyond the moon and into deep space aboard our Orion spacecraft on flights that help pave the way for missions to Mars.
5. What will their roles be?

After completing two years of general training, these astronaut candidates will be considered full astronauts, eligible to be assigned spaceflight missions. While they wait for their turn, they will be given duties within the Astronaut Office at Johnson Space Center. Technical duties can range from supporting current missions in roles such as CAPCOM in Mission Control, to advising on the development of future spacecraft.
6. What will their training look like?

The first two years of astronaut candidate training will focus on the basic skills astronauts need. They’ll practice for spacewalks in Johnson’s 60-foot deep swimming pool, the Neutral Buoyancy Lab, which requires SCUBA certification. They’ll also simulate bringing visiting spacecraft in for a berthing to the space station using its robotic arm, Canadarm2, master the ins and outs of space station system and learn Russian.

And, whether they have previous experience piloting an aircraft of not, they’ll learn to fly our fleet of T-38s. In addition, they’ll perfect their expeditionary skills, such as leadership and fellowship, through activities like survival training and geology treks.
7. What kinds of partners will they work with?

They will join a team that supports missions going on at many different NASA centers across the country, but they’ll also interact with commercial partners developing spaceflight hardware. In addition, they will work with our international partners around the globe: ESA (the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and the Russian space agency, Roscosmos.
8. How does the selection process work?

All 18,353 of the applications submitted were reviewed by human resources experts to determine if they met the basic qualifications. Those that did were then each reviewed by a panel of about 50 people, made up primarily of current astronauts. Called the Astronaut Rating Panel, that group narrowed to applicants down to a few hundred of what they considered the most highly qualified individuals, whose references were then checked.

From that point, a smaller group called the Astronaut Selection Board brought in the top 120 applicants for an intense round of interviews and some initial medical screening tests. That group is further culled to the top 50 applicants afterward, who are brought back for a second round of interviews and additional screening. The final candidates are selected from that group.
9. How do they get notified?

Each applicant selected to become an astronaut receives a phone call from the head of the Flight Operations Directorate at our Johnson Space Center and the chief of the astronaut office. They’re asked to share the good news with only their immediate family until their selection has been officially announced.
10. How does the on boarding process work?

Astronaut candidates will report for duty at Johnson Space Center in August 2017, newly fitted flight suits in tow, and be sworn into civil service. Between their selection and their report for duty, they will make arrangements to leave their current positions and relocate with their family to Houston, Texas.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Training Requirements for New Astronauts
After evaluating a record number of applications, we will introduce our newest class of astronaut candidates on June 7!

Upon reporting to duty at our Johnson Space Center in Houston, the new astronaut candidates will complete two years of training before they are eligible to be assigned to a mission.
Here are the five training criteria they must check off to graduate from astronaut candidate to astronaut:
1. T-38 Jets

Astronauts have been training in T-38 jets for more than 35 years because the sleek, white jets require crew members to think quickly in dynamic situations and to make decisions that have real consequences. This type of mental experience is critical to preparing for the rigors of spaceflight. To check off this training criteria, astronaut candidates must be able to safely operate in the T-38 as either a pilot or back seater.
2. International Space Station Systems

We are currently flying astronauts to the International Space Station every few months. Astronauts aboard the space station are conducting experiments benefitting humanity on Earth and teaching us how to live longer in space. Astronaut candidates learn to operate and maintain the complex systems aboard the space station as part of their basic training.
3. Spacewalks

Spacewalks are the hardest thing, physically and mentally, that astronauts do. Astronaut candidates must demonstrate the skills to complete complex spacewalks in our Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (giant pool used to simulate weightlessness). In order to do so, they will train on the life support systems within the spacesuit, how to handle emergency situations that can arise and how to work effectively as a team to repair the many critical systems aboard the International Space Station to keep it functioning as our science laboratory in space.
4. Robotics

Astronaut candidates learn the coordinate systems, terminology and how to operate the space station’s robotic arm. They train in Canada for a two week session where they develop more complex robotics skills including capturing visiting cargo vehicles with the arm. The arm, built by the Canadian Space Agency, is capable of handling large cargo and hardware, and helped build the entire space station. It has latches on either end, allowing it to be moved by both flight controllers on the ground and astronauts in space to various parts of the station.
5. Russian Language

The official languages of the International Space Station are English and Russian, and all crewmembers – regardless of what country they come from – are required to know both. NASA astronauts train with their Russian crew mates and launch on the Russian Soyuz vehicle, so it makes sense that they should be able to speak Russian. Astronaut candidates start learning the language at the beginning of their training. They train on this skill every week, as their schedule allows, to keep in practice.
Now, they are ready for their astronaut pin!
After completing this general training, the new astronaut candidates could be assigned to missions performing research on the International Space Station, launching from American soil on spacecraft built by commercial companies, and launching on deep space missions on our new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket.

Watch the Astronaut Announcement LIVE!
We will introduce our new astronaut candidates at 2 p.m. EDT Wednesday, June 7, from our Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Watch live online at nasa.gov/live or on NASA’s Facebook Page.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Friday Stroll? How About a Spacewalk?
On Friday, May 12, NASA astronauts Peggy Whitson and Jack Fischer will venture outside the International Space Station, into the vacuum of space, for a spacewalk.

Space Fact: This will be the 200th spacewalk performed on the space station!
You can watch their entire 6.5 hour spacewalk live online! (Viewing info below!) To tell the two astronauts apart in their bulky spacewalk suits, Whitson will be wearing the suit with red stripes, while Jack Fischer will have white stripes.

Space Fact: The first-ever spacewalk on the International Space Station was performed on Dec. 7, 1998.
For Peggy, this will be her ninth spacewalk! She actually holds the record for most spacewalks by a female astronaut. For Fischer, this is his first time in space, and will be his first spacewalk. You can see from the below Tweet, he’s pretty excited!

Once both astronauts venture outside the Quest airlock, their tasks will focus on:
Replacing a large avionic box that supplies electricity and data connections to the science experiments
Replacing hardware stored outside the station
Specifically, the ExPRESS Carrier Avionics, or ExPCA will be replaced with a unit delivered to the station last month aboard the Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo spacecraft.

Ever wonder how astronauts prepare and practice for these activities? Think about it, wearing a bulky spacesuit (with gloves!), floating in the vacuum of space, PLUS you have to perform complex tasks for a period of ~6.5 hours!
In order to train on Earth, astronauts complete tasks in our Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL). It’s a gigantic pool with a full mock up of the International Space Station! Here’s a clip of astronauts practicing to install the ExPCA in that practice pool at Johnson Space Center in Houston.

In addition, Whitson and Fischer will install a connector that will route data to the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and help the crew determine the most efficient way to conduct future maintenance on the cosmic ray detector.

The astronauts will also install a protective shield on the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3, which was moved in March. This adapter will host a new international docking port for the arrival of commercial crew spacecraft.

Finally, the duo will rig a new high-definition camera and pair of wireless antennas to the exterior of the outpost.
Watch the Spacewalk Live!

Live coverage will begin at 6:30 a.m. EDT, with spacewalk activities starting at 8 a.m. EDT.
Stream the entire spacewalk live online at nasa.gov/live
OR
Watch live on the International Space Station Facebook page starting at 7:00 a.m. EDT
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

"A classic that I never get tired of: the orange solar panel in front of the blue–white background and the curvature of Earth" wrote astronaut Thomas Pesquet (@thom_astro) of the European Space Agency from aboard the International Space Station.
The space station serves as the world's leading laboratory for conducting cutting-edge microgravity research, and is the primary platform for technology development and testing in space to enable human and robotic exploration of destinations beyond low-Earth orbit, including Mars.
Credit: NASA/ESA
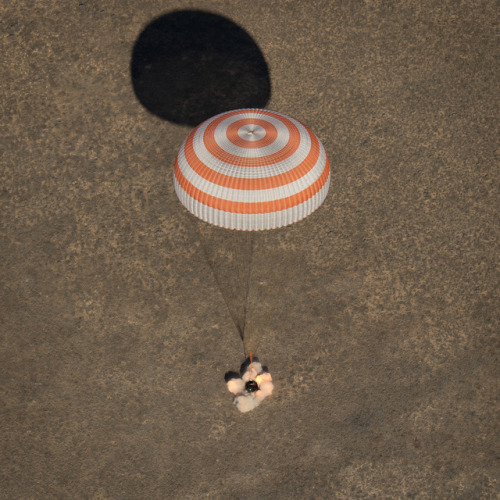

Touchdown!
A Soyuz spacecraft is seen as it lands with astronaut Shane Kimbrough of NASA and Russian Flight Engineers Sergey Ryzhikov and Andrey Borisenko near the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan on Monday, April 10. Kimbrough, Ryzhikov, and Borisenko are returning after 173 days in space onboard the International Space Station.
While living and working aboard the space station, the crew members contributed to hundreds of experiments in biology, biotechnology, physical science and Earth science aboard the world-class orbiting laboratory. For example, the Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells investigation had crew members observe cell growth and other characteristics in microgravity.
Results from this investigation could lead to the treatment of diseases and injury in space, and provide a way to improve stem cell production for medical therapies on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Spacewalk complete and new astronaut record set! Shane Kimbrough and Peggy Whitson of NASA successfully reconnected cables and electrical connections on an adapter-3 that will provide the pressurized interface between the station and the second of two international docking adapters to be delivered to the complex to support the dockings of U.S. commercial crew spacecraft in the future. The duo were also tasked with installing four thermal protection shields on the Tranquility module of the International Space Station.
Having completed her eighth spacewalk, Whitson now holds the record for the most spacewalks and accumulated time spacewalking by a female astronaut. Spacewalkers have now spent a total of 1,243 hours and 42 minutes outside the station during 199 spacewalks in support of assembly and maintenance of the orbiting laboratory.
Astronaut Thomas Pesquet of ESA posted this image and wrote, ' Shane and Peggy on their way to their first #spacewalk tasks.'
Credit: ESA/NASA
Put to the Test: Orion Service Module
Blasted with sound, shaken for hours and pyro detonated, the Orion Service Module Completes Ground Tests at our Glenn Research Center
We recently completed a structural integrity evaluation on the test version of the Orion service module at our Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. Designed to ensure the module can withstand launch atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the battery of tests was conducted in stages over a 16-month period.
The 13-ton European service module will power, propel and cool Orion, while supplying vital oxygen and water to its crew during future missions.
The Powerhouse: Space Launch System and Orion

Our Space Launch System is an advanced launch vehicle that will usher in a new era of human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit. SLS, with its unparalleled power and capabilities, will launch missions to explore deep-space destinations aboard our Orion spacecraft.

What is Orion? Named after one of the largest constellations in the night sky and drawing from more than 50 years of spaceflight research and development, the Orion spacecraft will be the safest, most advanced spacecraft ever built. It will be flexible and capable enough to take astronauts to a variety of deep destinations, including Mars.
Welcome to the Buckeye State

In November 2015, the full-sized test version of the Orion service module arrived at Cleveland Hopkins Airport aboard an Antonov AN-124. After being unloaded from one of the world’s largest transport aircraft, the module was shipped more than 50 miles by truck to Plum Brook for testing.
Spread Your Wings

The first step of the service module’s ground test journey at Plum Brook’s Space Power Facility, saw one of its 24-foot solar array wings deployed to verify operation of the power system. The test confirmed the array extended and locked into place, and all of the wing mechanisms functioned properly.
Can You Hear SLS Now?

The SLS will produce a tremendous amount of noise as it launches and climbs through our atmosphere. In fact, we’re projecting the rocket could produce up to 180 decibels, which is louder than 20 jet engines operating at the same time.
While at the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility, the service module was hit with more than 150 decibels and 20-10,000 hertz of sound pressure. Microphones were placed inside the test environment to confirm it matched the expected acoustic environment during launch.
After being blasted by sound, it was time to rock the service module, literally.
Shake Without the Bake
Launching atop the most powerful rocket ever built – we’re talking more than eight million pounds of thrust – will subject Orion to stresses never before experienced in spaceflight.
To ensure the launch doesn’t damage any vital equipment, the engineering team utilized the world’s most powerful vibration table to perform nearly 100 different tests, ranging from 2.5 Hz to 100 Hz, on the module in the summer of 2016.
Gotta Keep ‘Em Separated
The team then moved the Orion test article from the vibration table into the high bay for pyroshock tests, which simulated the shock the service module will experience as it separates from the SLS during launch.
Following the sound, vibration and separation tests, a second solar array wing deployment was conducted to ensure the wing continued to properly unfurl and function.
Headed South for the Summer

The ground test phase was another crucial step toward the eventual launch of Exploration Mission-1, as it validated extensive design prep and computer modeling, and verified the spacecraft met our safety and flight requirements.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Space & Football Facts You Probably Didn’t Know
There are more connections between space and football than you may have originally thought. Here are a few examples of how...
1. The International Space Station and a football field are basically the same size

Yes, that’s right! The International Space Station measures 357 feet end-to-end. That’s almost equivalent to the length of a football field including the end zones (360 feet).
2. It would take over 4,000 footballs to fill the Orion spacecraft

Our Orion spacecraft is being designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, like Mars! It will launch atop the most powerful rocket ever built, the Space Launch System rocket. If you were to fill the Orion spacecraft with footballs instead of crew members, you would fit a total of 4,625!
3. Our new Space Launch System rocket is taller than a football field is long

We’re building the most powerful rocket ever, the Space Launch System. At its full height it will stand 384 feet – 24 feet taller than a football field is long.
4. The crew living on space station will see the day begin and end…twice…during the Super Bowl

An average NFL game lasts more than three hours. Traveling at 17,500 mph, the crew on the space station will see two sunrises and two sunsets in that time…they see 16 sunrises and sunsets each day!
5. Playing football on Mars would be…lighter

On Mars, a football would weigh less than half a pound, while a 200-pund football player would weigh just about 75 pounds.
6. It would take over 3,000 hours for a football to reach the Moon

Talk about going long…if you threw a football to the Moon at 60 mph, the average speed of an NFL pass, it would take 3,982 hours, or 166 days, to get there. The quickest trip to the Moon was the New Horizons probe, which zipped pass the Moon in just 8 hours 35 minutes on its way to Pluto
7. The longest field goal kick in history would’ve been WAY easier to make on Mars

The longest field goal kick in NFL history is 64 yards. On Mars, at 1/3 the gravity of Earth, that same field goal, ignoring air resistance, could have been made from almost two football fields away (192 yards).
8. A quarterback would be able to throw even further on Mars

Aerodynamic drag doesn’t happen on Mars. With a very thin atmosphere and low gravity to drag the ball down, a quarterback could throw the football three times as far as he could on Earth. A receiver would have to be much further down the field to catch the throw
9. Football players and astronauts both need to exercise every day

Football players must be quick and powerful, honing the physical skills necessary for their unique positions. In space, maintaining physical fitness is a top priority, since astronauts will lose bone and muscle mass if they do not keep up their strength and conditioning.
10. Clear team communication is important on the football field AND in space

During football games, calling plays and relaying information from coaches on the sidelines or in the booth to players on the field is essential. Coaches communicate directly with quarterbacks and a defensive player between plays via radio frequencies. They must have a secure and reliable system that keeps their competitors from listening in and also keeps loud fan excitement from drowning out what can be heard. Likewise, reliable communication with astronauts in space and robotic spacecraft exploring far into the solar system is key to our mission success.
A radio and satellite communications network allows space station crew members to talk to the ground-based team at control centers, and for those centers to send commands to the orbital complex.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Back-to-Back Friday Spacewalks
On Friday, Jan. 6 and Friday, Jan. 13, astronauts on the International Space Station will step outside to perform spacewalks.

What’s a spacewalk? It’s any time an astronaut gets out of a vehicle or spacecraft while in space. It can also be called an EVA (extravehicular activity).
Astronauts go on spacewalks for many reasons. These activities allow crew members to work outside their spacecraft (in this case the space station).

So what specific tasks will astronauts perform in these two upcoming spacewalks? Let’s take a look…
Both spacewalks are being performed to upgrade the orbital outpost’s power system.

The crew members will install adapter plates and hook up electrical connections for six new lithium-ion batteries that were delivered to the station in December.

NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Peggy Whitson will perform the first spacewalk on Jan. 6. The work will continue Jan. 13 during the second spacewalk, which will be conducted by Kimbrough and ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet.

Prior to each spacewalk, the new batteries will be robotically extracted from a pallet to replace 12 older nickel-hydrogen batteries through a series of robotic operations.
Watch LIVE Spacewalk Coverage
Friday, Jan. 6 Coverage begins at 5:30 a.m. EST, with astronauts venturing outside at 7 a.m. Watch HERE
Friday, Jan. 13 Coverage begins at 5:30 a.m. EST, with astronauts venturing outside at 7 a.m. Watch HERE
Watch for more...
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Will We Safely Send the First Humans to the Red Planet?
We’ve been exploring the Red Planet for over 50 years -- Mariner 4 launched on this day (Nov. 28) in 1964 and took the first photos of Mars from space the following summer.

We first explored the surface 40 years ago (Viking, 1976) and have had a continuous scientific presence on Mars for nearly 20 years, starting with the landing of the Pathfinder lander and Sojourner rover on July 4, 1997.
We currently have three orbiters – MAVEN, MRO and Mars Odyssey – and two rovers – Curiosity and Opportunity – actively exploring Mars.
These robotic explorers have already taught us a lot about the Red Planet, and future missions will teach us even more about how humans can live and work on the surface.

After sending humans on space exploration missions for the last 50 years, we have gained the experience and knowledge to send the first people to Mars. We are working across all areas to prepare for that historic day and want to share our progress with you.
Building the ride to Mars: NASA’s Space Launch System.
Our ride to Mars, the Space Launch System, is being built right now to meet the challenges of exploring deep space. When it comes to our journey to Mars and beyond, there are no small steps. Our video series by the same name breaks down those steps to show how SLS will send missions to the Red Planet.

Living on the Space Station will help humans live safely on Mars.
New crew members of Expedition 50 will soon conduct more than 250 experiments on the International Space Station. More than 2,000 experiments have already been done!
Experiments in fields such as biology, Earth science, physical sciences and human research are helping us unlock the knowledge needed to enable humans to live in space for long durations. If you missed the recent launch, check out NASA TV for a replay.

Testing Orion helps crew live and work in space and get home safely.
Scheduled to launch atop the Space Launch System rocket for the first time in 2018, an uncrewed Orion will travel farther into space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever gone before. When Orion returns to Earth, splashing down into the Pacific Ocean, it will take a landing and recovery group to safely return the capsule and crew back to land. A variety of testing on the ground, including to structures and parachutes, is helping make sure Orion can safely carry crew to new destinations in the solar system.

In late October, this recovery group, including NASA’s Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, the U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force and contractor employees, completed its fifth successful practice run to recover Orion aboard the USS San Diego.

We're using high resolution imagery from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to learn more about potential landing sites for a human mission.
Who knows what surprises the Red Planet holds?
Our Curiosity Rover has discovered all kinds of interesting Mars features including meteorites. How do you learn more about a meteorite? Zap it with lasers, of course.

This golf-ball-sized, iron-nickel meteorite was recently found on Mars where ancient lakebed environments once existed. Named “Egg Rock” for the area in which it was found, it is the first meteorite to be examined using a laser-firing spectrometer.
By studying the conditions on Mars with vehicles like Curiosity, scientists are able to help prepare future astronauts to live on Mars.
How do you prepare the tallest rocket ever built for its first launch?
Another important component in successfully launching the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft on a Journey to Mars is the infrastructure work being done by our Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy Space Center.

While efforts at our Vehicle Assembly Building continue, we hope you’ll be making your plans to join us at the launch pad for the first flight of SLS with Orion in 2018!
Preparing for a human journey to Mars
The next Mars rover will launch in 2020, and will investigate a region of Mars where the ancient environment may have been favorable for microbial life, probing the Martian rocks for evidence of past life.

It will collect samples and cache them on the surface for potential return to Earth by a future mission. Mars 2020 will also conduct the first investigation into the usability and availability of Martian resources, including oxygen, in preparation for human missions.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Thanksgiving...in Space
Since 2000, humans have continuously lived and worked on the International Space Station. That means plenty of crew members have celebrated holidays off the Earth.

Although they’re observing the same holidays, they do so in a slightly different way because of the unique environment 250 miles above the Earth.
Consider the differences of living on Earth and in space…

Food scientists must develop foods that will be easier to handle and consume in an environment without gravity. The food must not require refrigeration and also provide the nutrition humans need to remain healthy.

Freeze drying food allows it to remain stable at room temperature, while also significantly reducing its weight.

Did you know that all the food sent to the space station is precooked? Sending precooked food means that it requires no refrigeration and is either ready to eat or can be prepared by simply adding water or by heating.

The only exception are the fruit and vegetables stowed in the fresh food locker. The food comes in either freeze-dried containers or thermostabilized pouches. If freeze-dried in a vacuum sealed package, the astronauts have a rehydration system in-flight, which they use restore moisture in their food. If thermostabilized, the packaging is designed to preserve the food similar to canned products, but instead in a flexible, multi-layered pouch.
So what will the space station crew eat this year (2016) for Thanksgiving?
Turkey
Cherry/Blueberry Cobbler
Candied Yams
Rehydratable Cornbread Dressing
Rehydratable Green Beans and Mushrooms
Rehydratable Mashed Potatoes
What are you bringing to Thanksgiving on Earth this year? Treat your family and friends astronaut-style with this cornbread dressing recipe straight out of our Space Food Systems Laboratory…no freeze drying required!

For spaceflight preparation:
Baked dressing is transferred to metal tray and freeze-dried accordingly. One serving of cornbread dressing shall weigh approximately 145 g prior to freeze-drying and 50 g after freeze-drying.
Learn more about our Food Systems Laboratory in this Facebook Live video: https://www.facebook.com/ISS/videos/1359709837395277/
Happy Thanksgiving!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Want to Send Your Art to the International Space Station?!
For children ages 4-12, we’re hosting an art contest! Get the details:





We are working with Boeing and SpaceX to build human spaceflight systems, like rockets and spacecraft, to take astronauts to the International Space Station. These companies will fly astronauts to orbit around Earth while we focus on plans to explore deeper into our solar system.

Get out your art supplies and use your creative imagination to show us the present and future of traveling in space!

There are no grocery stores in space, but there may soon be farms. Very small farms that are important to a crew conducting a mission to deep space. That’s because our astronauts will need to grow some of their own food. Researchers on Earth and astronauts on the International Space Station are already showing what is needed to grow robust plants in orbit.

What would you take to space? Astronaut Suni Williams took a cutout of her dog, Gorbie, on her first mission to the International Space Station.

Kids 4 to 12, draw what you would take and enter it in our Children’s Artwork Calendar contest! Your entry could be beamed to the space station!


Go to http://go.nasa.gov/2fvRLNf for more information about the competition’s themes, rules and deadlines plus the entry form.


Get your parent's permission, of course!
Email your entry form and drawing to us at: ksc-connect2ccp@mail.nasa.gov

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Vote While You float: An Astronaut Voting Story
With the excitement of getting to the polls on Election Day many people will have a hard time keeping their feet on the ground, but astronauts who vote literally have to strap themselves down so they don’t float away.
Astronauts orbit the Earth at 17,000 miles per hour, but thanks to a bill passed by Texas legislatures in 1997 that put in place technical voting procedure for astronauts – nearly all of whom live in Texas – they also have the ability to vote from space!

Image Kjell Lindgren released on social media of the US flag floating in the Cupola module (11/12/2015)
For astronauts, the voting process starts a year before launch, when astronauts are able to select which elections (local/state/federal) that they want to participate in while in space. Then, six months before the election, astronauts are provided with a standard form: the “Voter Registration and Absentee Ballot Request – Federal Post Card Application.”
‘Space voting’ was first used the same year it was implemented in 1997. NASA astronaut David Wolf became the first American to vote in space while on the Russian Mir Space Station.

STS-86 crewmember David Wolf, the first American to vote in space, relaxes in the Spacehab module while Space Shuttle Atlantis was docked to Mir (10/16/1997)
While astronauts don’t have to wait in line for his ballot like the rest of us, there is one disadvantage to voting in space: they miss out on the highly coveted “I Voted” sticker.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
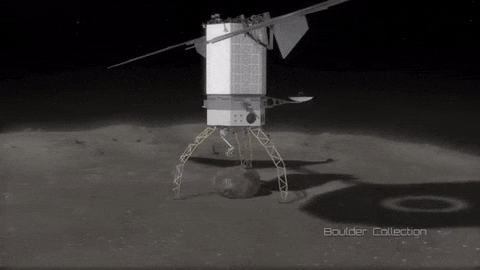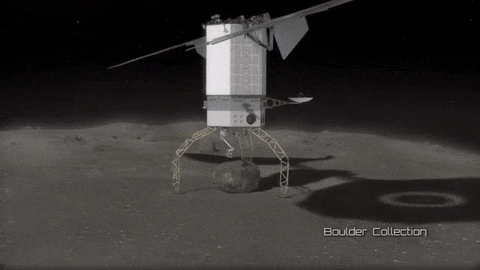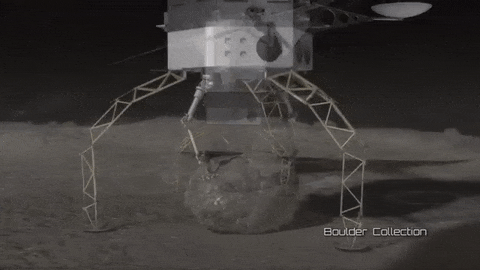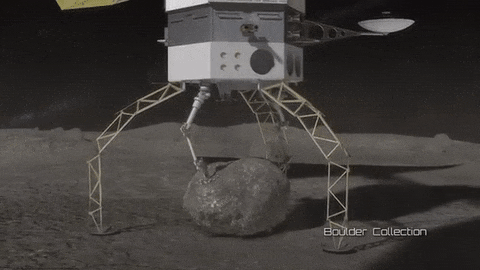
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Another Station Upgrade:
Spacewalkers Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins to install new TV cameras
On Thursday, Sept. 1, U.S. astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will conduct the station’s 195th American spacewalk. As part of their activities, the pair will install the first of several enhanced high-definition television cameras that will monitor activities outside the station, including the comings and goings of visiting cargo and crew vehicles

Working on the station’s backbone, or truss, Williams and Rubins will retract a thermal radiator that is part of the station’s cooling system.

As was the case for their first spacewalk together on Aug. 19, Williams will be designated as extravehicular crew member 1 (EV1), wearing a spacesuit with a red stripe, while Rubins will be EV2, wearing a suit with no stripes.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Thursday, Sept. 1; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Spacewalk Friday: Installing a New "Parking Spot" on Station
This Friday, Aug. 19, two U.S. astronauts will install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.

Commercial crew flights from Florida’s Space Coast to the International Space Station will restore America’s human spaceflight launch capability and increase the time U.S. crews can dedicate to scientific research.

The adapter being installed (imaged below) was launched on a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft and arrived on orbit July 20. This ring is known as an International Docking Adapter, or IDA, and its main purpose is to provide a port for spacecraft bringing astronauts to the station in the future. Outfitted with a host of sensors and systems, the adapter is built so spacecraft systems can automatically perform all the steps of arrival and docking with the station without input from the astronauts.
NASA astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will perform the spacewalk to install the equipment this Friday, Aug. 19. This will be the fourth spacewalk in Williams’ career and the first for Rubins.

Four previous spacewalks...like the one below...helped set the stage for installation of this docking adapter. During those previous spacewalks, other crew members laid hundreds of feet of power and data cables outside the space station.

On Wednesday, the robotics team using the Canadarm2 and its attached “Dextre” manipulator, will reach into the SpaceX Dragon trunk and pull out the docking adapter and position it for Friday’s spacewalk activities.

The morning of the spacewalk, while the astronauts are getting suited up, the robotic arm will position the docking adaptor near the port so that it will be ready for installation.

The two astronauts will venture outside the space station to install the first International Docking Adapter (IDA). This new adapter port will provide a parking space for U.S. Commercial Crew vehicles.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Friday, Aug. 19; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Station Research: Cardiovascular Health
Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In February, our focus is cardiovascular health, which coincides with the American Hearth Month.
Like bones and muscle, the cardiovascular system deconditions (gets weaker) in microgravity. Long-duration spaceflight may increase the risk of damage and inflammation in the cardiovascular system primarily from radiation, but also from psychological stress, reduced physical activity, diminished nutritional standards and, in the case of extravehicular activity, increased oxygen exposure.

Even brief periods of exposure to reduced-gravity environments can result in cardiovascular changes such as fluid shifts, changes in total blood volume, heartbeat and heart rhythm irregularities and diminished aerobic capacity.

The weightless environment of space also causes fluid shifts to occur in the body. This normal shift of fluids to the upper body in space causes increased inter-cranial pressure which could be reducing visual capacity in astronauts. We are currently testing how this can be counteracted by returning fluids to the lower body using a “lower body negative pressure” suit, also known as Chibis.
Spaceflight also accelerates the aging process, and it is important to understand this process to develop specific countermeasures. Developing countermeasures to keep astronauts’ hearts healthy in space is applicable to heart health on Earth, too!

On the space station, one of the tools we have to study heart health is the ultrasound device, which uses harmless sound waves to take detailed images of the inside of the body. These images are then viewed by researchers and doctors inside Mission Control. So with minimal training on ultrasound, remote guidance techniques allow astronauts to take images of their own heart while in space. These remote medicine techniques can also be beneficial on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com