Your gateway to endless inspiration
Nasa - Blog Posts
Do you guys (everyone at mission control) have inside jokes?
What is the best about being mission control?
As someone who's about to go to college to hopefully be astronaut if everything goes to plan. What is some good advice you wish someone told you?
out of all the roles you've had in the past, which one do you feel has best prepared you to be a flight director?
I really want to work for NASA but I do not have a background in science or engineering. Are there any career paths at NASA that I could still achieve?
how can one work in nasa? it's my dream to work in nasa someday, right now, I'm just a high schooler but I've been planning out my trajectory so some advice and tips would be helpful.
Did what you study in college prepare you for this career choice? How did you figure out this career was something you were interested in?
How did you get to where you are now? and di you always know that this is where you wanted to end up?


Tumblr, this is Houston speaking! The flight directors Answer Time with Chloe Mehring and Diane Dailey is live. Stay tuned to learn about what happens in mission control, how to become a flight director, and what Hollywood sometimes gets wrong about the job. View ALL the answers HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Black Hole Friday Deals!

Get these deals before they are sucked into a black hole and gone forever! This “Black Hole Friday,” we have some cosmic savings that are sure to be out of this world.
Your classic black holes — the ultimate storage solution.
Galactic 5-for-1 special! Learn more about Stephan’s Quintet.
Limited-time offer game DLC! Try your hand at the Roman Space Observer Video Game, Black Hole edition, available this weekend only.
Standard candles: Exploding stars that are reliably bright. Multi-functional — can be used to measure distances in space!
Feed the black hole in your stomach. Spaghettification’s on the menu.
Act quickly before the stars in this widow system are gone!
Add some planets to your solar system! Grab our Exoplanet Bundle.
Get ready to ride this (gravitational) wave before this Black Hole Merger ends!
Be the center of attention in this stylish accretion disk skirt. Made of 100% recycled cosmic material.
Should you ever travel to a black hole? No. But if you do, here’s a free guide to make your trip as safe* as possible. *Note: black holes are never safe.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Moonbound: One Year Since Artemis I
On this day last year, the Artemis I rocket and spacecraft lit up the sky and embarked on the revolutionary mission to the Moon and back. The first integrated flight test of the rocket and spacecraft continued for 25.5 days, validating NASA’s deep exploration systems and setting the stage for humanity’s return to the lunar surface.

On Nov. 16, 2022, the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket met or exceeded all expectations during its debut launch on Artemis I. The twin solid rocket booster motors responsible for producing more than 7 million pounds of thrust at liftoff reached their performance target, helping SLS and the Orion spacecraft reach a speed of about 4,000 mph in just over two minutes before the boosters separated.

Quite a few payloads caught a ride aboard the Orion spacecraft on the Artemis I mission: In addition to a number of small scientific satellites called CubeSats, a manikin named Commander Moonikin Campos sat in the commander’s seat. A Snoopy doll served as a zero-gravity indicator — something that floats inside the spacecraft to demonstrate microgravity.

During the mission, Orion performed two lunar flybys, coming within 80 miles of the lunar surface. At its farthest distance during the mission, Orion traveled nearly 270,000 miles from our home planet, more than 1,000 times farther than where the International Space Station orbits Earth. This surpassed the record for distance traveled by a spacecraft designed to carry humans, previously set during Apollo 13.

The Orion spacecraft arrived back home to planet Earth on Dec. 11, 2022. During re-entry, Orion endured temperatures about half as hot as the surface of the Sun at about 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Within about 20 minutes, Orion slowed from nearly 25,000 mph to about 20 mph for its parachute-assisted splashdown.

Recovery teams successfully retrieved the spacecraft and delivered it back to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for de-servicing operations, which included removing the payloads (like Snoopy and Commander Moonikin Campos) and analyzing the heat shield.

With the Artemis I mission under our belt, we look ahead to Artemis II — our first crewed mission to the Moon in over 50 years. Four astronauts will fly around the Moon inside Orion, practicing piloting the spacecraft and validating the spacecraft’s life support systems. The Artemis II crew includes: NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, and CSA astronaut Jeremy Hansen.
As we look ahead to Artemis II, we build upon the incredible success of the Artemis I mission and recognize the hard work and achievements of the entire Artemis team. Go Artemis!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

What’s It Like to Work in NASA’s Mission Control Center?
In the latest installment of our First Woman graphic novel series, we see Commander Callie Rodriguez embark on the next phase of her trailblazing journey, as she leaves the Moon to take the helm at Mission Control.

Flight directors work in Mission Control to oversee operations of the International Space Station and Artemis missions to the Moon. They have a unique, overarching perspective focused on integration between all the systems that make a mission a success – flight directors have to learn a little about a lot.
Diane Dailey and Chloe Mehring were selected as flight directors in 2021. They’ll be taking your questions about what it’s like to lead teams of flight controllers, engineers, and countless professionals, both agencywide and internationally, in an Answer Time session on Nov. 28, 2023, from noon to 1 p.m. EST (9-10 a.m. PST) here on our Tumblr!
Like Callie, how did their unique backgrounds and previous experience, prepare them for this role? What are they excited about as we return to the Moon?
🚨 Ask your questions now by visiting https://nasa.tumblr.com/ask.
Diane Dailey started her career at NASA in 2006 in the space station Environmental Control and Life Support Systems (ECLSS) group. As an ECLSS flight controller, she logged more than 1,700 hours of console time, supported 10 space shuttle missions, and led the ECLSS team. She transitioned to the Integration and System Engineering (ISE) group, where she was the lead flight controller for the 10th and 21st Commercial Resupply Services missions for SpaceX. In addition, she was the ISE lead for NASA’s SpaceX Demo-1 and Demo-2 crew spacecraft test flights. Dailey was also a capsule communicator (Capcom) controller and instructor.
She was selected as a flight director in 2021 and chose her call sign of “Horizon Flight” during her first shift in November of that year. She has since served as the Lead Flight director for the ISS Expedition 68, led the development of a contingency spacewalk, and led a spacewalk in June to install a new solar array on the space station. She is currently working on development of the upcoming Artemis II mission and the Human Lander Systems which will return humanity to the moon. Dailey was raised in Lubbock, Texas, and graduated from Texas A&M University in College Station with a bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering. She is married and a mother of two. She enjoys cooking, traveling, and spending time outdoors.
Chloe Mehring started her NASA career in 2008 in the Flight Operations’ propulsion systems group and supported 11 space shuttle missions. She served as propulsion support officer for Exploration Flight Test-1, the first test flight of the Orion spacecraft that will be used for Artemis missions to the Moon. Mehring was also a lead NASA propulsion officer for SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft and served as backup lead for the Boeing Starliner spacecraft. She was accepted into the 2021 Flight Director class and worked her first shift in February 2022, taking on the call sign “Lion Flight”. Since becoming certified, she has worked over 100 shifts, lead the NG-17 cargo resupply mission team, and executed two United States spacewalks within 10 days of each other. She became certified as a Boeing Starliner Flight Director, sat console for the unmanned test flight in May 2022 (OFT-2) and will be leading the undock team for the first crewed mission on Starliner in the spring of next year. She originally is from Mifflinville, Pennsylvania, and graduated with a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering from The Pennsylvania State University in State College. She is a wife, a mom to one boy, and she enjoys fitness, cooking and gardening.

Astronomers used three of NASA's Great Observatories to capture this multiwavelength image showing galaxy cluster IDCS J1426.5+3508. It includes X-rays recorded by the Chandra X-ray Observatory in blue, visible light observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in green, and infrared light from the Spitzer Space Telescope in red. This rare galaxy cluster has important implications for understanding how these megastructures formed and evolved early in the universe.
How Astronomers Time Travel
Let’s add another item to your travel bucket list: the early universe! You don’t need the type of time machine you see in sci-fi movies, and you don’t have to worry about getting trapped in the past. You don’t even need to leave the comfort of your home! All you need is a powerful space-based telescope.
But let’s start small and work our way up to the farthest reaches of space. We’ll explain how it all works along the way.

This animation illustrates how fast light travels between Earth and the Moon. The farther light has to travel, the more noticeable its speed limit becomes.
The speed of light is superfast, but it isn’t infinite. It travels at about 186,000 miles (300 million meters) per second. That means that it takes time for the light from any object to reach our eyes. The farther it is, the more time it takes.
You can see nearby things basically in real time because the light travel time isn’t long enough to make a difference. Even if an object is 100 miles (161 kilometers) away, it takes just 0.0005 seconds for light to travel that far. But on astronomical scales, the effects become noticeable.

This infographic shows how long it takes light to travel to different planets in our solar system.
Within our solar system, light’s speed limit means it can take a while to communicate back and forth between spacecraft and ground stations on Earth. We see the Moon, Sun, and planets as they were slightly in the past, but it's not usually far enough back to be scientifically interesting.
As we peer farther out into our galaxy, we use light-years to talk about distances. Smaller units like miles or kilometers would be too overwhelming and we’d lose a sense of their meaning. One light-year – the distance light travels in a year – is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers). And that’s just a tiny baby step into the cosmos.
The Sun’s closest neighboring star, Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 light-years away. That means we see it as it was about four years ago. Betelgeuse, a more distant (and more volatile) stellar neighbor, is around 700 light-years away. Because of light’s lag time, astronomers don’t know for sure whether this supergiant star is still there! It may have already blasted itself apart in a supernova explosion – but it probably has another 10,000 years or more to go.

What looks much like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals previously obscured areas of star birth.
The Carina Nebula clocks in at 7,500 light-years away, which means the light we receive from it today began its journey about 3,000 years before the pyramids of Giza in Egypt were built! Many new stars there have undoubtedly been born by now, but their light may not reach Earth for thousands of years.

An artist’s concept of our Milky Way galaxy, with rough locations for the Sun and Carina nebula marked.
If we zoom way out, you can see that 7,500 light-years away is still pretty much within our neighborhood. Let’s look further back in time…

This stunning image by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope features the spiral galaxy NGC 5643. Looking this good isn’t easy; 30 different exposures, for a total of nine hours of observation time, together with Hubble’s high resolution and clarity, were needed to produce an image of such exquisite detail and beauty.
Peering outside our Milky Way galaxy transports us much further into the past. The Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large galactic neighbor, is about 2.5 million light-years away. And that’s still pretty close, as far as the universe goes. The image above shows the spiral galaxy NGC 5643, which is about 60 million light-years away! That means we see it as it was about 60 million years ago.
As telescopes look deeper into the universe, they capture snapshots in time from different cosmic eras. Astronomers can stitch those snapshots together to unravel things like galaxy evolution. The closest ones are more mature; we see them nearly as they truly are in the present day because their light doesn’t have to travel as far to reach us. We can’t rewind those galaxies (or our own), but we can get clues about how they likely developed. Looking at galaxies that are farther and farther away means seeing these star cities in ever earlier stages of development.
The farthest galaxies we can see are both old and young. They’re billions of years old now, and the light we receive from them is ancient since it took so long to traverse the cosmos. But since their light was emitted when the galaxies were young, it gives us a view of their infancy.

This animation is an artist’s concept of the big bang, with representations of the early universe and its expansion.
Comparing how fast objects at different distances are moving away opened up the biggest mystery in modern astronomy: cosmic acceleration. The universe was already expanding as a result of the big bang, but astronomers expected it to slow down over time. Instead, it’s speeding up!
The universe’s expansion makes it tricky to talk about the distances of the farthest objects. We often use lookback time, which is the amount of time it took for an object’s light to reach us. That’s simpler than using a literal distance, because an object that was 10 billion light-years away when it emitted the light we received from it would actually be more than 16 billion light-years away right now, due to the expansion of space. We can even see objects that are presently over 30 billion light-years from Earth, even though the universe is only about 14 billion years old.

This James Webb Space Telescope image shines with the light from galaxies that are more than 13.4 billion years old, dating back to less than 400 million years after the big bang.
Our James Webb Space Telescope has helped us time travel back more than 13.4 billion years, to when the universe was less than 400 million years old. When our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope launches in a few years, astronomers will pair its vast view of space with Webb’s zooming capabilities to study the early universe in better ways than ever before. And don’t worry – these telescopes will make plenty of pit stops along the way at other exciting cosmic destinations across space and time.
Learn more about the exciting science Roman will investigate on X and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Hot New Planetary System Just Dropped.
We hope you like your planetary systems extra spicy. 🔥
A new system of seven sizzling planets has been discovered using data from our retired Kepler space telescope.
Named Kepler-385, it’s part of a new catalog of planet candidates and multi-planet systems discovered using Kepler.
The discovery helps illustrate that multi-planetary systems have more circular orbits around the host star than systems with only one or two planets.
Our Kepler mission is responsible for the discovery of the most known exoplanets to date. The space telescope’s observations ended in 2018, but its data continues to paint a more detailed picture of our galaxy today.
Here are a few more things to know about Kepler-385:

All seven planets are between the size of Earth and Neptune.

Its star is 10% larger and 5% hotter than our Sun.

This system is one of over 700 that Kepler’s data has revealed.
The planets’ orbits have been represented in sound.
Now that you’ve heard a little about this planetary system, get acquainted with more exoplanets and why we want to explore them.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

For the Benefit of All: Assistive Tech Developed from NASA Tech
What do modern cochlear implants and robotic gloves have in common? They were derived from NASA technology. We’ve made it easier to find and use our patented inventions that could help create products that enhance life for people with disabilities.
October is National Disability Employment Awareness Month, which highlights the contributions of American workers with disabilities – many of whom use assistive technology on the job. Take a look at these assistive technologies that are NASA spinoffs.

Low-Vision Headsets
The Joint Optical Reflective Display (JORDY) device is a headset that uses NASA image processing and head-mounted display technology to enable people with low vision to read and write. JORDY enhances individuals’ remaining sight by magnifying objects up to 50 times and allowing them to change contrast, brightness, and display modes. JORDY's name was inspired by Geordi La Forge, a blind character from “Star Trek: The Next Generation” whose futuristic visor enabled him to see.

Cochlear Implants
Work that led to the modern cochlear implant was patented by a NASA engineer in the 1970s. Following three failed corrective surgeries, Adam Kissiah combined his NASA electronics know-how with research in the Kennedy Space Center technical library to build his own solution for people with severe-to-profound hearing loss who receive little or no benefit from hearing aids. Several companies now make the devices, which have been implanted in hundreds of thousands of people around the world.

Robotic Gloves
Ironhand, from Swedish company Bioservo Technologies, is the world’s first industrial-strength robotic glove for factory workers and others who perform repetitive manual tasks. It helps prevent stress injuries but has been especially warmly received by workers with preexisting hand injuries and conditions. The glove is based on a suite of patents for the technology developed by NASA and General Motors to build the hands of the Robonaut 2 humanoid robotic astronaut.

Smart Glasses
Neurofeedback technology NASA originally developed to improve pilots’ attention has been the basis for products aimed at helping people manage attention disorders without medication. The devices measure brainwave output to gauge attention levels according to the “engagement index” a NASA engineer created. Then, they show the results to users, helping them learn to voluntarily control their degree of concentration. One such device is a pair of smart glasses from Narbis, whose lenses darken as attention wanes.

Anti-Gravity Treadmills
A NASA scientist who developed ways to use air pressure to simulate gravity for astronauts exercising in space had the idea to apply the concept for the opposite effect on Earth. After licensing his technology, Alter-G Inc. developed its anti-gravity G-Trainer treadmill, which lets users offload some or all of their weight while exercising. The treadmills can help people recover from athletic or brain injuries, and they allow a safe exercise regimen for others with long-term conditions such as arthritis.

Wireless Muscle Sensors
Some of the most exciting assistive technologies to spin off may be yet to come. Delsys Inc. developed electromyographic technology to help NASA understand the effects of long-term weightlessness on astronauts’ muscles and movements. Electromyography detects and analyzes electrical signals emitted when motor nerves trigger movement. Among the company’s customers are physical therapists developing exercise routines to help patients recover from injuries. But some researchers are using the technology to attempt recoveries that once seemed impossible, such as helping paralyzed patients regain movement, letting laryngectomy patients speak, and outfitting amputees with artificial limbs that work like the real thing.
To further enhance the lives of people with disabilities, NASA has identified a selection of patented technologies created for space missions that could spur the next generation of assistive technology here on Earth.
Want to learn more about assistive technologies already in action? Check out NASA Spinoff to find products and services that wouldn’t exist without space exploration.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Hurry! You Can Catch a Ride to Jupiter with NASA
Well, at least your name can.
One of the planet Jupiter’s largest and most intriguing moons is called Europa. Evidence hints that beneath its icy shell, Europa hides an ocean of liquid water – more water than all of Earth’s oceans combined. In 2024, our Europa Clipper robotic spacecraft sets sail to take a closer look…and when it launches, your name can physically be aboard! Here’s how:
NASA’s Message in a Bottle campaign invites people around the world to sign their names to a poem written by the U.S. Poet Laureate, Ada Limón. The poem connects the two water worlds — Earth, yearning to reach out and understand what makes a world habitable, and Europa, waiting with secrets yet to be explored.

The poem will be engraved on Europa Clipper, along with participants' names that will be physically etched onto microchips mounted on the spacecraft. Together, the poem and names will travel 1.8 billion miles to the Jupiter system.

Signing up is easy! Just go to this site to sign your name to the poem and get on board. You can send your name en español, too. Envía tu nombre aquí.
The Europa Clipper launch window opens in October 2024, but don’t wait – everyone’s names need to be received this year so they can be loaded onto the spacecraft in time. Sign up by Dec. 31, 2023.
We hope you’ll be riding along with us! Follow the mission at europa.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Don’t Say “Bye, Bye, Bye” To Your Vision: Solar Eclipse Safety Tips
On Oct. 14, 2023, many people across North, Central, and South America will have an opportunity to view a “ring of fire” eclipse – an annular solar eclipse – when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun! During an annular eclipse, it is never safe to look directly at the Sun without specialized eye protection designed for solar viewing. To spread the word, *NSYNC's Lance Bass stopped by to share some tips on how to stay safe while viewing a solar eclipse.
Check out these detailed viewing maps to see if you will be able to see the entire or partial solar eclipse. If you are, make sure your solar viewing glasses have the ISO certification 12312-2. You can also check with local libraries or science museums to see if they have safe solar viewing glasses to hand out. You can also make a simple pinhole camera at home with some paper and aluminum foil: go.nasa.gov/pinholeprojector
Everyone online can watch the eclipse with NASA. Set a reminder to watch live: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LlY79zjud-Q
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Let's Explore a Metal-Rich Asteroid 🤘
Between Mars and Jupiter, there lies a unique, metal-rich asteroid named Psyche. Psyche’s special because it looks like it is part or all of the metallic interior of a planetesimal—an early planetary building block of our solar system. For the first time, we have the chance to visit a planetary core and possibly learn more about the turbulent history that created terrestrial planets.
Here are six things to know about the mission that’s a journey into the past: Psyche.

1. Psyche could help us learn more about the origins of our solar system.
After studying data from Earth-based radar and optical telescopes, scientists believe that Psyche collided with other large bodies in space and lost its outer rocky shell. This leads scientists to think that Psyche could have a metal-rich interior, which is a building block of a rocky planet. Since we can’t pierce the core of rocky planets like Mercury, Venus, Mars, and our home planet, Earth, Psyche offers us a window into how other planets are formed.

2. Psyche might be different than other objects in the solar system.
Rocks on Mars, Mercury, Venus, and Earth contain iron oxides. From afar, Psyche doesn’t seem to feature these chemical compounds, so it might have a different history of formation than other planets.
If the Psyche asteroid is leftover material from a planetary formation, scientists are excited to learn about the similarities and differences from other rocky planets. The asteroid might instead prove to be a never-before-seen solar system object. Either way, we’re prepared for the possibility of the unexpected!

3. Three science instruments and a gravity science investigation will be aboard the spacecraft.
The three instruments aboard will be a magnetometer, a gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer, and a multispectral imager. Here’s what each of them will do:
Magnetometer: Detect evidence of a magnetic field, which will tell us whether the asteroid formed from a planetary body
Gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer: Help us figure out what chemical elements Psyche is made of, and how it was formed
Multispectral imager: Gather and share information about the topography and mineral composition of Psyche
The gravity science investigation will allow scientists to determine the asteroid’s rotation, mass, and gravity field and to gain insight into the interior by analyzing the radio waves it communicates with. Then, scientists can measure how Psyche affects the spacecraft’s orbit.

4. The Psyche spacecraft will use a super-efficient propulsion system.
Psyche’s solar electric propulsion system harnesses energy from large solar arrays that convert sunlight into electricity, creating thrust. For the first time ever, we will be using Hall-effect thrusters in deep space.

5. This mission runs on collaboration.
To make this mission happen, we work together with universities, and industry and NASA to draw in resources and expertise.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the mission and is responsible for system engineering, integration, and mission operations, while NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Services Program manages launch operations and procured the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
Working with Arizona State University (ASU) offers opportunities for students to train as future instrument or mission leads. Mission leader and Principal Investigator Lindy Elkins-Tanton is also based at ASU.
Finally, Maxar Technologies is a key commercial participant and delivered the main body of the spacecraft, as well as most of its engineering hardware systems.

6. You can be a part of the journey.
Everyone can find activities to get involved on the mission’s webpage. There's an annual internship to interpret the mission, capstone courses for undergraduate projects, and age-appropriate lessons, craft projects, and videos.
You can join us for a virtual launch experience, and, of course, you can watch the launch with us on Oct. 12, 2023, at 10:16 a.m. EDT!
For official news on the mission, follow us on social media and check out NASA’s and ASU’s Psyche websites.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

HBCU Students Make Moves with NASA Tech
In September 2023, students at HBCUs participated in a hackathon at the National HBCU Week Conference, where they used NASA’s technologies to create solutions to problems that affect Black communities. The winning team, Team Airtek, proposed a nano-sensor array for medical diagnoses that would give students on HBCU campuses a non-invasive, non-intensive way to test themselves for precursors for diseases and illnesses like diabetes and COVID.
The hackathon they participated in is a modified version of the full NASA Minority University Research and Education Project Innovation and Tech Transfer Idea Competition (MITTIC) that takes place each fall and spring semester at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
No matter what you’re studying, you can join the MITTIC competition and come up with new and innovative tech to help your community and the world.
MITTIC could be the beginning of your career pathway: Teams can go on exclusive NASA tours and network with industry experts. Show off your entrepreneurial skills and your team could earn money—and bragging rights.
Don’t wait too long to apply or to share with someone who should apply! The deadline for proposals is Oct. 16, 2023. Apply here: https://microgravityuniversity.jsc.nasa.gov/nasamittic.
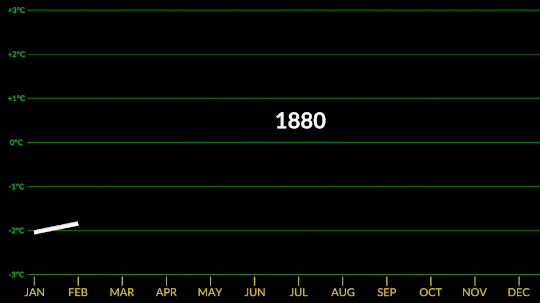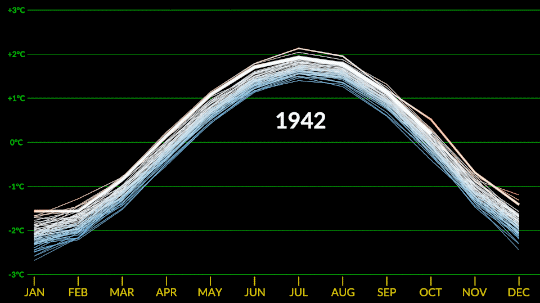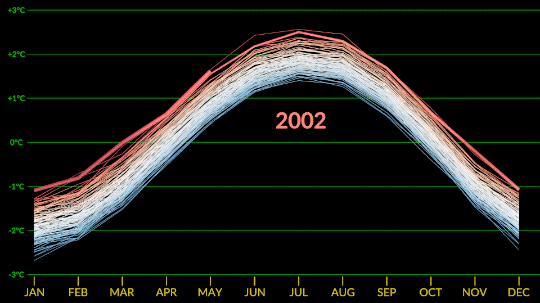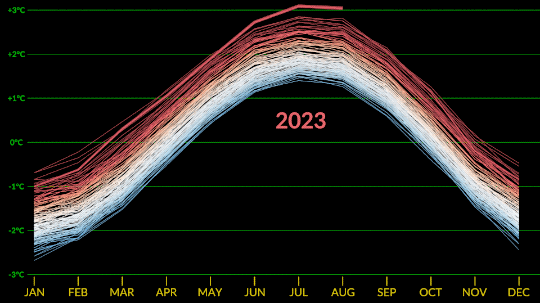
Confirmed: Summer 2023 Hottest in NASA’s Record
All three months of summer 2023 broke records. July 2023 was the hottest month ever recorded, and the hottest July. June 2023 was the hottest June, and August 2023 was the hottest August.
NASA’s temperature record, GISTEMP, starts in 1880, when consistent, modern recordkeeping became possible. Our record uses millions of measurements of surface temperature from weather stations, ships and ocean buoys, and Antarctic research stations. Other agencies and organizations who keep similar global temperature records find the same pattern of long-term warming.
Global temperatures are rising from increased emissions of greenhouse gasses, like carbon dioxide and methane. Over the last 200 years, humans have raised atmospheric CO2 by nearly 50%, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels.
Drivers of climate change, both natural and human-caused, leave distinct fingerprints. Through observations and modeling, NASA researchers confirm that the current warming is the result of human activities, particularly increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Top Study Tips from NASA

Study smarter this school year! We asked scientists, engineers, astronauts, and experts from across NASA about their favorite study tips – and they delivered. Here are a few of our favorites:

Study with friends
Find friends that are like-minded and work together to understand the material better. Trading ideas with a friend on how to tackle a problem can help you both strengthen your understanding.

Create a study environment
Find a quiet space or put on headphones so you can focus. You might not be able to get to the International Space Station yet, but a library, a study room, or a spot outside can be a good place to study. If it’s noisy around you, try using headphones to block out distractions.

Take breaks
Don’t burn yourself out! Take a break, go for a walk, get some water, and come back to it.
Looking for more study tips? Check out this video for all ten tips to start your school year off on the right foot!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
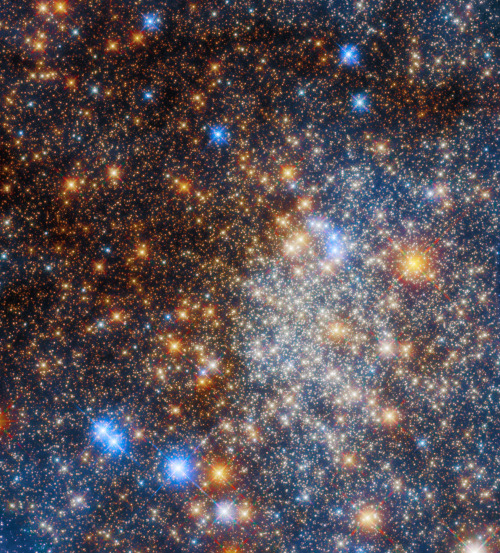

Pumpkin space latte, anyone? ☕
Hubble captured this festive array of stars, Terzan 12, found in the Milky Way about 15,000 light-years from Earth. The stars in this cluster are bound together by gravity in a sphere-like shape and are shrouded in gas and dust. As the starlight travels through that gas and dust to Earth, blue light scatters, leaving the redder wavelengths to come through.
Download the full-resolution image here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Guy Bluford Changed the Course of Space History
On Aug. 30, 1983, Guion Bluford, better known as Guy, became the first African American to fly to space. An accomplished jet pilot and aerospace engineer, Bluford became part of NASA’s 1978 astronaut class that included the first African American, the first Asian American, and the first women astronauts.
He and the other crew members of mission STS-8 were aboard the orbiter Challenger as it lifted off from Kennedy Space Center in Florida; it was the first nighttime launch and landing of the Space Shuttle program. While aboard, he and the other crew members deployed the Indian National Satellite (INSAT-1B), operated a Canadian-built robot arm, conducted experiments with live cell samples, and participated in studies measuring the effects of spaceflight on humans.
Guy Bluford chased his childhood dream of becoming an aerospace engineer, and in doing so, changed history and encouraged other Black astronauts to follow in his footsteps.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space—and for milestones like this!

The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s flight harness is transferred from the mock-up structure to the spacecraft flight structure.
Your Body is Wired Like a NASA Space Telescope. Sort Of.
If our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope were alive, its nervous system would be the intricate wiring, or “harness,” that helps different parts of the observatory communicate with one another. Just like the human body sends information through nerves to function, Roman will send commands through this special harness to help achieve its mission: answering longstanding questions about dark energy, dark matter, and exoplanets, among other mind-bending cosmic queries.
Roman’s harness weighs around 1,000 pounds and is made of about 32,000 wires and 900 connectors. If those parts were laid out end-to-end, they would be 45 miles long from start to finish. Coincidentally, the human body’s nerves would span the same distance if lined up. That’s far enough to reach nearly three-fourths of the way to space, twice as far as a marathon, or eight times taller than Mount Everest!

An aerial view of the harness technicians working to secure Roman’s harness to the spacecraft flight structure.
Over a span of two years, 11 technicians spent time at the workbench and perched on ladders, cutting wire to length, carefully cleaning each component, and repeatedly connecting everything together.
Space is usually freezing cold, but spacecraft that are in direct sunlight can get incredibly hot. Roman’s harness went through the Space Environment Simulator – a massive thermal vacuum chamber – to expose the components to the temperatures they’ll experience in space. Technicians “baked” vapors out of the harness to make sure they won’t cause problems later in orbit.

Technicians work to secure Roman’s harness to the interior of the spacecraft flight structure. They are standing in the portion of the spacecraft bus where the propellant tanks will be mounted.
The next step is for engineers to weave the harness through the flight structure in Goddard’s big clean room, a space almost perfectly free of dust and other particles. This process will be ongoing until most of the spacecraft components are assembled. The Roman Space Telescope is set to launch by May 2027.
Learn more about the exciting science this mission will investigate on X and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Roman's primary structure hangs from cables as it moves into the big clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
What Makes the Clean Room So Clean?
When you picture NASA’s most important creations, you probably think of a satellite, telescope, or maybe a rover. But what about the room they’re made in? Believe it or not, the room itself where these instruments are put together—a clean room—is pretty special.
A clean room is a space that protects technology from contamination. This is especially important when sending very sensitive items into space that even small particles could interfere with.
There are two main categories of contamination that we have to keep away from our instruments. The first is particulate contamination, like dust. The second is molecular contamination, which is more like oil or grease. Both types affect a telescope’s image quality, as well as the time it takes to capture imagery. Having too many particles on our instruments is like looking through a dirty window. A clean room makes for clean science!

Two technicians clean the floor of Goddard’s big clean room.
Our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland has the largest clean room of its kind in the world. It’s as tall as an eight-story building and as wide as two basketball courts.
Goddard’s clean room has fewer than 3,000 micron-size particles per cubic meter of air. If you lined up all those tiny particles, they’d be no longer than a sesame seed. If those particles were the size of 16-inch (0.4-meter) inflatable beach balls, we’d find only 3,000 spread throughout the whole body of Mount Everest!

A clean room technician observes a sample under a microscope.
The clean room keeps out particles larger than five microns across, just seven percent of the width of an average human hair. It does this via special filters that remove around 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns and larger from incoming air. Six fans the size of school buses spin to keep air flowing and pressurize the room. Since the pressure inside is higher, the clean air keeps unclean air out when doors open.

A technician analyzes a sample under ultraviolet light.
In addition, anyone who enters must wear a “bunny suit” to keep their body particles away from the machinery. A bunny suit covers most of the person inside. Sometimes scientists have trouble recognizing each other while in the suits, but they do get to know each other’s mannerisms very well.

This illustration depicts the anatomy of a bunny suit, which covers clean room technicians from head to toe to protect sensitive technology.
The bunny suit is only the beginning: before putting it on, team members undergo a preparation routine involving a hairnet and an air shower. Fun fact – you’re not allowed to wear products like perfume, lotion, or deodorant. Even odors can transfer easily!

Six of Goddard’s clean room technicians (left to right: Daniel DaCosta, Jill Bender, Anne Martino, Leon Bailey, Frank D’Annunzio, and Josh Thomas).
It takes a lot of specialists to run Goddard’s clean room. There are 10 people on the Contamination Control Technician Team, 30 people on the Clean Room Engineering Team to cover all Goddard missions, and another 10 people on the Facilities Team to monitor the clean room itself. They check on its temperature, humidity, and particle counts.

A technician rinses critical hardware with isopropyl alcohol and separates the particulate and isopropyl alcohol to leave the particles on a membrane for microscopic analysis.
Besides the standard mopping and vacuuming, the team uses tools such as isopropyl alcohol, acetone, wipes, swabs, white light, and ultraviolet light. Plus, they have a particle monitor that uses a laser to measure air particle count and size.
The team keeping the clean room spotless plays an integral role in the success of NASA’s missions. So, the next time you have to clean your bedroom, consider yourself lucky that the stakes aren’t so high!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Navigating Deep Space by Starlight
On August 6, 1967, astrophysicist Jocelyn Bell Burnell noticed a blip in her radio telescope data. And then another. Eventually, Bell Burnell figured out that these blips, or pulses, were not from people or machines.

The blips were constant. There was something in space that was pulsing in a regular pattern, and Bell Burnell figured out that it was a pulsar: a rapidly spinning neutron star emitting beams of light. Neutron stars are superdense objects created when a massive star dies. Not only are they dense, but neutron stars can also spin really fast! Every star we observe spins, and due to a property called angular momentum, as a collapsing star gets smaller and denser, it spins faster. It’s like how ice skaters spin faster as they bring their arms closer to their bodies and make the space that they take up smaller.

The pulses of light coming from these whirling stars are like the beacons spinning at the tops of lighthouses that help sailors safely approach the shore. As the pulsar spins, beams of radio waves (and other types of light) are swept out into the universe with each turn. The light appears and disappears from our view each time the star rotates.

After decades of studying pulsars, astronomers wondered—could they serve as cosmic beacons to help future space explorers navigate the universe? To see if it could work, scientists needed to do some testing!
First, it was important to gather more data. NASA’s NICER, or Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer, is a telescope that was installed aboard the International Space Station in 2017. Its goal is to find out things about neutron stars like their sizes and densities, using an array of 56 special X-ray concentrators and sensitive detectors to capture and measure pulsars’ light.

But how can we use these X-ray pulses as navigational tools? Enter SEXTANT, or Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology. If NICER was your phone, SEXTANT would be like an app on it.
During the first few years of NICER’s observations, SEXTANT created an on-board navigation system using NICER’s pulsar data. It worked by measuring the consistent timing between each pulsar’s pulses to map a set of cosmic beacons.

When calculating position or location, extremely accurate timekeeping is essential. We usually rely on atomic clocks, which use the predictable fluctuations of atoms to tick away the seconds. These atomic clocks can be located on the ground or in space, like the ones on GPS satellites. However, our GPS system only works on or close to Earth, and onboard atomic clocks can be expensive and heavy. Using pulsar observations instead could give us free and reliable “clocks” for navigation. During its experiment, SEXTANT was able to successfully determine the space station’s orbital position!

We can calculate distances using the time taken for a signal to travel between two objects to determine a spacecraft’s approximate location relative to those objects. However, we would need to observe more pulsars to pinpoint a more exact location of a spacecraft. As SEXTANT gathered signals from multiple pulsars, it could more accurately derive its position in space.

So, imagine you are an astronaut on a lengthy journey to the outer solar system. You could use the technology developed by SEXTANT to help plot your course. Since pulsars are reliable and consistent in their spins, you wouldn’t need Wi-Fi or cell service to figure out where you were in relation to your destination. The pulsar-based navigation data could even help you figure out your ETA!

None of these missions or experiments would be possible without Jocelyn Bell Burnell’s keen eye for an odd spot in her radio data decades ago, which set the stage for the idea to use spinning neutron stars as a celestial GPS. Her contribution to the field of astrophysics laid the groundwork for research benefitting the people of the future, who yearn to sail amongst the stars.
Keep up with the latest NICER news by following NASA Universe on X and Facebook and check out the mission’s website. For more on space navigation, follow @NASASCaN on X or visit NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation website.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
NASA Inspires Your Crafty Creations for World Embroidery Day
It’s amazing what you can do with a little needle and thread! For #WorldEmbroideryDay, we asked what NASA imagery inspired you. You responded with a variety of embroidered creations, highlighting our different areas of study.
Here’s what we found:
Webb’s Carina Nebula

Wendy Edwards, a project coordinator with Earth Science Data Systems at NASA, created this embroidered piece inspired by Webb’s Carina Nebula image. Captured in infrared light, this image revealed for the first time previously invisible areas of star birth. Credit: Wendy Edwards, NASA. Pattern credit: Clare Bray, Climbing Goat Designs
Wendy Edwards, a project coordinator with Earth Science Data Systems at NASA, first learned cross stitch in middle school where she had to pick rotating electives and cross stitch/embroidery was one of the options. “When I look up to the stars and think about how incredibly, incomprehensibly big it is out there in the universe, I’m reminded that the universe isn’t ‘out there’ at all. We’re in it,” she said. Her latest piece focused on Webb’s image release of the Carina Nebula. The image showcased the telescope’s ability to peer through cosmic dust, shedding new light on how stars form.
Ocean Color Imagery: Exploring the North Caspian Sea

Danielle Currie of Satellite Stitches created a piece inspired by the Caspian Sea, taken by NASA’s ocean color satellites. Credit: Danielle Currie/Satellite Stitches
Danielle Currie is an environmental professional who resides in New Brunswick, Canada. She began embroidering at the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic as a hobby to take her mind off the stress of the unknown. Danielle’s piece is titled “46.69, 50.43,” named after the coordinates of the area of the northern Caspian Sea captured by LandSat8 in 2019.

An image of the Caspian Sea captured by Landsat 8 in 2019. Credit: NASA
Two Hubble Images of the Pillars of Creation, 1995 and 2015

Melissa Cole of Star Stuff Stitching created an embroidery piece based on the Hubble image Pillars of Creation released in 1995. Credit: Melissa Cole, Star Stuff Stitching
Melissa Cole is an award-winning fiber artist from Philadelphia, PA, USA, inspired by the beauty and vastness of the universe. They began creating their own cross stitch patterns at 14, while living with their grandparents in rural Michigan, using colored pencils and graph paper. The Pillars of Creation (Eagle Nebula, M16), released by the Hubble Telescope in 1995 when Melissa was just 11 years old, captured the imagination of a young person in a rural, religious setting, with limited access to science education.

Lauren Wright Vartanian of the shop Neurons and Nebulas created this piece inspired by the Hubble Space Telescope’s 2015 25th anniversary re-capture of the Pillars of Creation. Credit: Lauren Wright Vartanian, Neurons and Nebulas
Lauren Wright Vartanian of Guelph, Ontario Canada considers herself a huge space nerd. She’s a multidisciplinary artist who took up hand sewing after the birth of her daughter. She’s currently working on the illustrations for a science themed alphabet book, made entirely out of textile art. It is being published by Firefly Books and comes out in the fall of 2024. Lauren said she was enamored by the original Pillars image released by Hubble in 1995. When Hubble released a higher resolution capture in 2015, she fell in love even further! This is her tribute to those well-known images.
James Webb Telescope Captures Pillars of Creation

Darci Lenker of Darci Lenker Art, created a rectangular version of Webb’s Pillars of Creation. Credit: Darci Lenker of Darci Lenker Art
Darci Lenker of Norman, Oklahoma started embroidery in college more than 20 years ago, but mainly only used it as an embellishment for her other fiber works. In 2015, she started a daily embroidery project where she planned to do one one-inch circle of embroidery every day for a year. She did a collection of miniature thread painted galaxies and nebulas for Science Museum Oklahoma in 2019. Lenker said she had previously embroidered the Hubble Telescope’s image of Pillars of Creation and was excited to see the new Webb Telescope image of the same thing. Lenker could not wait to stitch the same piece with bolder, more vivid colors.
Milky Way

Darci Lenker of Darci Lenker Art was inspired by NASA’s imaging of the Milky Way Galaxy. Credit: Darci Lenker
In this piece, Lenker became inspired by the Milky Way Galaxy, which is organized into spiral arms of giant stars that illuminate interstellar gas and dust. The Sun is in a finger called the Orion Spur.
The Cosmic Microwave Background

This image shows an embroidery design based on the cosmic microwave background, created by Jessica Campbell, who runs Astrostitches. Inside a tan wooden frame, a colorful oval is stitched onto a black background in shades of blue, green, yellow, and a little bit of red. Credit: Jessica Campbell/ Astrostitches
Jessica Campbell obtained her PhD in astrophysics from the University of Toronto studying interstellar dust and magnetic fields in the Milky Way Galaxy. Jessica promptly taught herself how to cross-stitch in March 2020 and has since enjoyed turning astronomical observations into realistic cross-stitches. Her piece was inspired by the cosmic microwave background, which displays the oldest light in the universe.

The full-sky image of the temperature fluctuations (shown as color differences) in the cosmic microwave background, made from nine years of WMAP observations. These are the seeds of galaxies, from a time when the universe was under 400,000 years old. Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
GISSTEMP: NASA’s Yearly Temperature Release

Katy Mersmann, a NASA social media specialist, created this embroidered piece based on NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) global annual temperature record. Earth’s average surface temperature in 2020 tied with 2016 as the warmest year on record. Credit: Katy Mersmann, NASA
Katy Mersmann is a social media specialist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. She started embroidering when she was in graduate school. Many of her pieces are inspired by her work as a communicator. With climate data in particular, she was inspired by the researchers who are doing the work to understand how the planet is changing. The GISTEMP piece above is based on a data visualization of 2020 global temperature anomalies, still currently tied for the warmest year on record.
In addition to embroidery, NASA continues to inspire art in all forms. Check out other creative takes with Landsat Crafts and the James Webb Space telescope public art gallery.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Soaring into Aerospace: NASA Interns Take Flight at EAA AirVenture Oshkosh

Sustainable Aviation Ambassadors Alex Kehler, Bianca Legeza-Narvaez, Evan Gotchel, and Janki Patel pose in front of the NASA Pavilion at EAA AirVenture Oshkosh.
It’s that time of year again–EAA AirVenture Oshkosh is underway!
Boasting more than 650,000 visitors annually, EAA AirVenture Oshkosh, or “Oshkosh” for short, is an airshow and fly-in held by the Experimental Aircraft Association (EAA). Each year, flight enthusiasts and professionals from around the world converge on Oshkosh, Wisconsin, to engage with industry-leading organizations and businesses and celebrate past, present, and future innovation in aviation.
This year, four NASA interns with the Electrified Powertrain Flight Demonstration (EPFD) project count themselves among those 650,000+ visitors, having the unique opportunity to get firsthand experience with all things aerospace at Oshkosh.
Alex Kehler, Bianca Legeza-Narvaez, Evan Gotchel, and Janki Patel are Sustainable Aviation Ambassadors supporting the EPFD project, which conducts tests of hybrid electric aircraft that use electric aircraft propulsion technologies to enable a new generation of electric-powered aircraft. The focus of Alex, Bianca, Evan, and Janki’s internships cover everything from strategic communications to engineering, and they typically do their work using a laptop. But at Oshkosh, they have a special, more hands-on task: data collection.
“At Oshkosh, I am doing some data collection to better estimate how we can be prepared in the future,” said Janki, an Aerospace Engineering major from the University of Michigan. “Coming to Oshkosh has been an amazing experience… I can walk around and see people passionate about the work they do.”

The NASA Pavilion at EAA AirVenture Oshkosh is full of interactive exhibits and activities for visitors to engage with. NASA Interns Alex, Bianca, Evan, and Janki are collecting data in the pavilion to help improve future exhibits at Oshkosh.
In addition to gathering data to help inform future NASA exhibits and activities at Oshkosh, the interns also have the opportunity to engage with visitors and share their passion for aviation with other aero enthusiasts. For Evan, who is receiving his Master's in Aerospace Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology, “being able to be here and talk with people who are both young and old who are interested in what the future of flight could be has been so incredible.”

Alex, Evan, Bianca, and Janki pose in front of NASA’s Super Guppy, a specialized aircraft used to transport oversized cargo.
At Oshkosh, one memory in particular stands out for Alex, Bianca, Evan, and Janki: seeing NASA’s famous Super Guppy in person. With a unique hinged nose and a cargo area that's 25 feet in diameter and 111 feet long, the Super Guppy can carry oversized cargo that is impossible to transport with other cargo aircraft.
“We had a very lucky experience… We were able to not only see the Super Guppy, we got to get up close when it landed,” said Bianca, who is receiving her Master's in Business Administration with a specialization in Strategic Communications from Bowling Green State University. “From a learning experience, it gave me a way better basis on cargo aircraft and how they operate.”
For Alex, who is receiving his Master's in Aeronautical Engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology, it was exciting to see the Super Guppy’s older technology integrated with newer technologies up close. “There have been a lot of good memories, but I think the best one was the Super Guppy. It was cool to see this combination of 60’s and 70’s technology with this upgraded plane.”

Evan and Janki pose for a photo while walking around EAA AirVenture Oshkosh.
With Oshkosh coming to a close this Sunday, July 30, Alex, Bianca, Evan, and Janki also reflected on advice they have for future NASA interns on how they can get the most out of their internship: be curious and explore, connect with people who work in the field you’re interested in, and don’t be afraid to ask questions.
Alex advises potential NASA interns to “dream big and shoot for your goals, and divide that up into steps… In the end it will work out.” For Bianca, being open and exploring is key: “take opportunities, even if it’s the complete opposite thing that you were intending to do.”

“Ask questions all the time,” said Evan. “Even outside the internship, always continue asking people about what they are knowledgeable on.” And Janki encourages future interns to “Follow your own path. Get the help of mentors, but still do your own thing.”
Visiting Oshkosh and want to see NASA science in action? Stop by the NASA Pavilion, located at Aviation Gateway Park, and see everything from interactive exhibits on sustainable aviation, Advanced Air Mobility, Quesst, and Artemis to STEM activities–and you may even meet NASA pilots, engineers, and astronauts! At Oshkosh, the sky’s the limit.
Interested in interning with NASA? Head over to NASA’s internship website to learn more about internship opportunities with NASA and find your place in (aero)space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

The James Webb Space Telescope has just completed a successful first year of science. Let’s celebrate by seeing the birth of Sun-like stars in this brand-new image from the Webb telescope!
This is a small star-forming region in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. At 390 light-years away, it's the closest star-forming region to Earth. There are around 50 young stars here, all of them similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The darkest areas are the densest, where thick dust cocoons still-forming protostars. Huge red bipolar jets of molecular hydrogen dominate the image, appearing horizontally across the upper third and vertically on the right. These occur when a star first bursts through its natal envelope of cosmic dust, shooting out a pair of opposing jets into space like a newborn first stretching her arms out into the world. In contrast, the star S1 has carved out a glowing cave of dust in the lower half of the image. It is the only star in the image that is significantly more massive than the Sun.
Thanks to Webb’s sensitive instruments, we get to witness moments like this at the beginning of a star’s life. One year in, Webb’s science mission is only just getting started. The second year of observations has already been selected, with plans to build on an exciting first year that exceeded expectations. Here’s to many more years of scientific discovery with Webb.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI)

Space Craft! Make NASA-Inspired Creations for World Embroidery Day
It’s time to get crafty with some needle and thread. At NASA, we hope to inspire art of all kinds. To highlight #WorldEmbroideryDay on July 30, we want to know: does our imagery inspire you? Show us your art and we may feature it on social media.
How?
Search for a NASA image that inspires you. Here are a few places to get you started: Hubble, James Webb Space Telescope, Ocean Color, Landsat and Earth Observatory
Create. Over the years, we've seen a growing number of embroidered pieces that showcase our organization's research, especially with needlepoint.
Share your creation, along with the image it was inspired by, on social media using the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery. We will share selected pieces on July 30 for World Embroidery Day
Why?

NASA imagery has many functions. From studying distant galaxies to tracking ocean health, our scientists use these images to not only monitor our home planet, but better understand life beyond our solar system.
Embroidery is an ancient craft that has experienced a revival over the years. It involves decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Have you recently taken up embroidery? What images are you inspired by? We’d love to see it.
Image Resources for #NASAEmbroidery Inspiration
NASA Images
Hubble Image Gallery
NASA’s Ocean Color Image Gallery
James Webb Space Telescope
Landsat Image Gallery
Create and Share Your #NASAEmbroidery
Take a picture of your piece and upload it to Twitter, Instagram, Tumblr or Facebook. Make sure you use the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery so we know that you are taking part in the event and make sure that your privacy permissions allow us to view your post.
If the piece catches our eye, we may share your work on NASA’s main social media accounts as well as theme-related ones. We may also feature your art in a NASA Flickr gallery and our Tumblr pages. We’ll contact you directly to grant us permission to feature your work. You can follow @NASA on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook for embroidery creations, which will be featured from July 30-Aug. 1
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Of course Saturn brought its ring light.
On June 25, 2023, our James Webb Space Telescope made its first near-infrared observations of Saturn. The planet itself appears extremely dark at this infrared wavelength, since methane gas absorbs almost all the sunlight falling on the atmosphere. The icy rings, however, stay relatively bright, leading to Saturn’s unusual appearance in this image.
This new image of Saturn clearly shows details within the planet’s ring system, several of the planet’s moons (Dione, Enceladus, and Tethys), and even Saturn’s atmosphere in surprising and unexpected detail.
These observations from Webb are just a hint at what this observatory will add to Saturn’s story in the coming years as the science team delves deep into the data to prepare peer-reviewed results.
Download the full-resolution image, both labeled and unlabeled, from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!